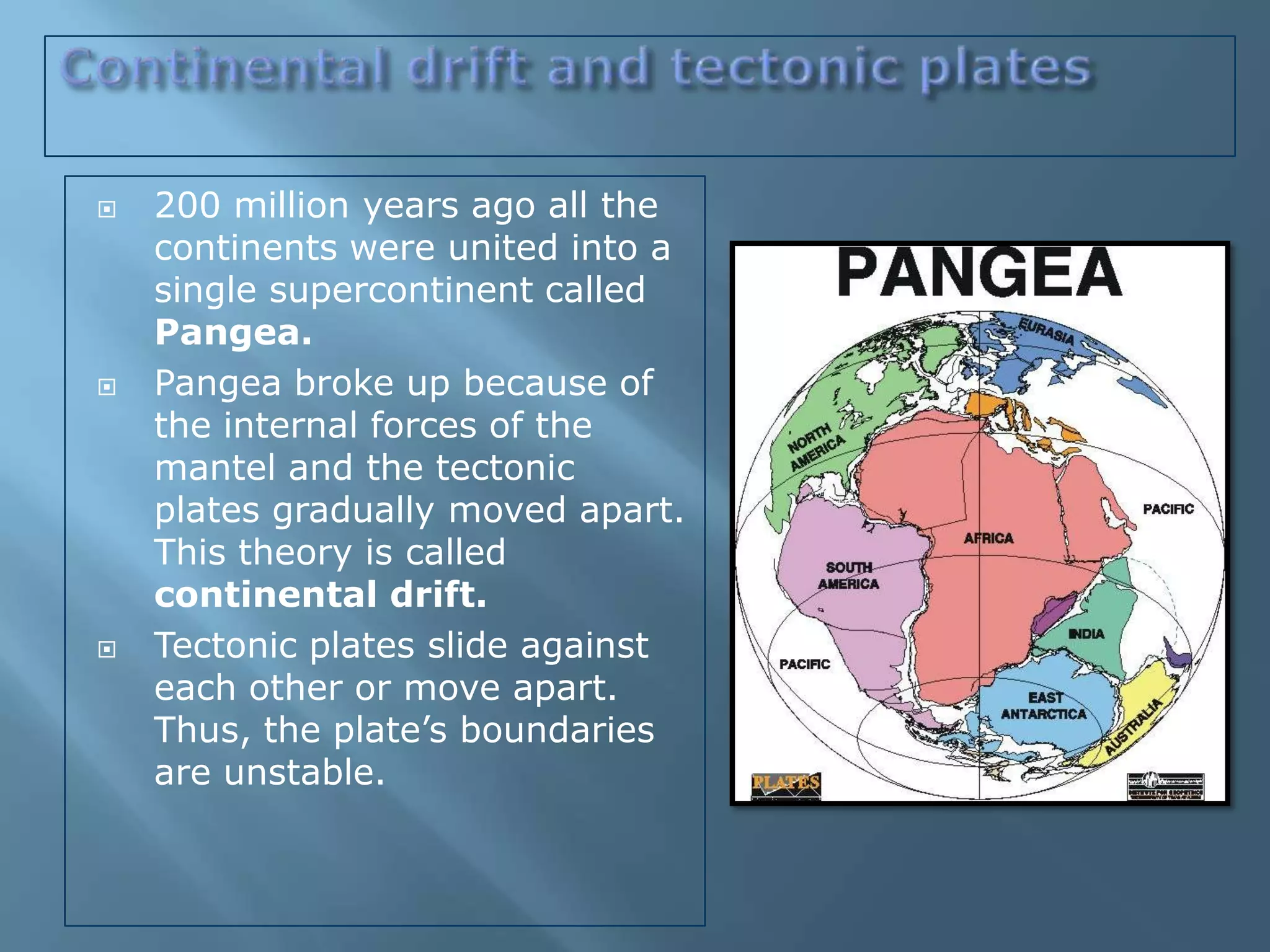
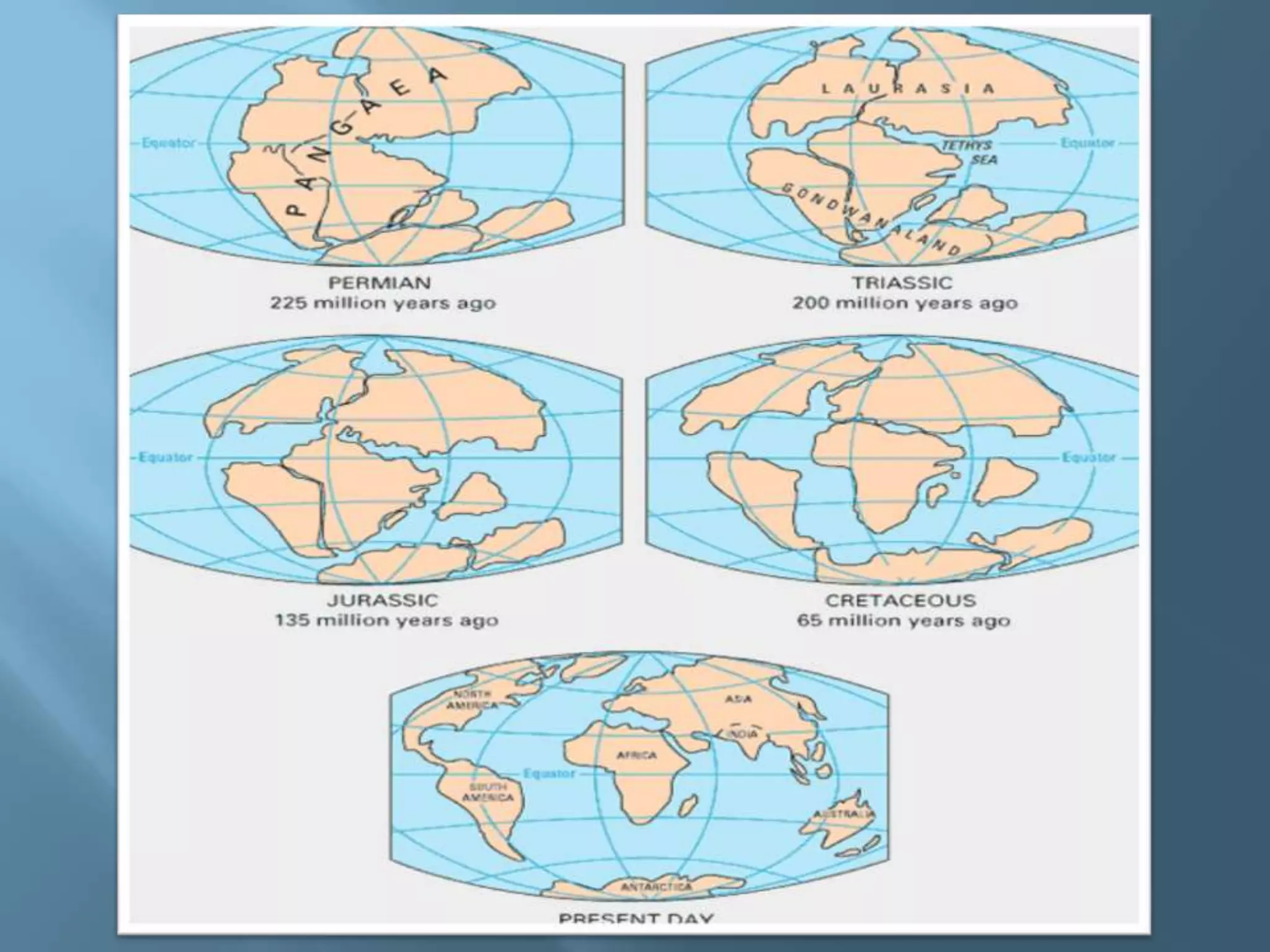
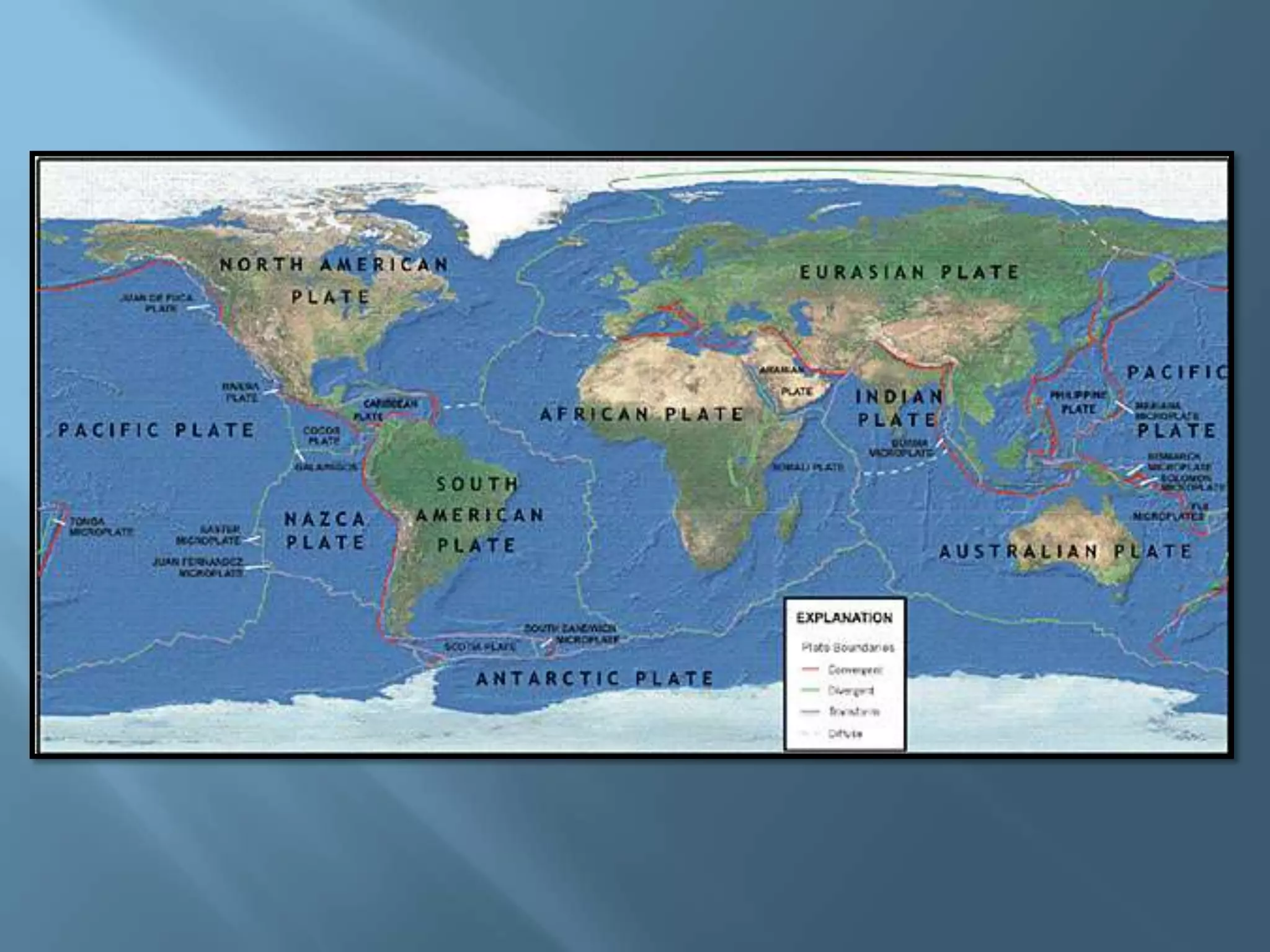
