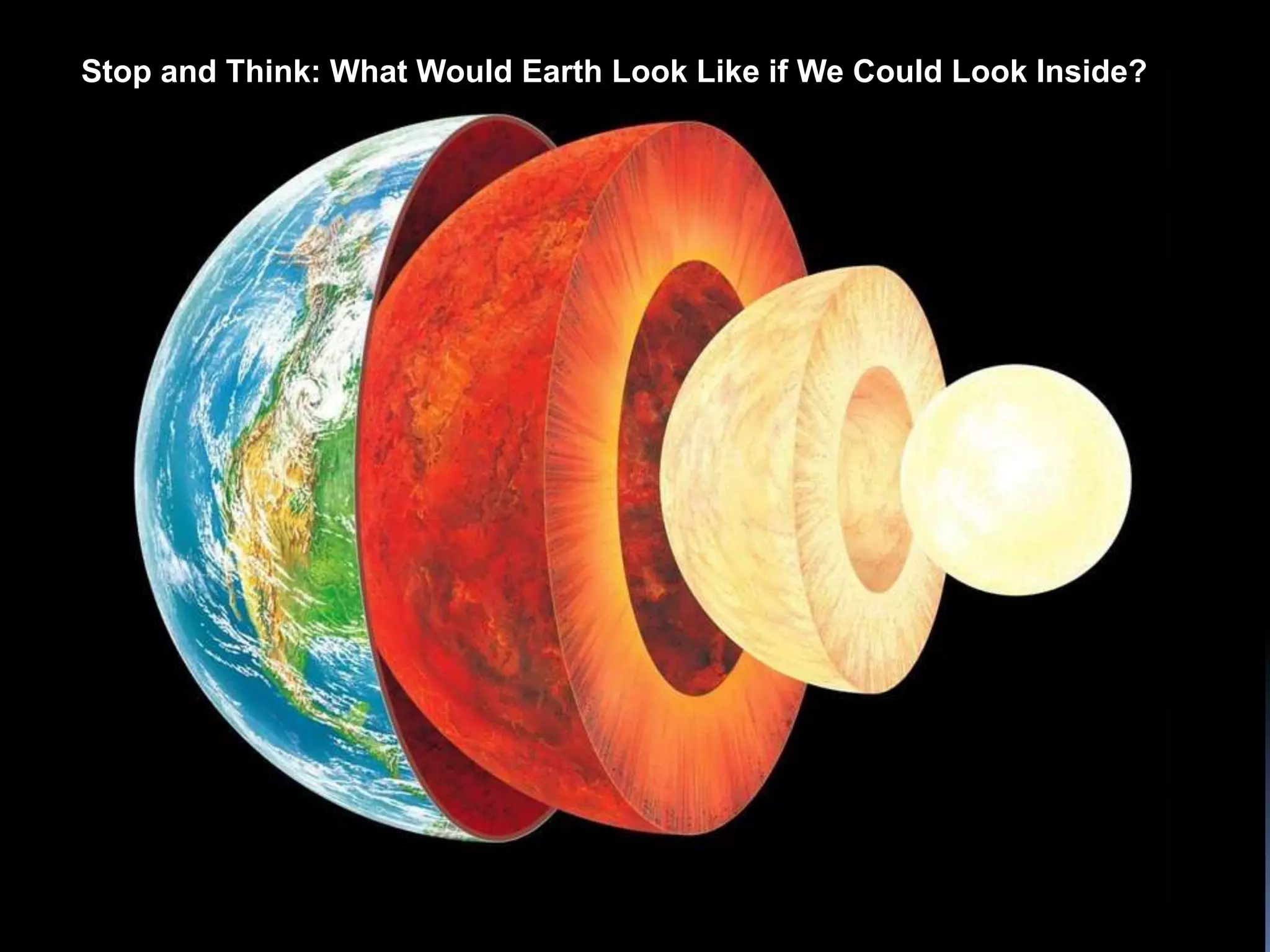
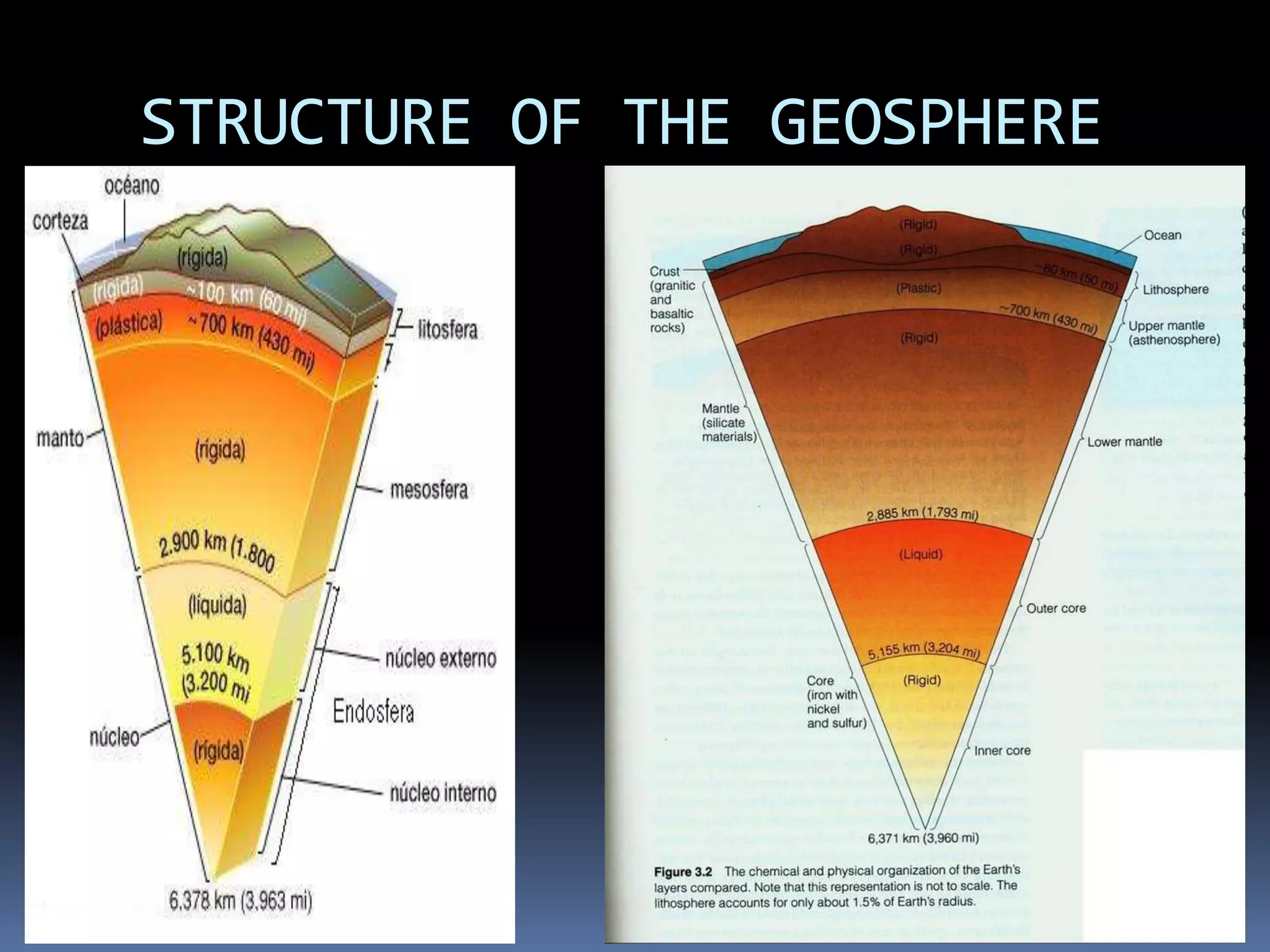
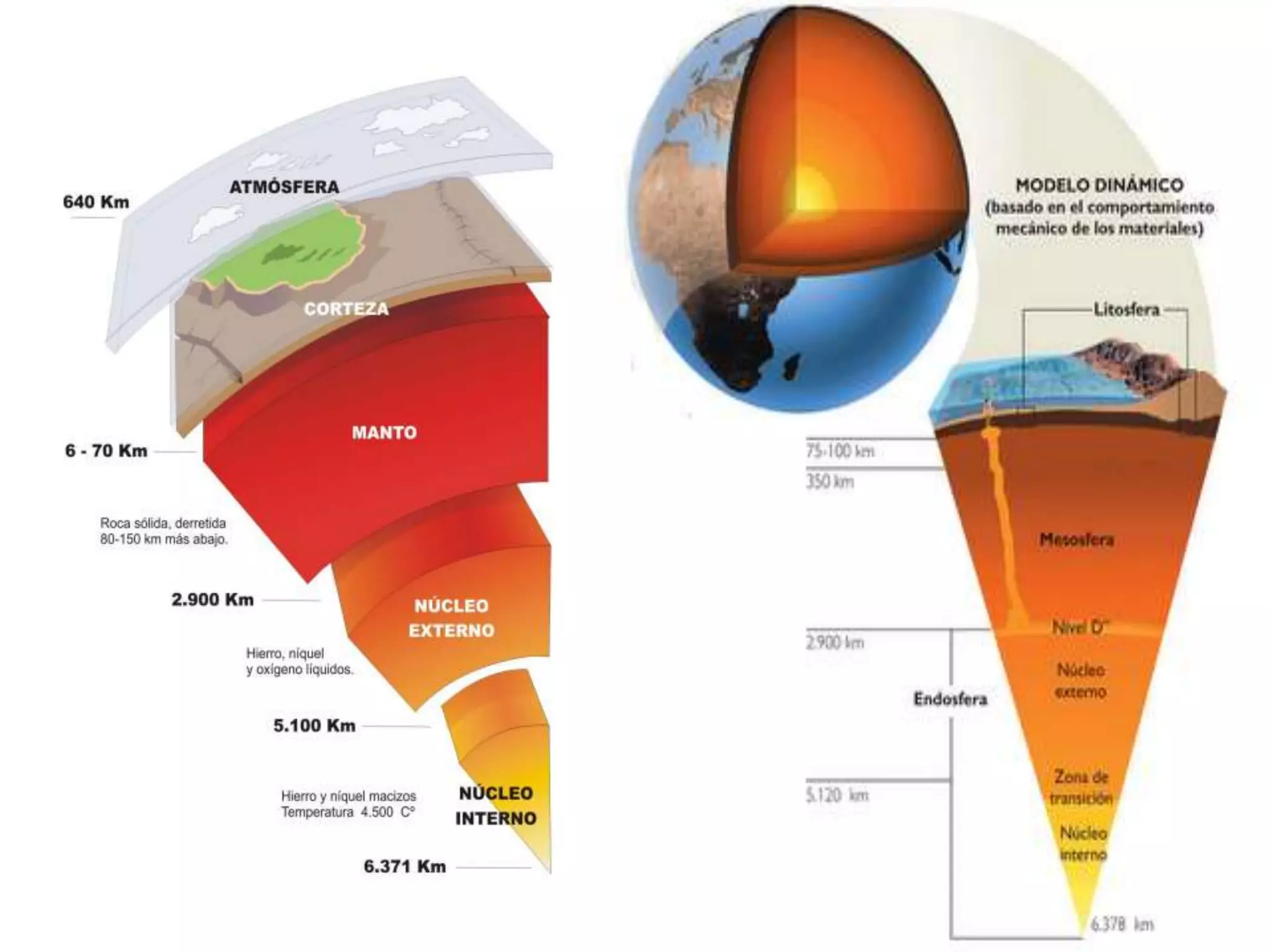
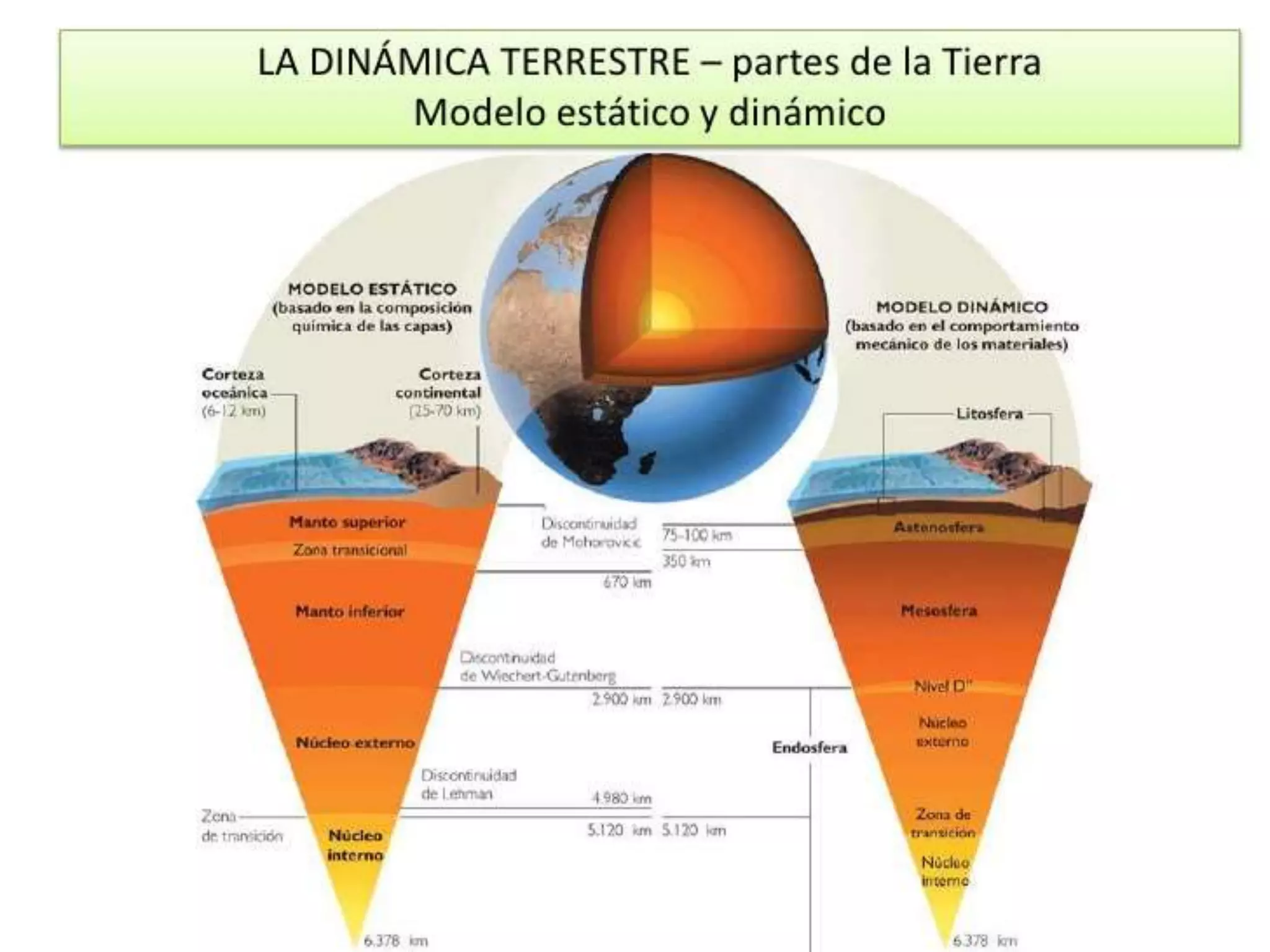
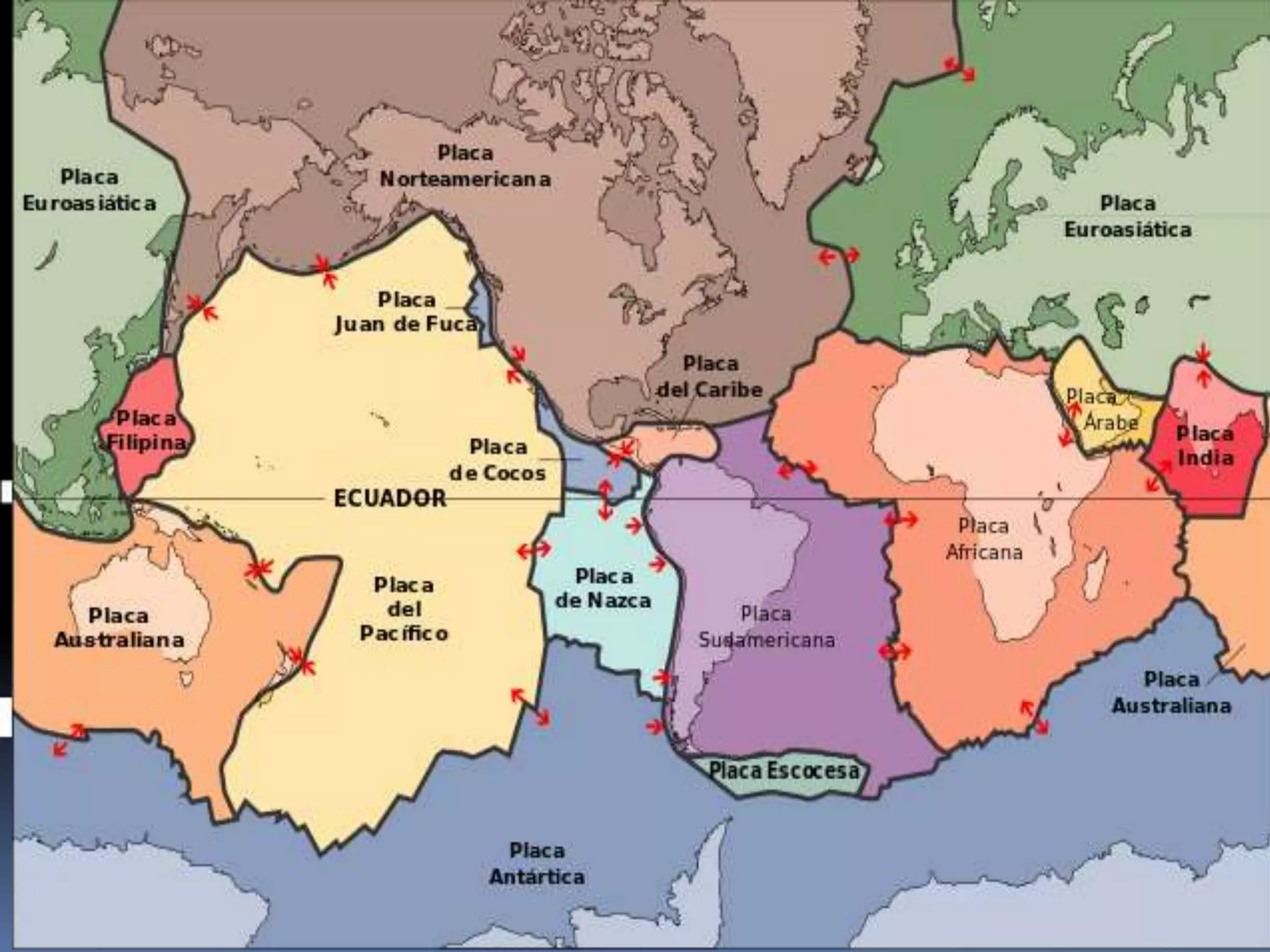
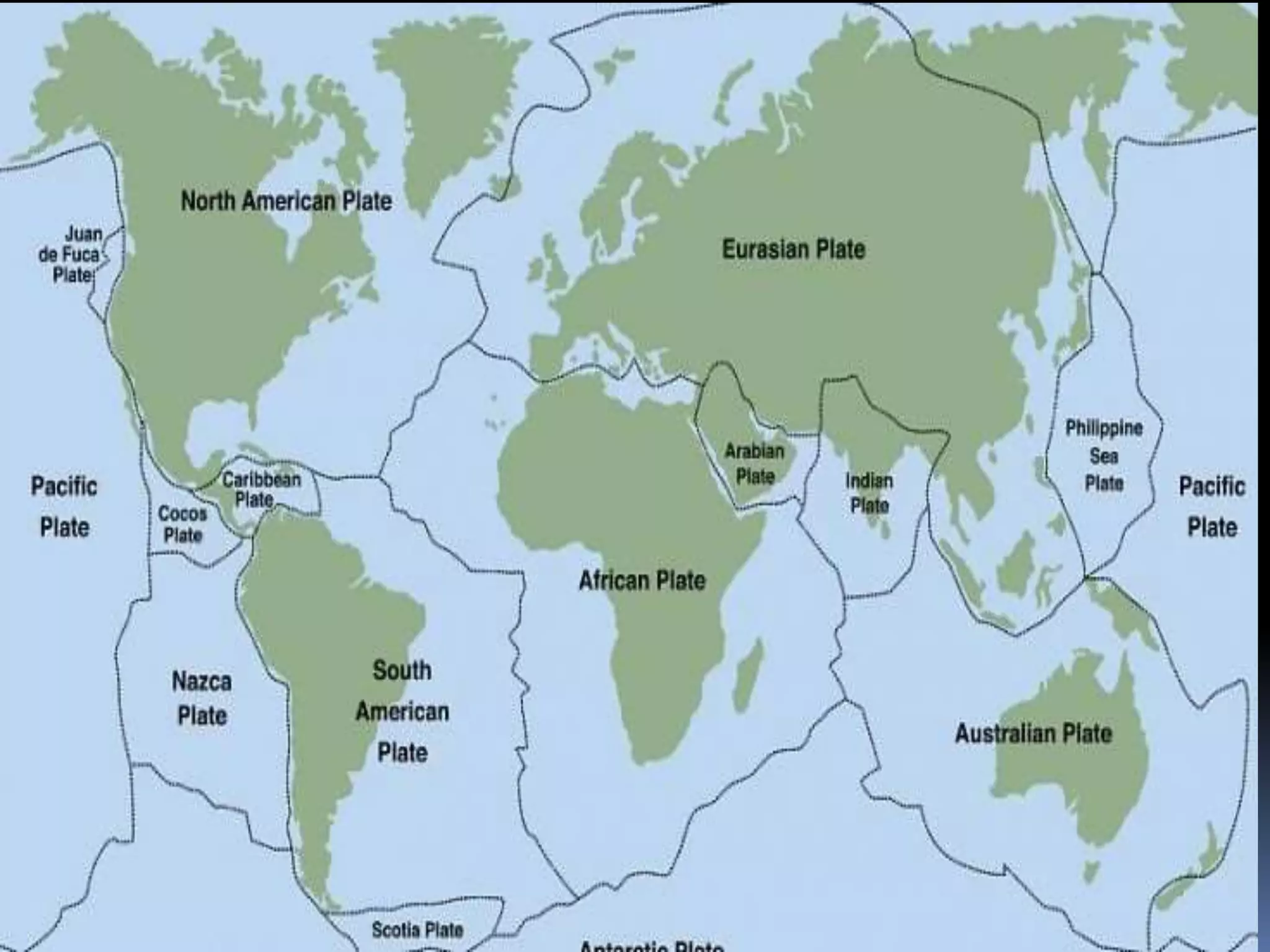