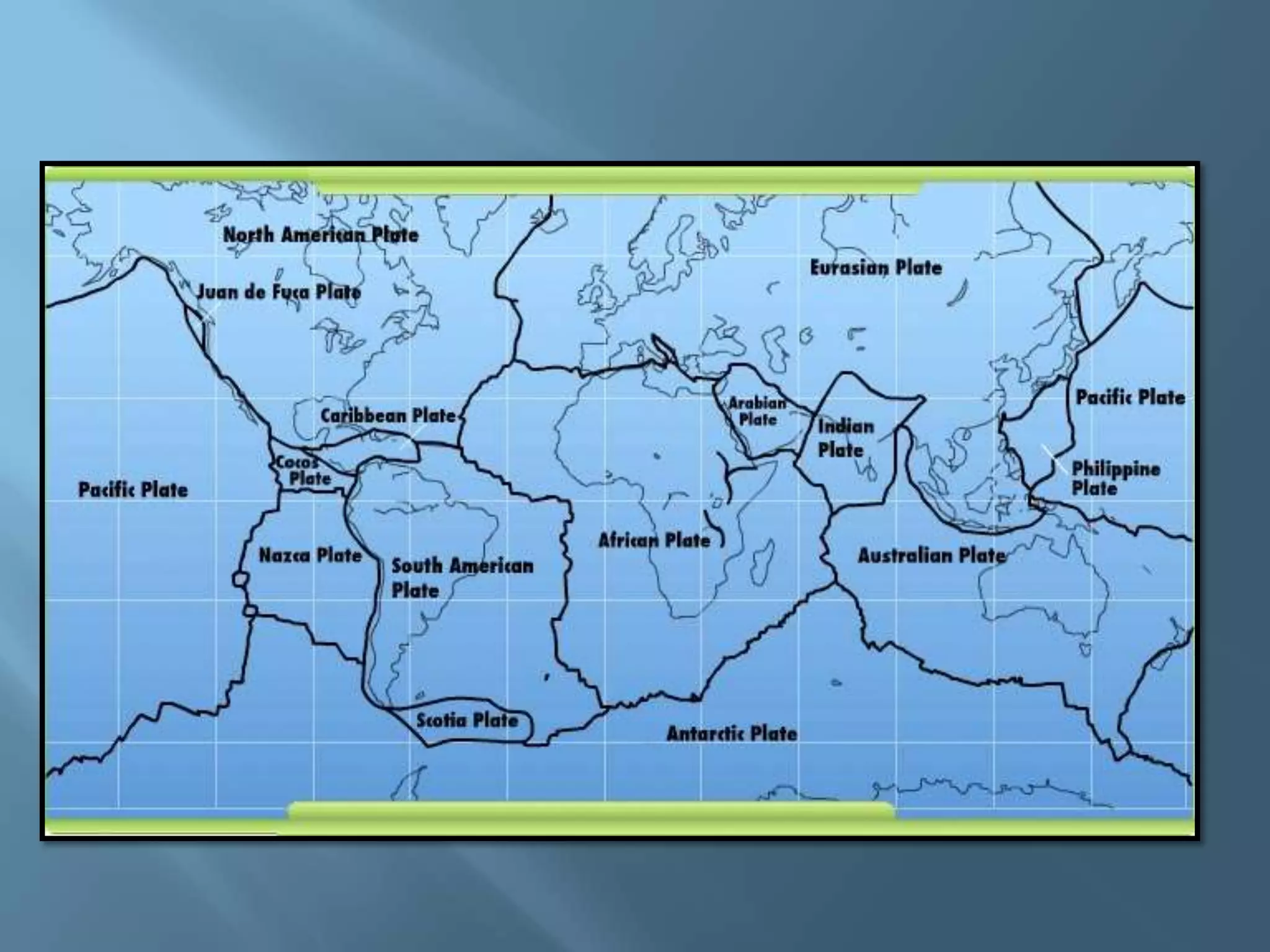
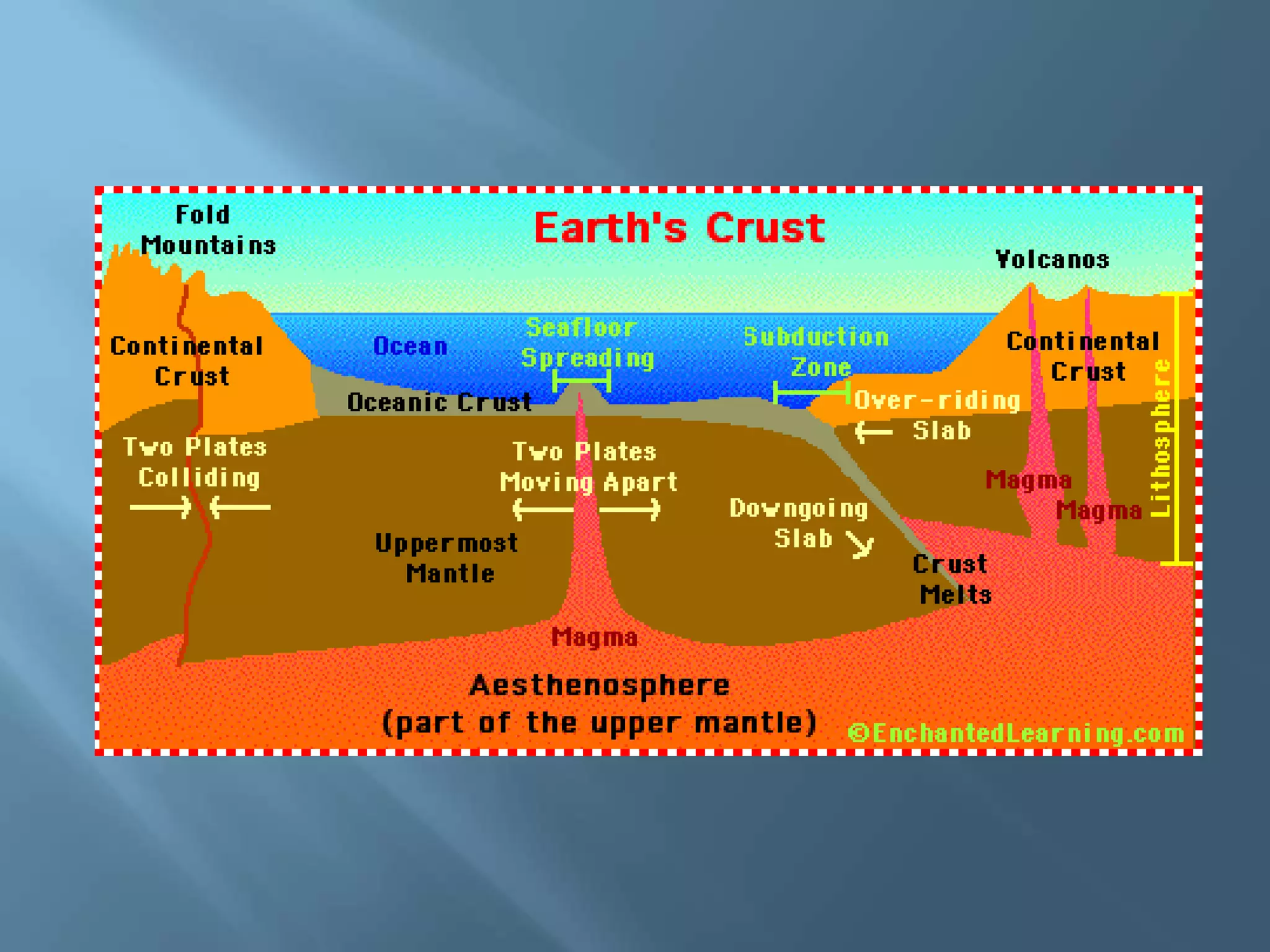