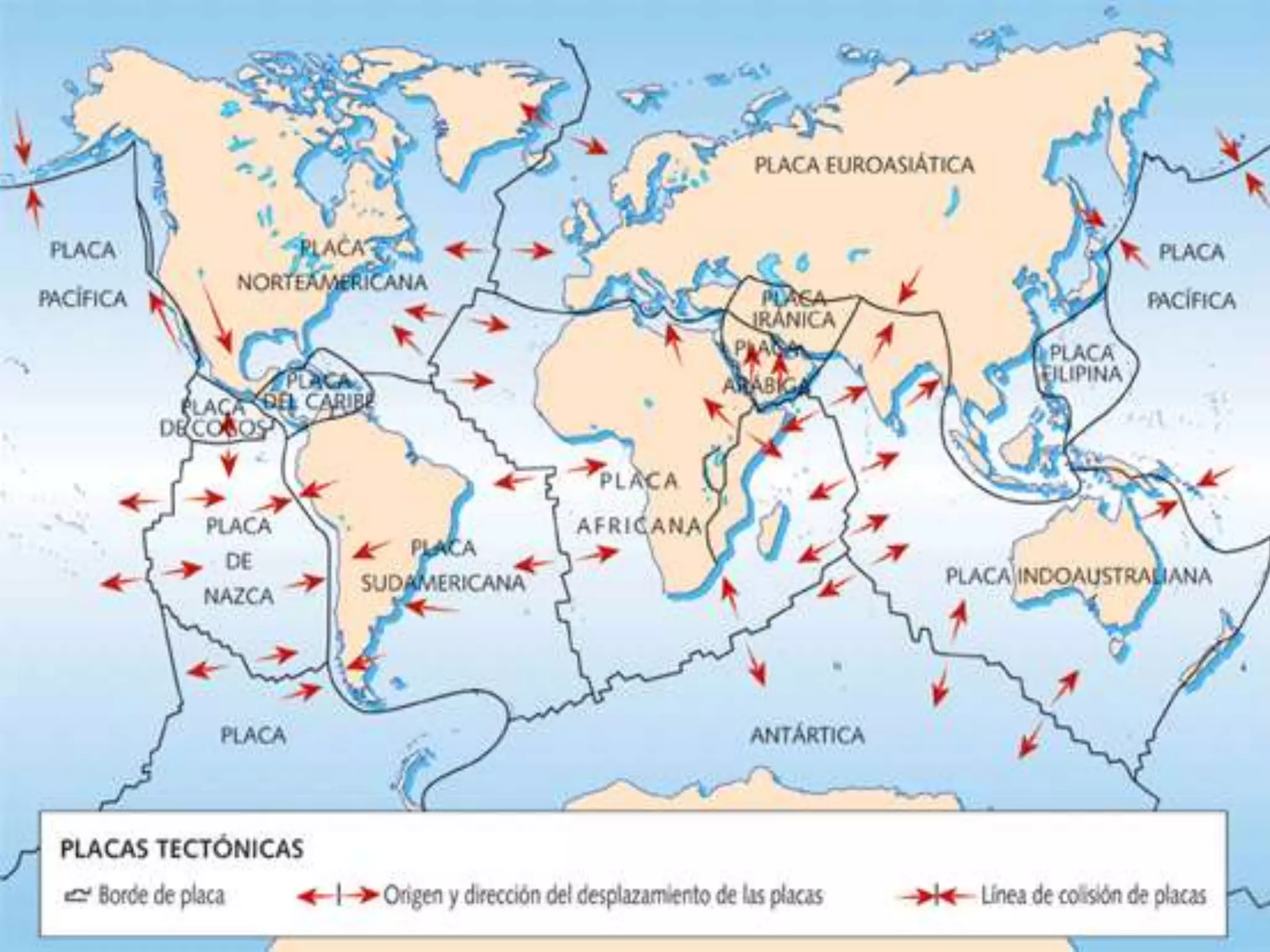
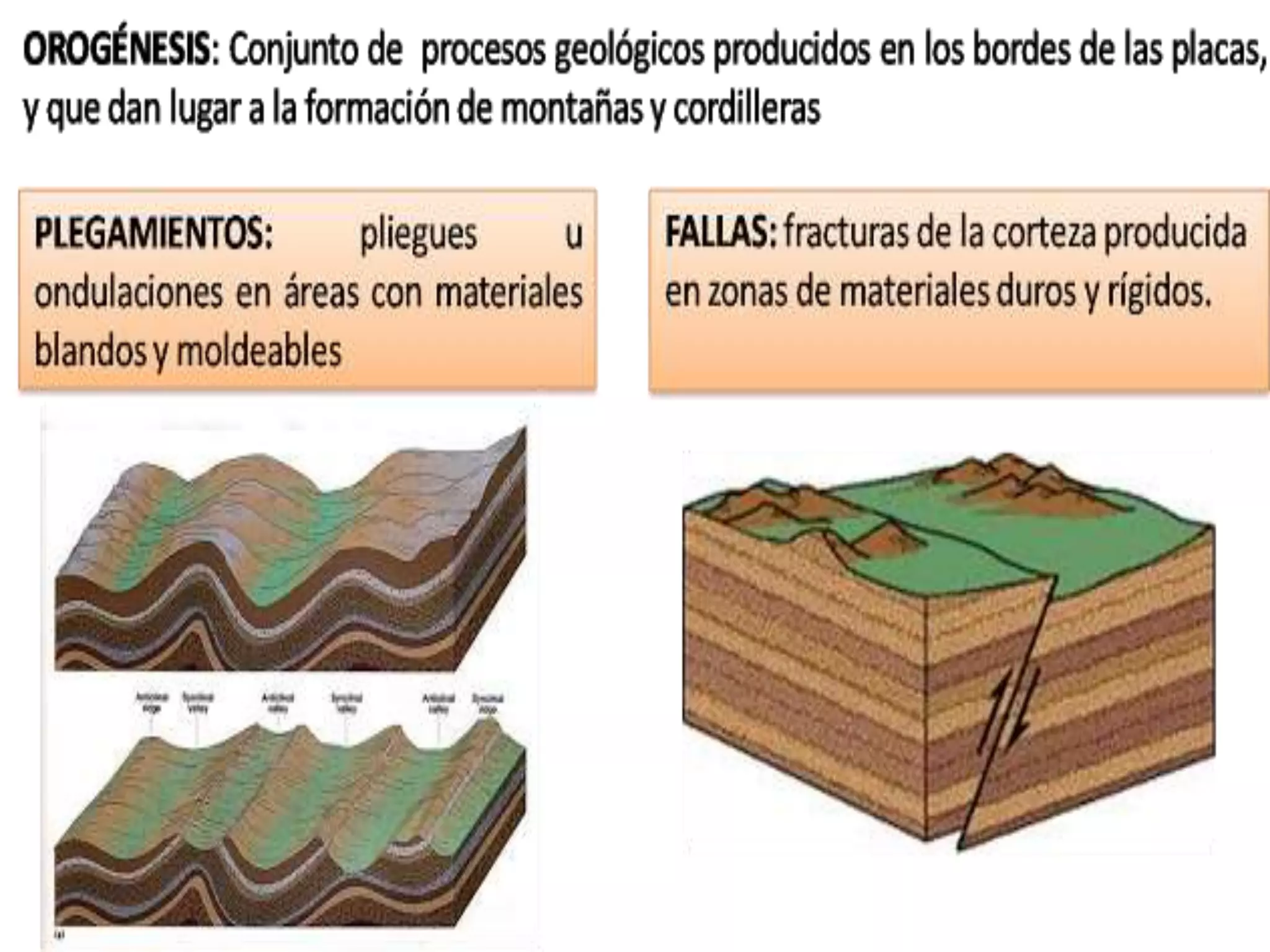
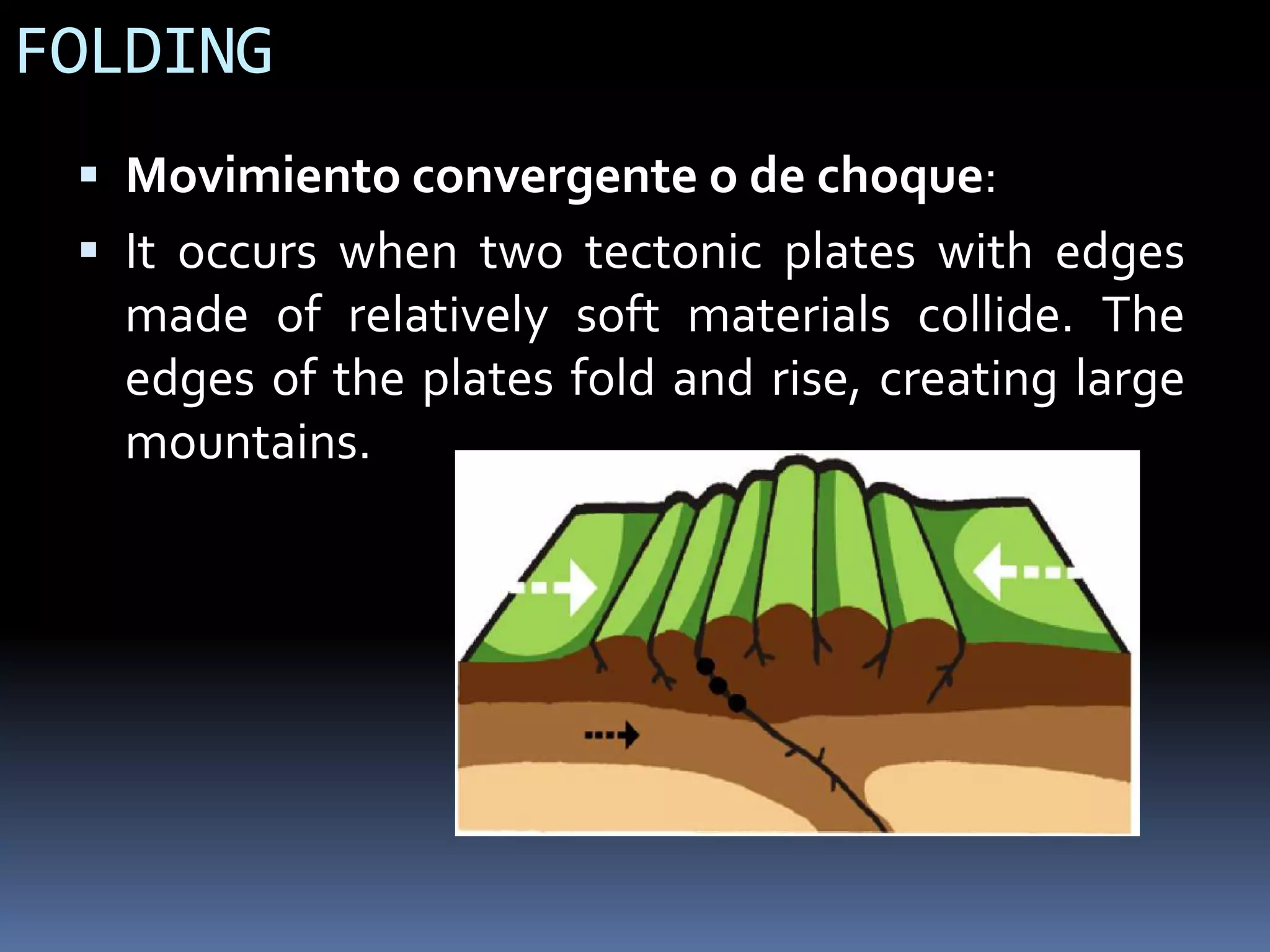
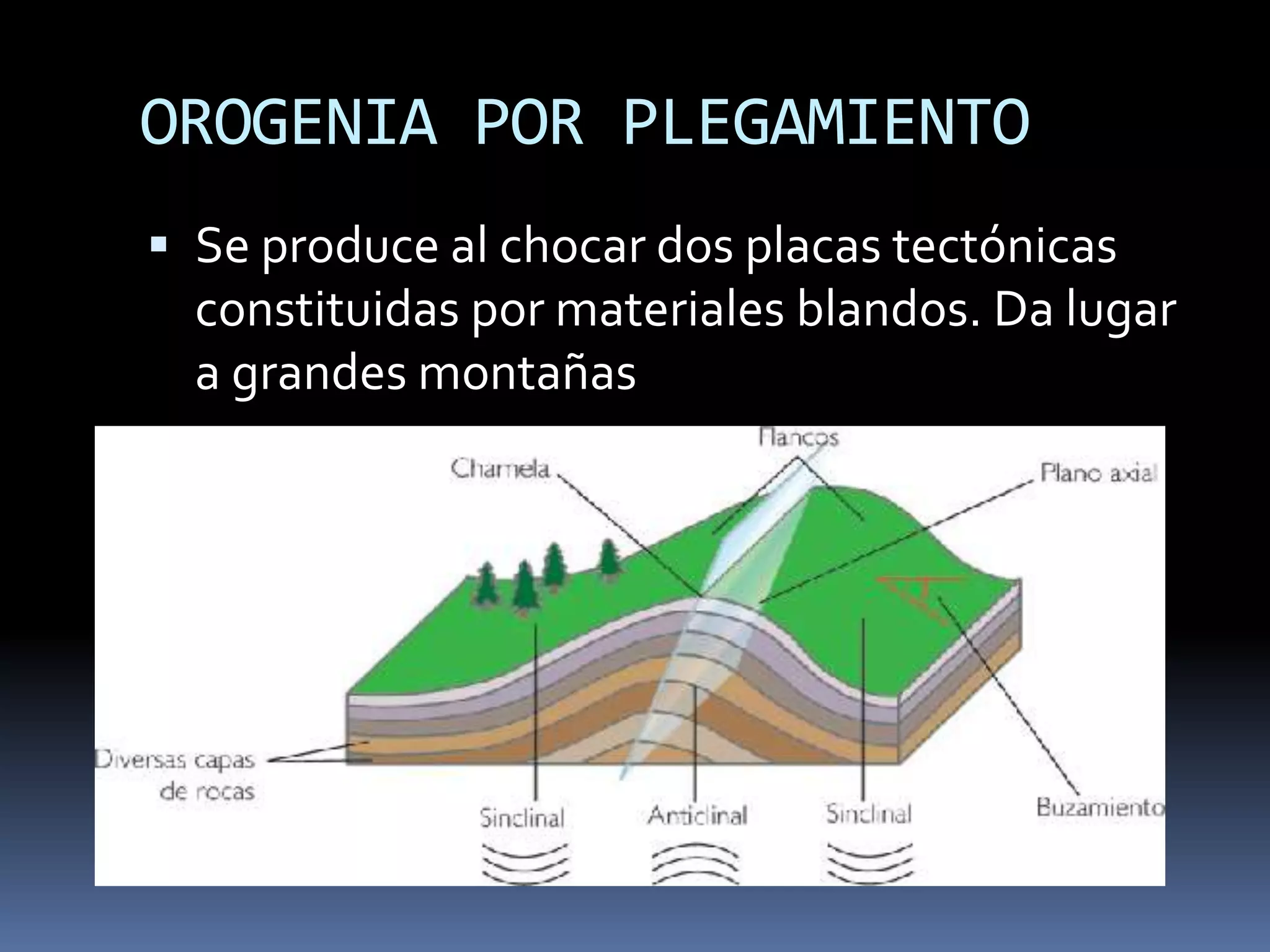
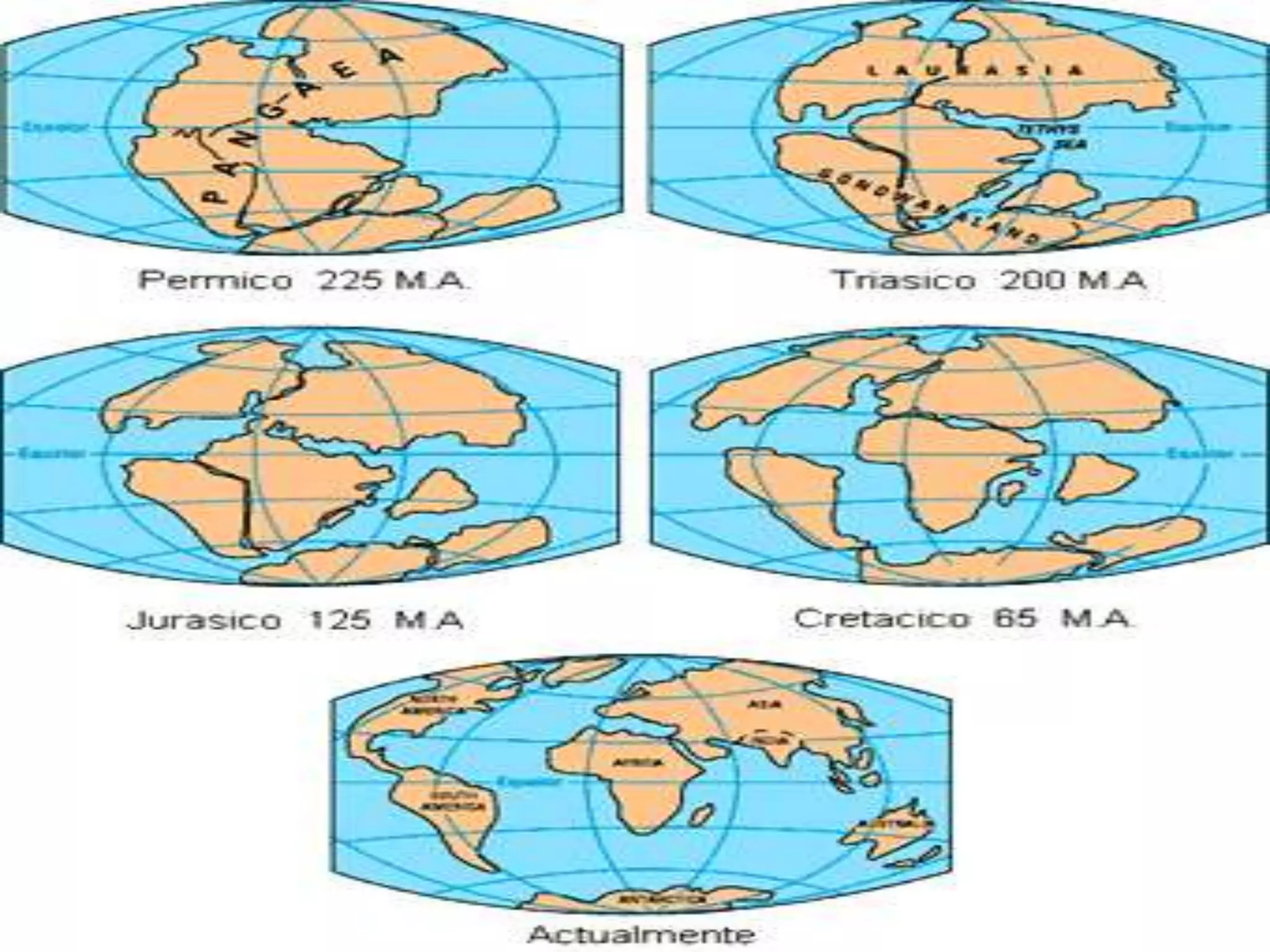