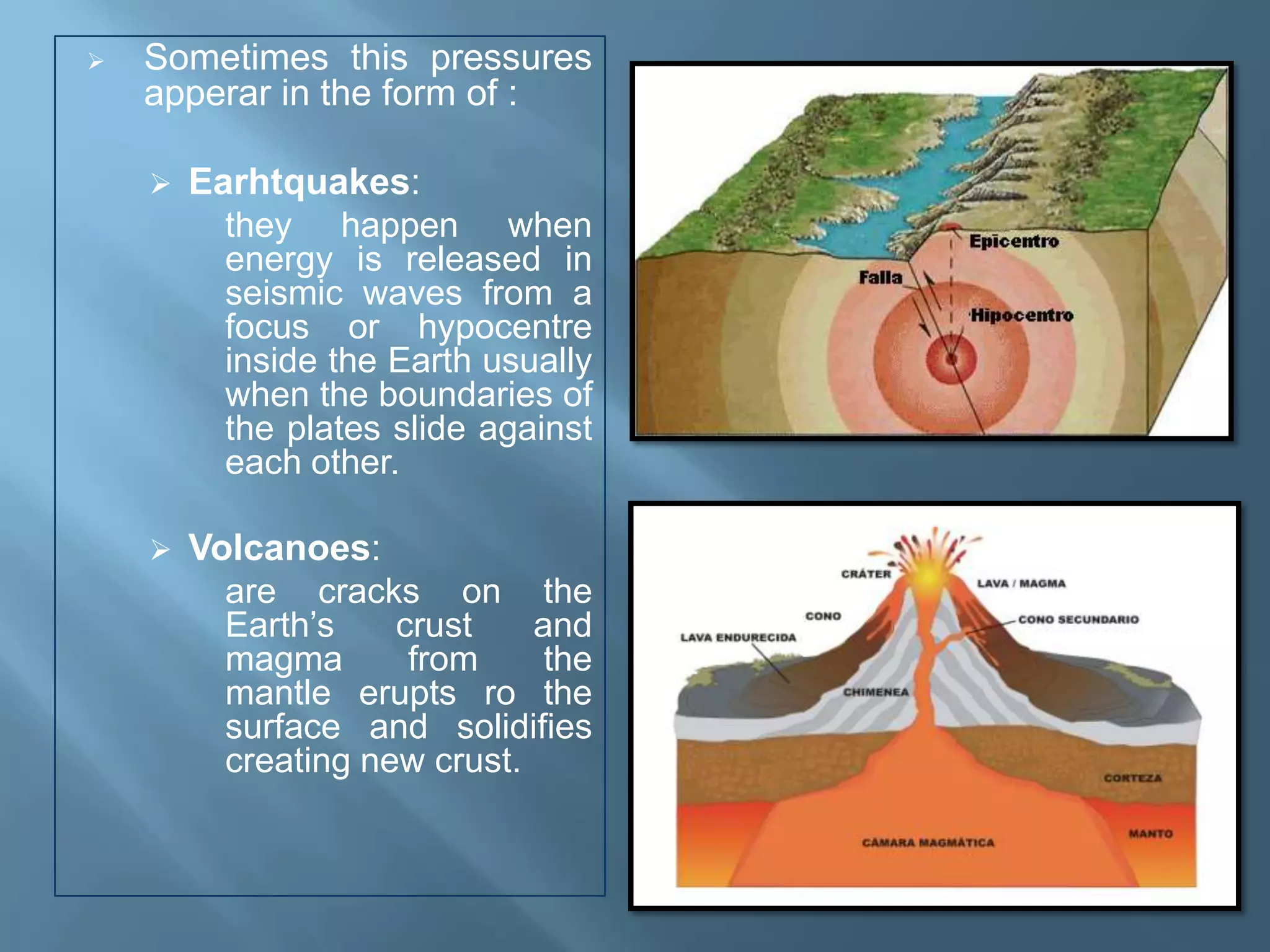
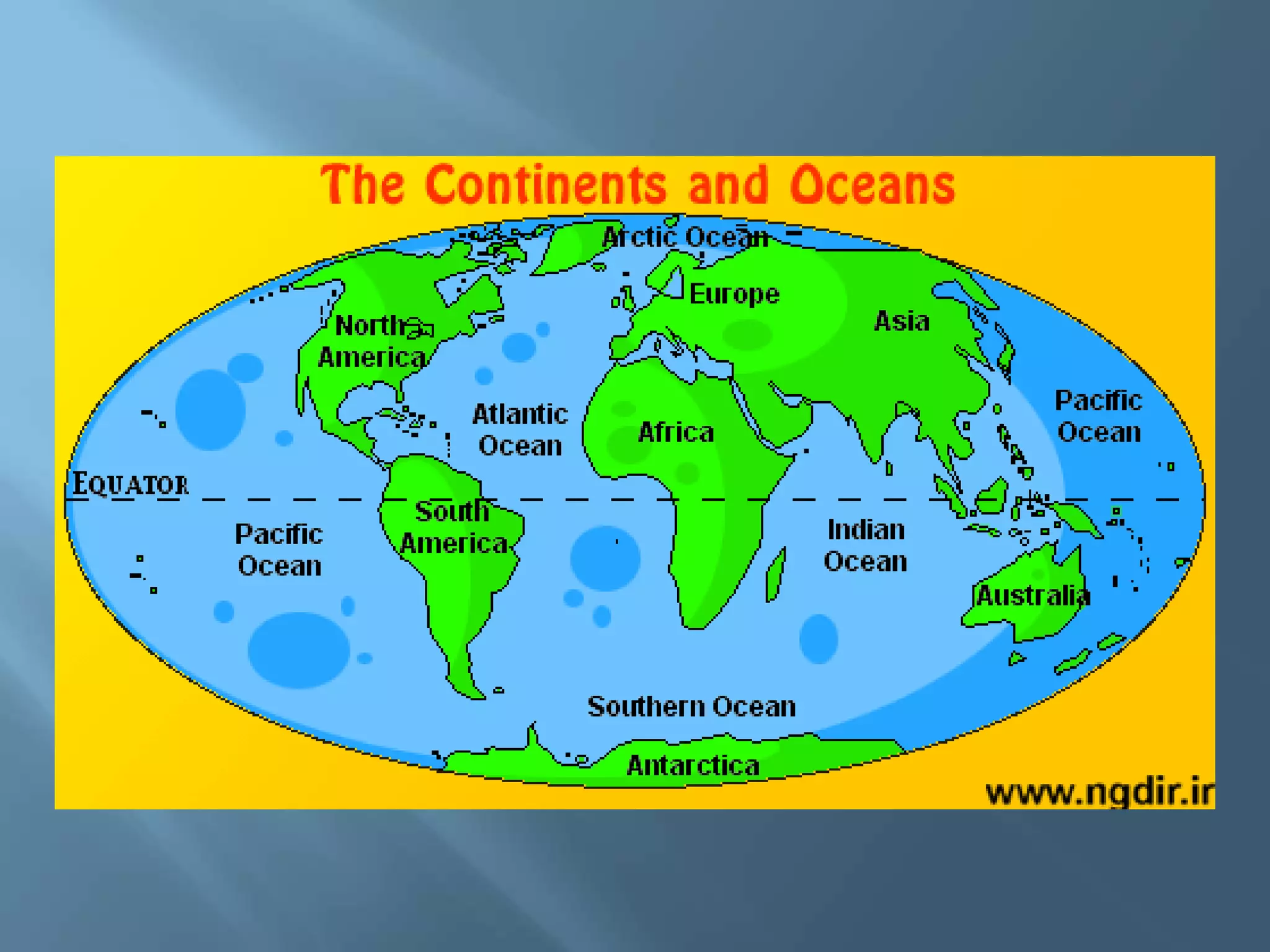
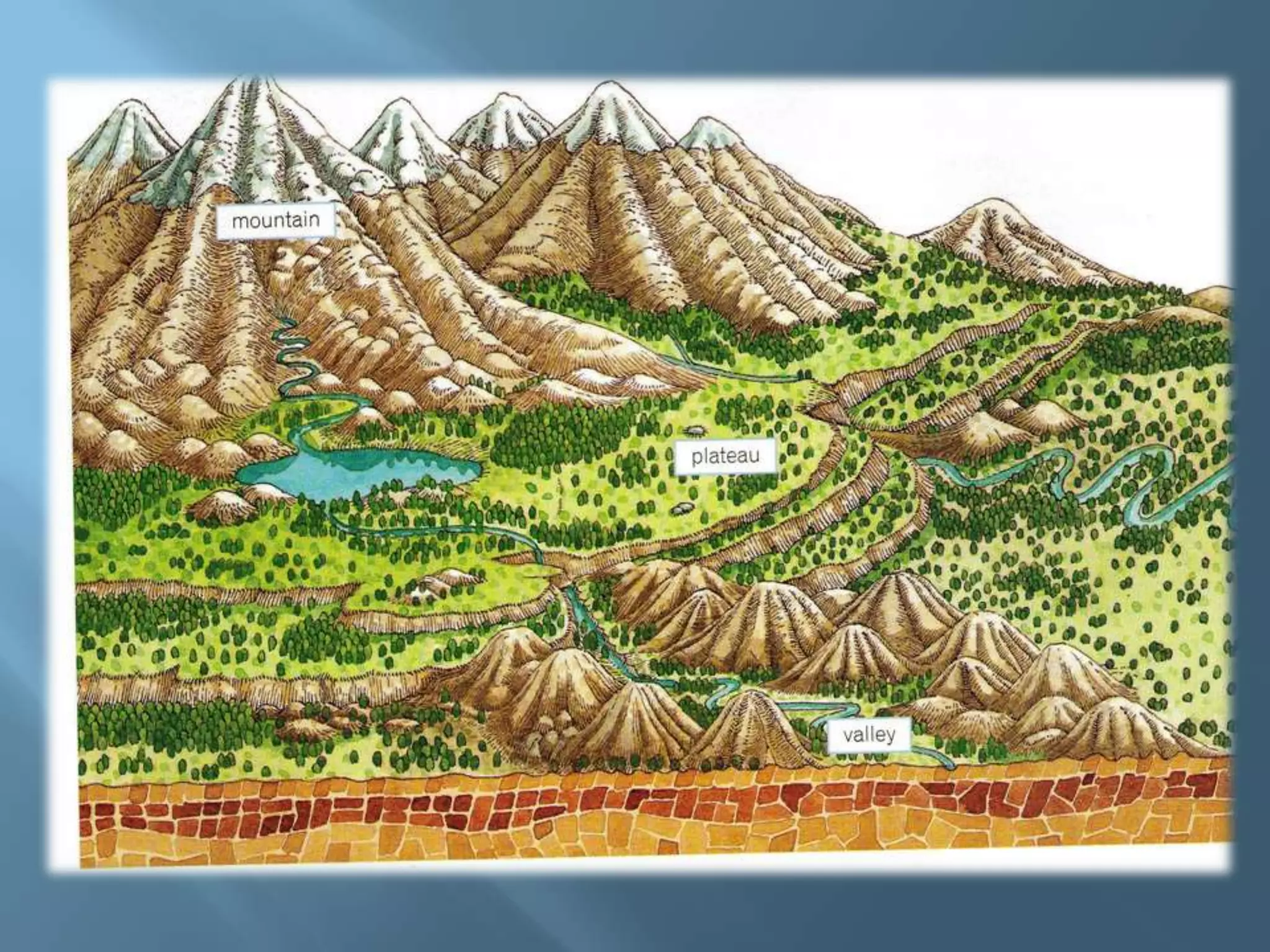