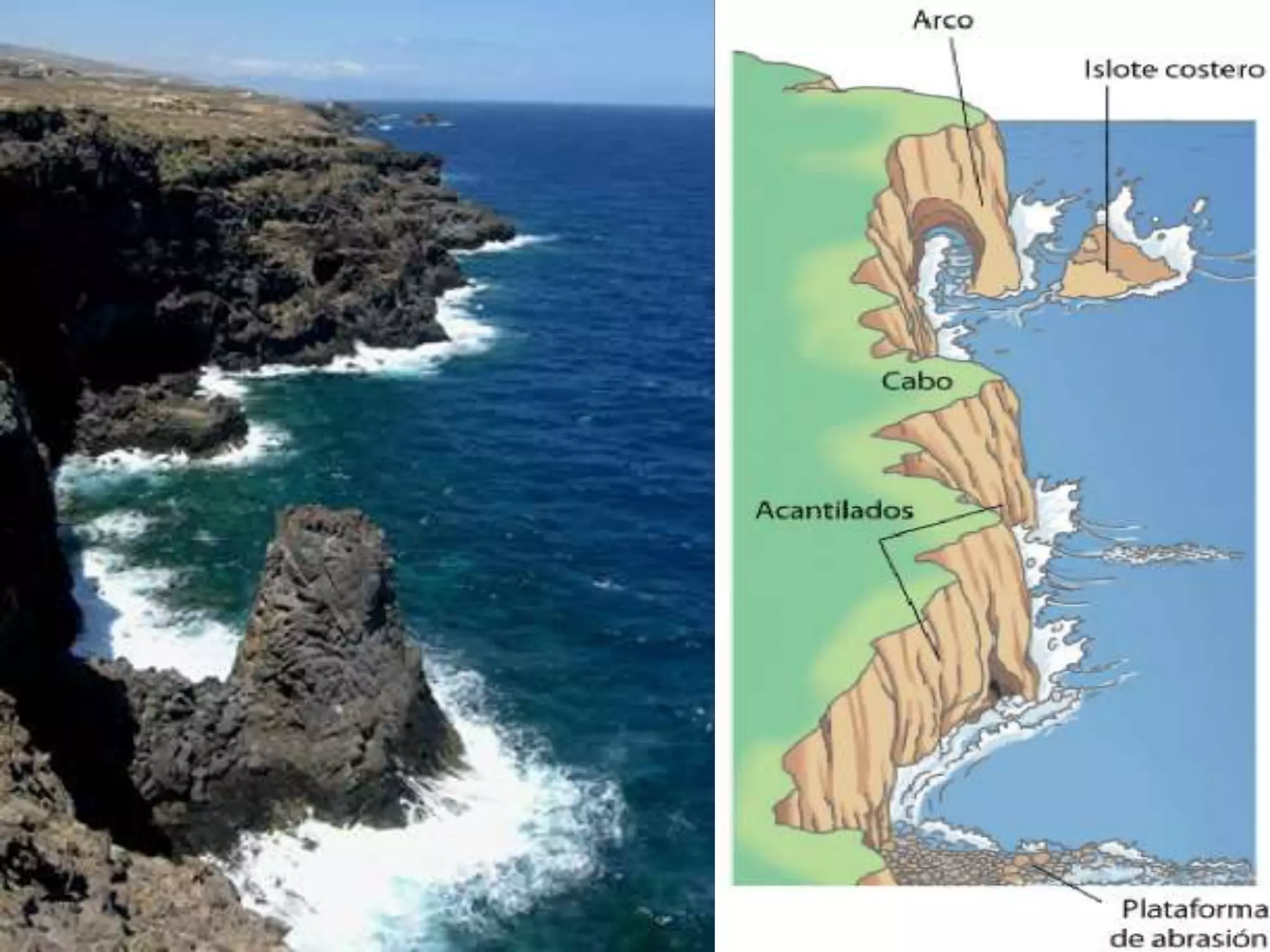
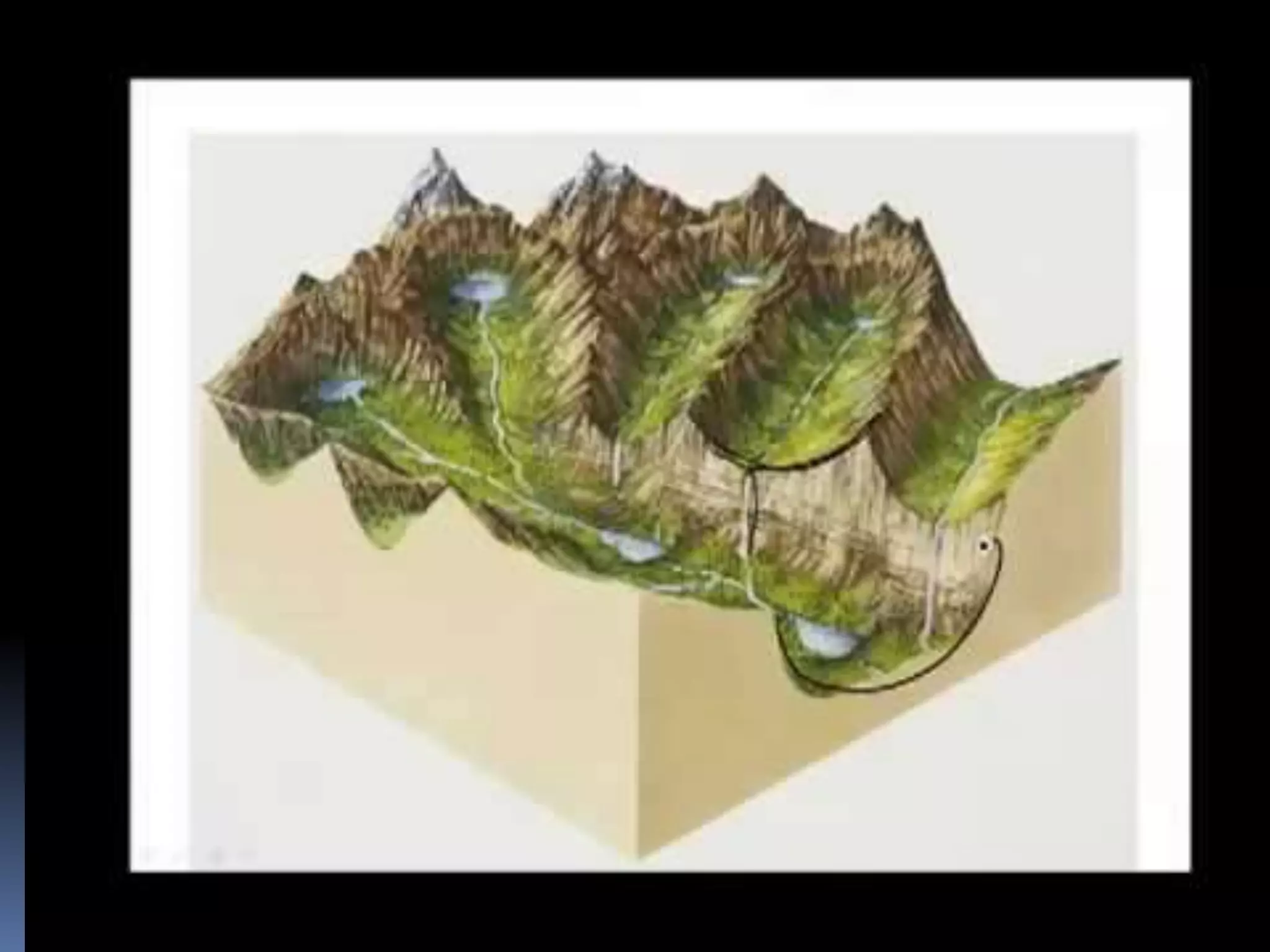
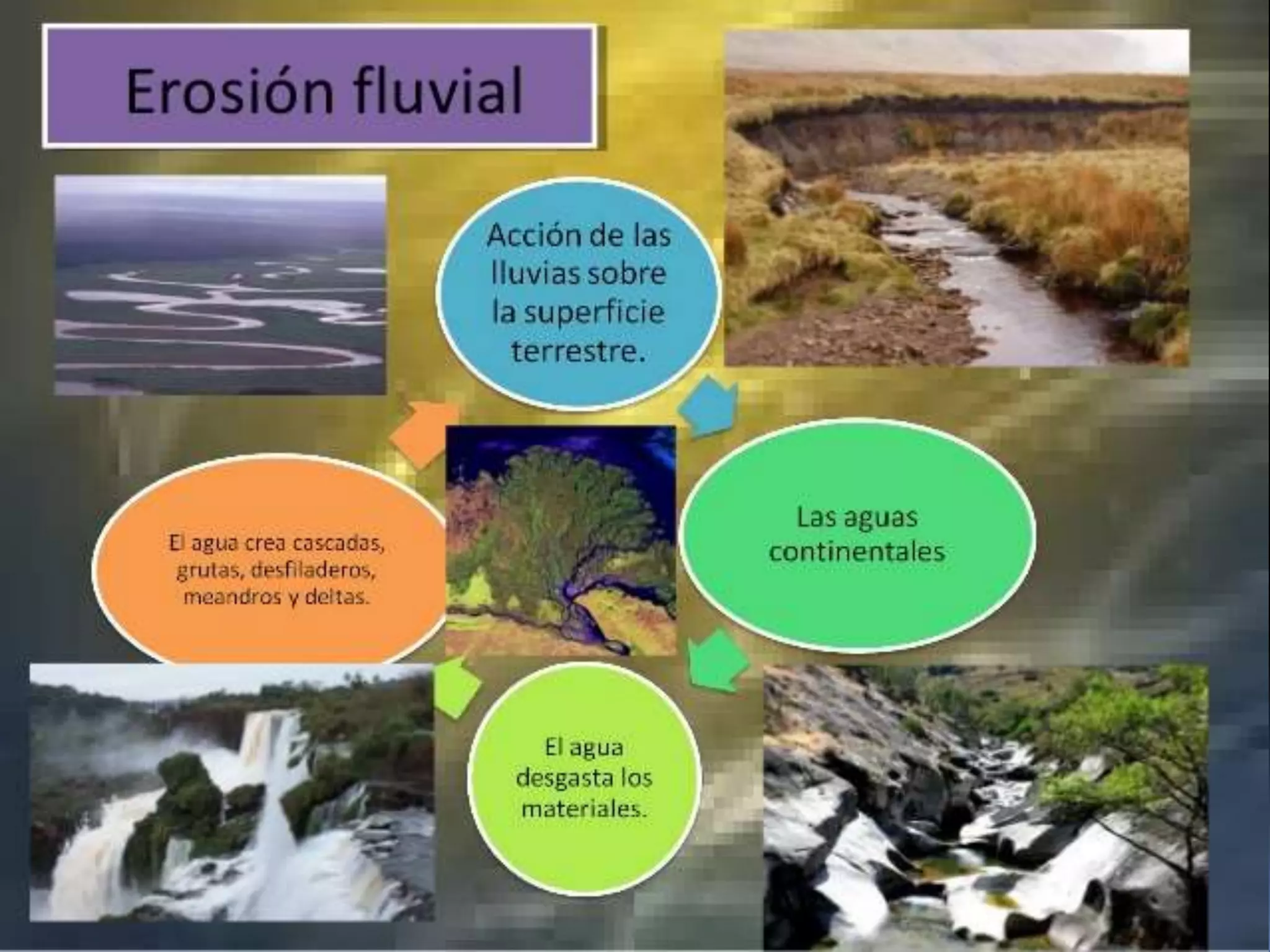
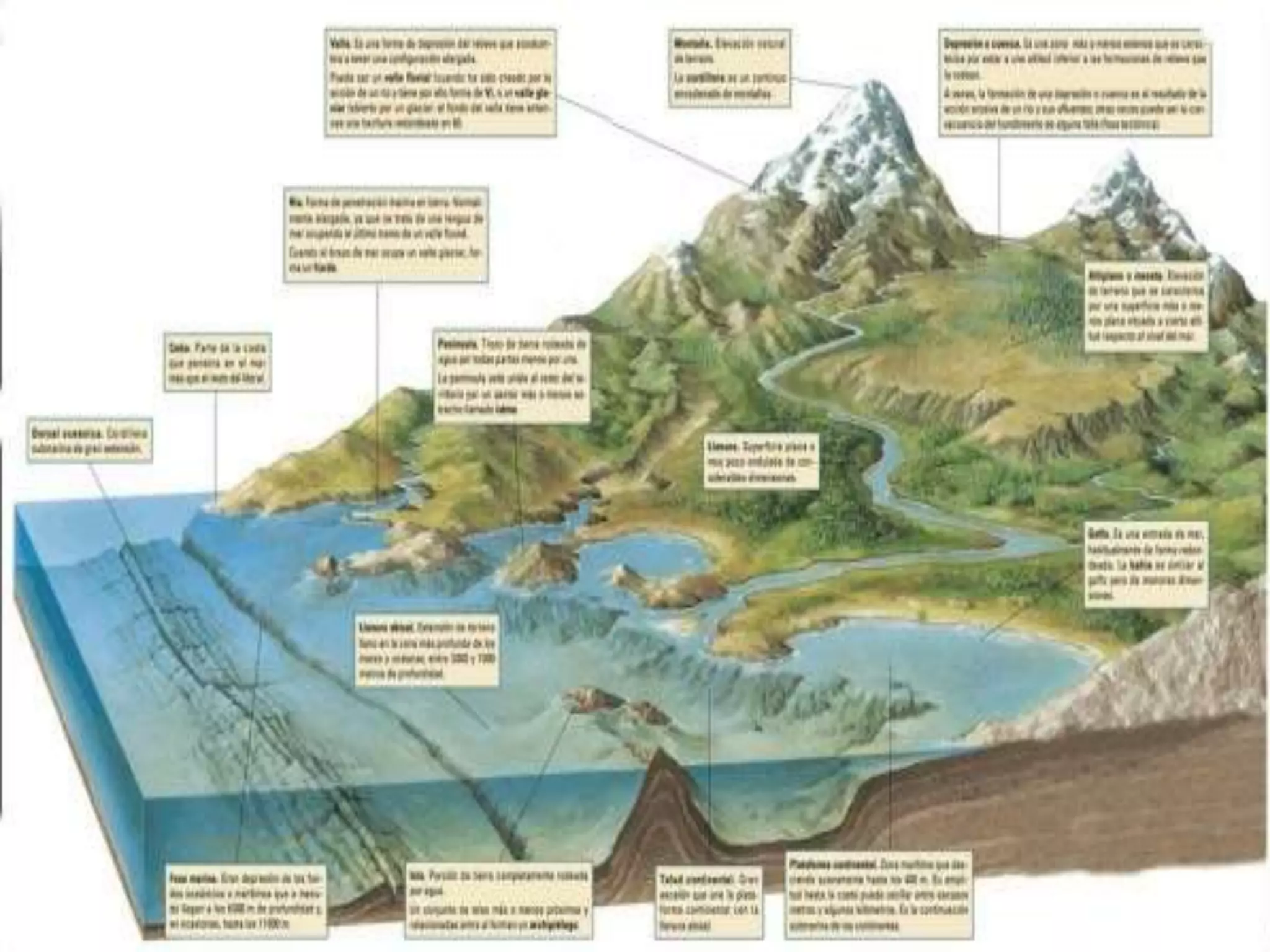
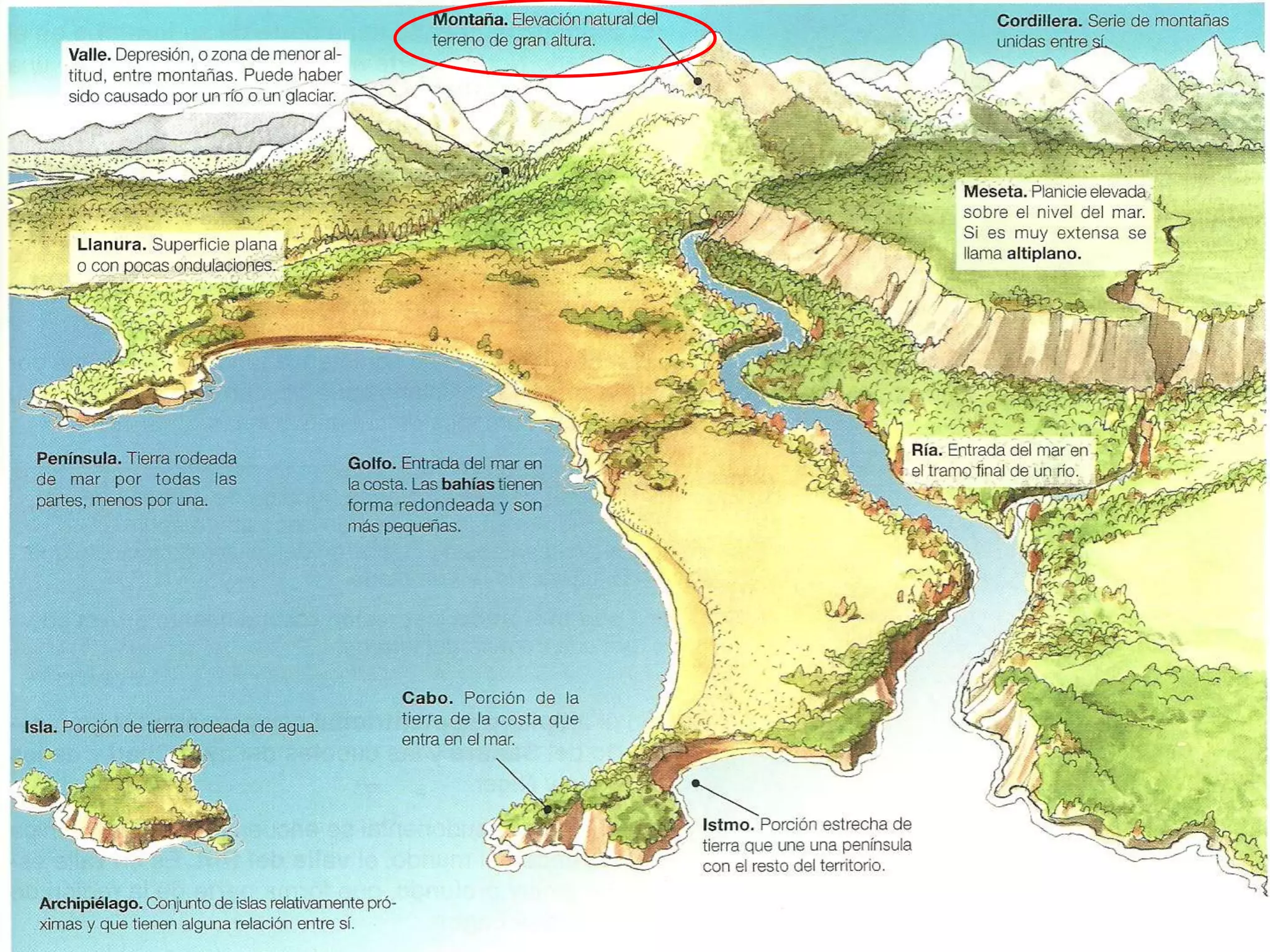