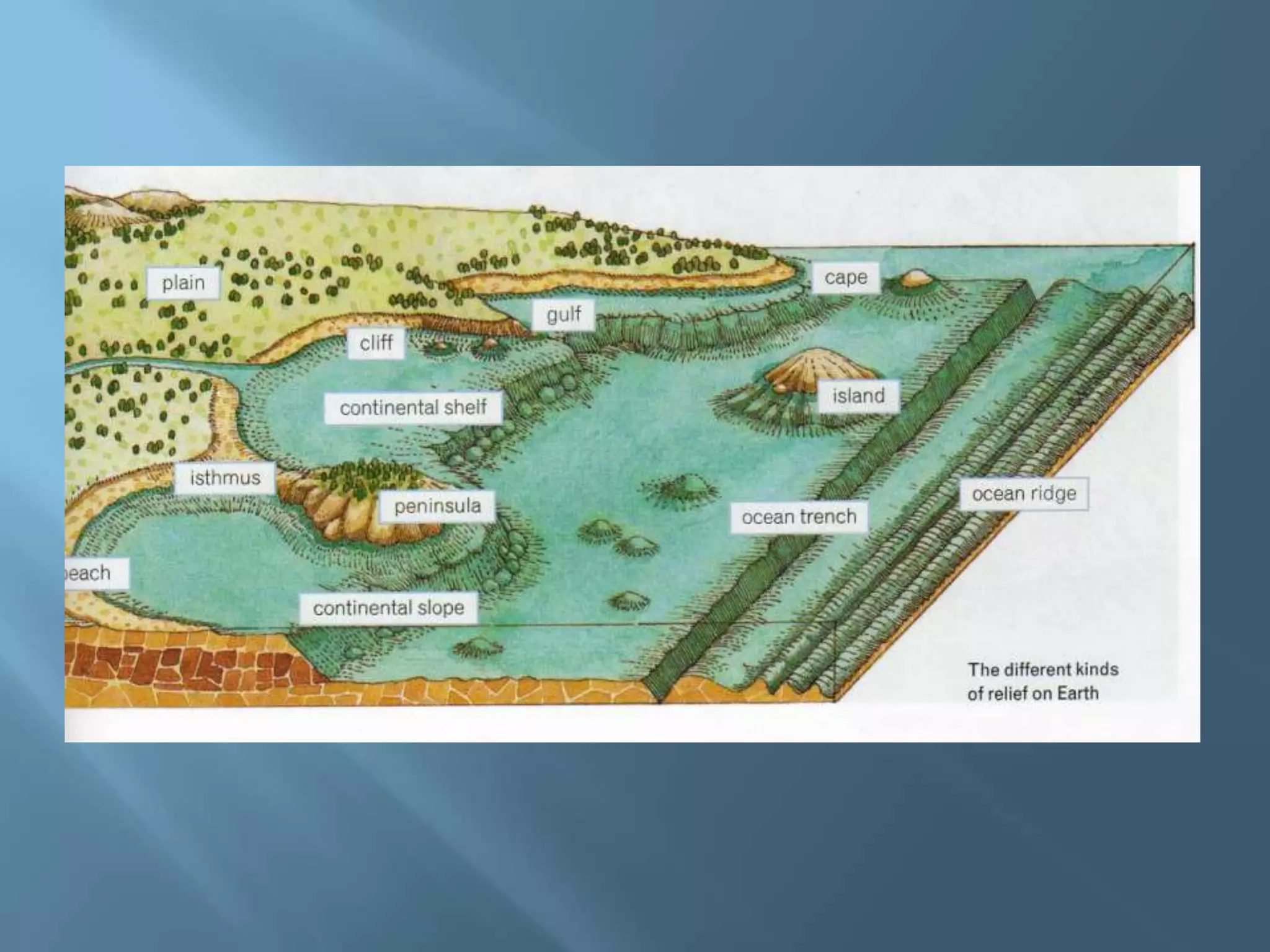
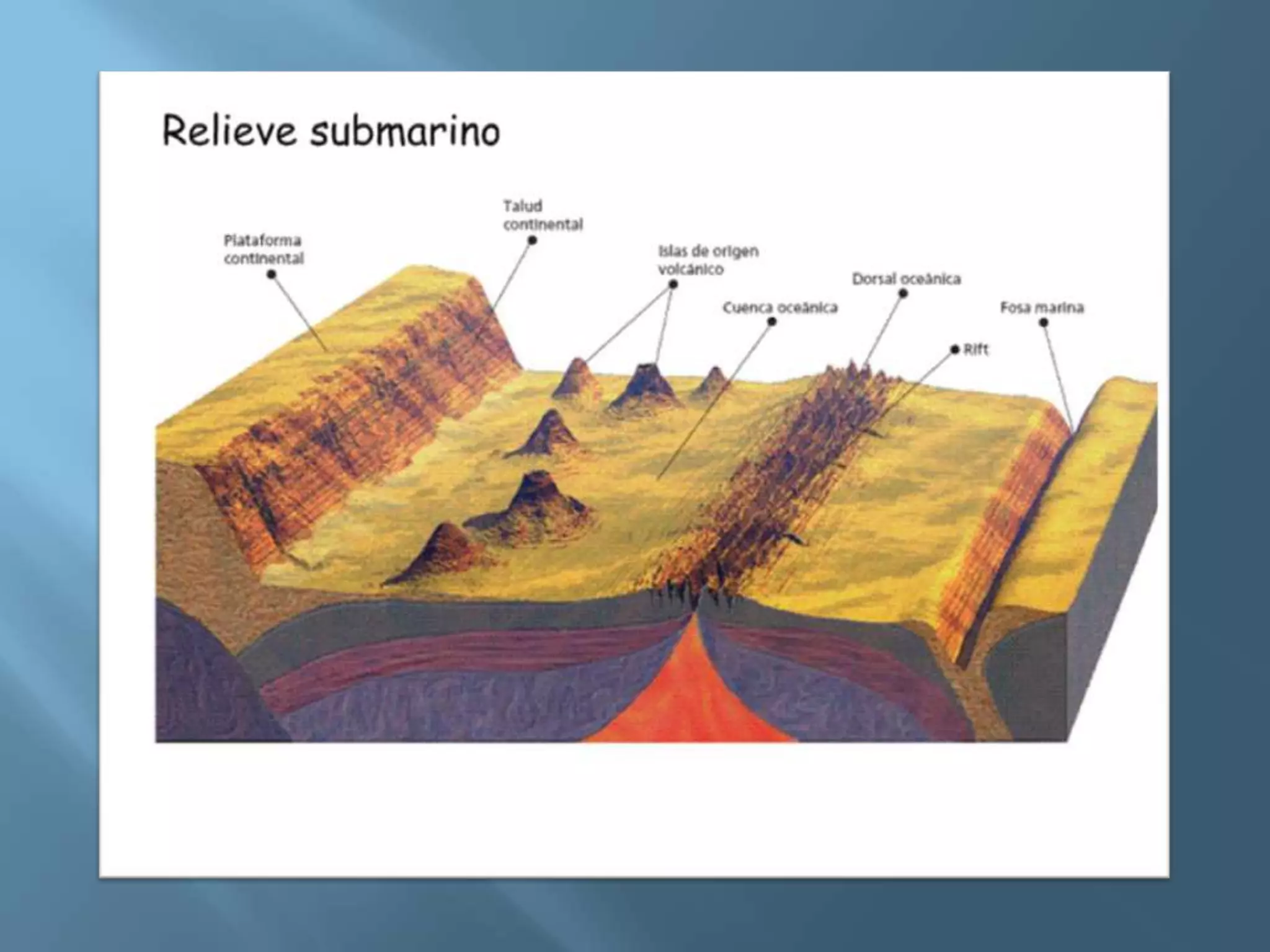
The lithosphere is the Earth's rocky crust, formed of minerals and divided into tectonic plates that interact with each other. Internal forces like folding and faulting, along with external agents such as water and wind, shape the Earth's relief, leading to features like mountains, valleys, and plains. Continental drift theory explains how continents once formed a supercontinent called Pangaea, which broke apart due to tectonic movement.