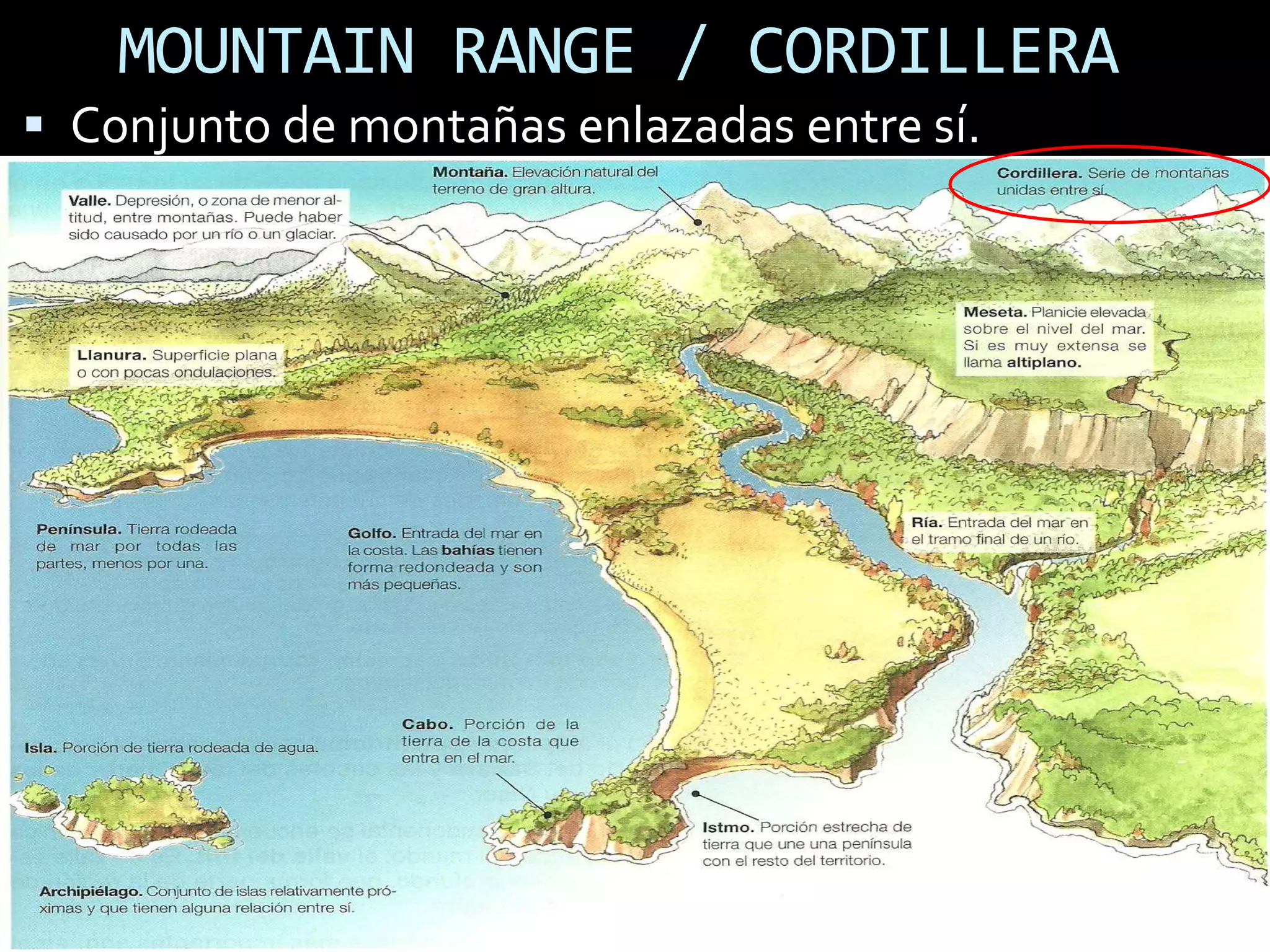
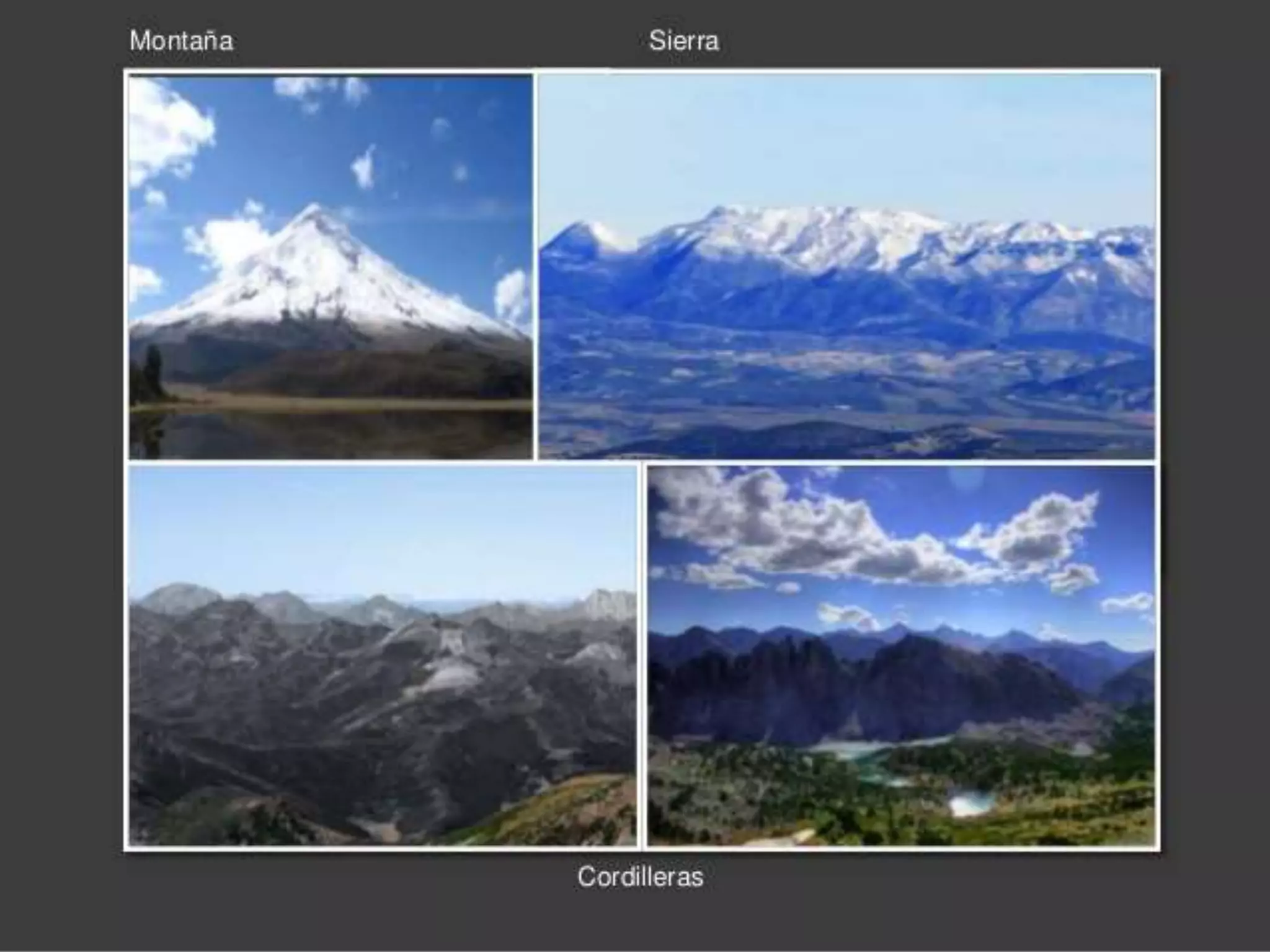
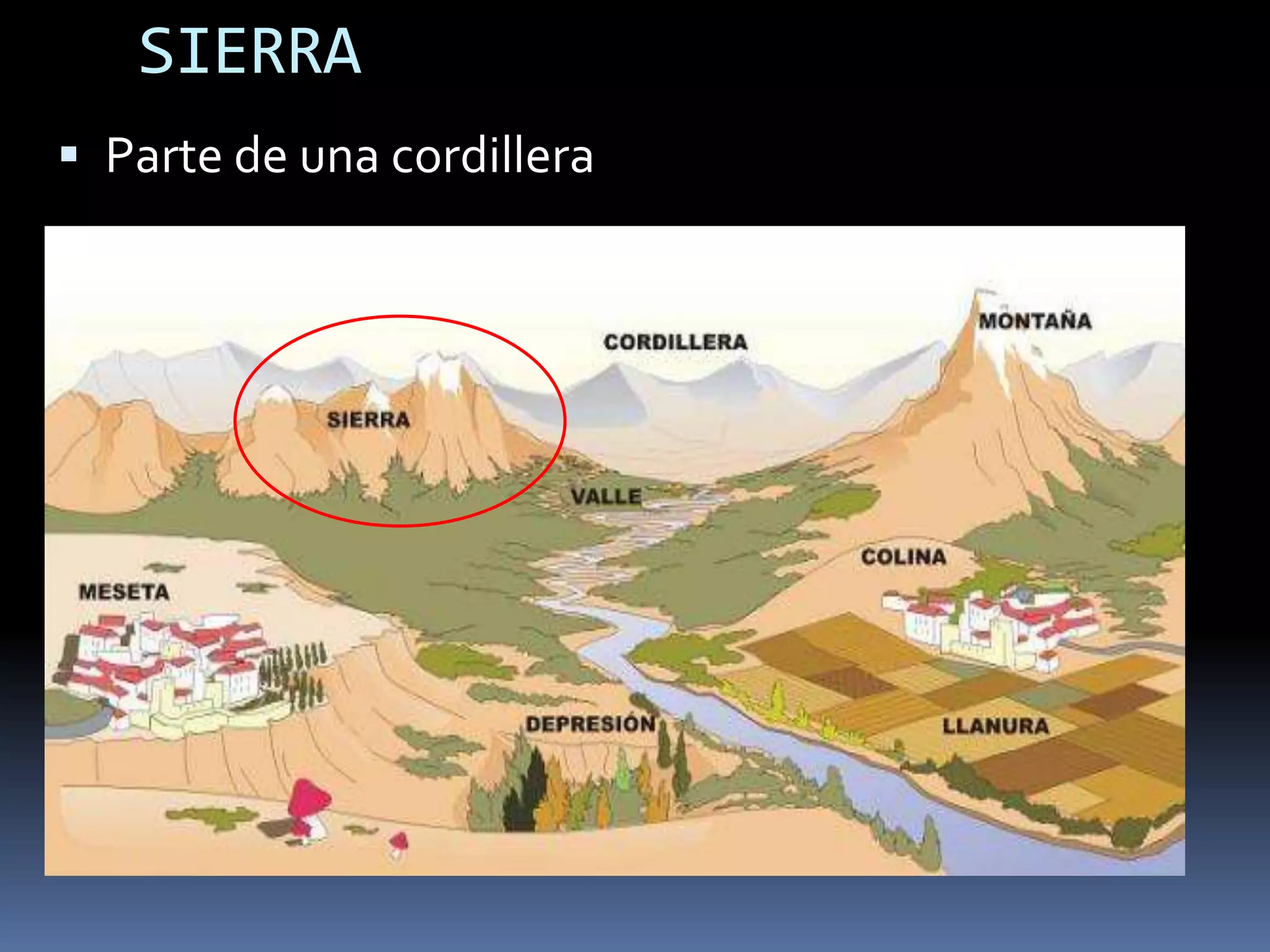
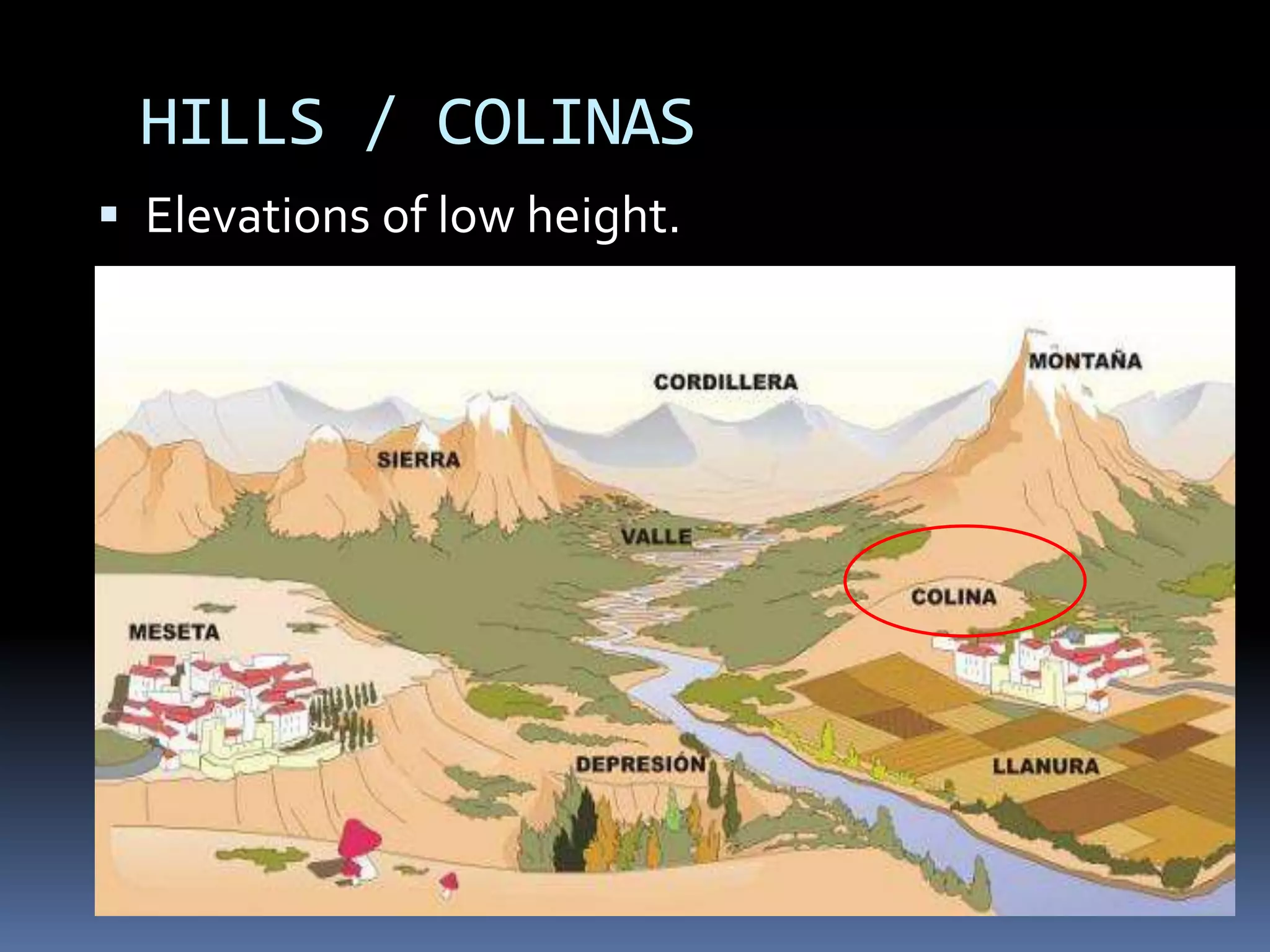
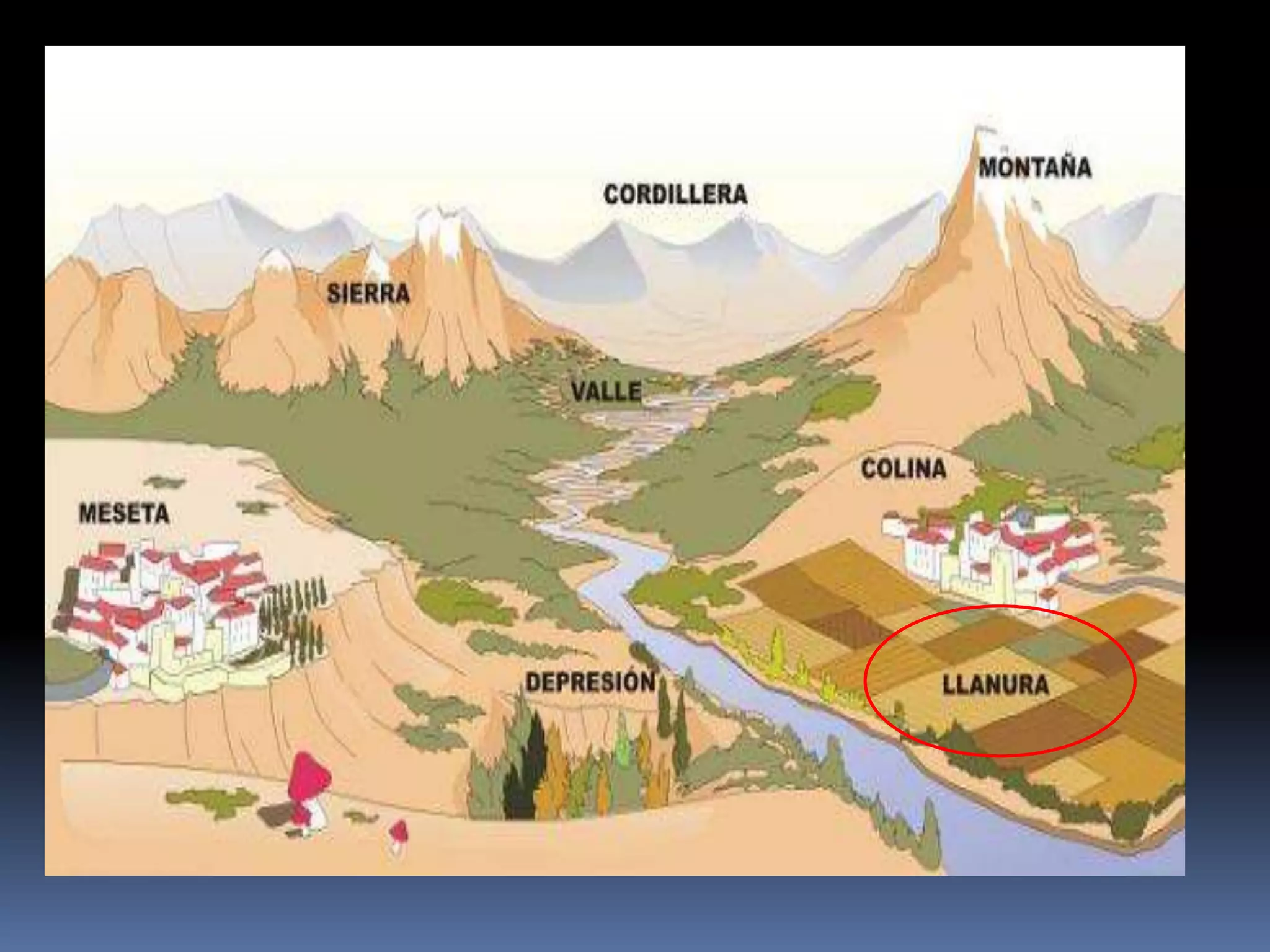
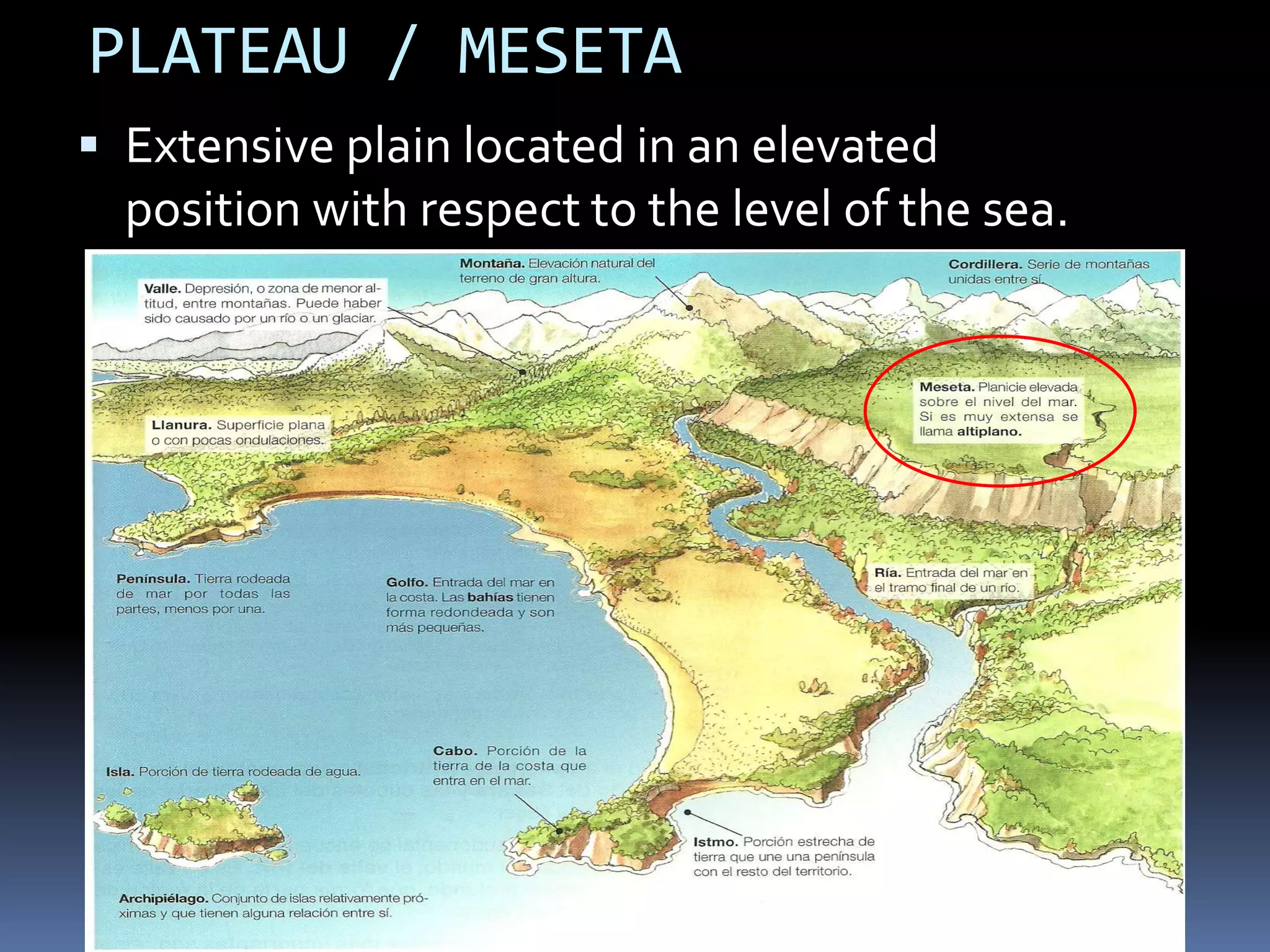
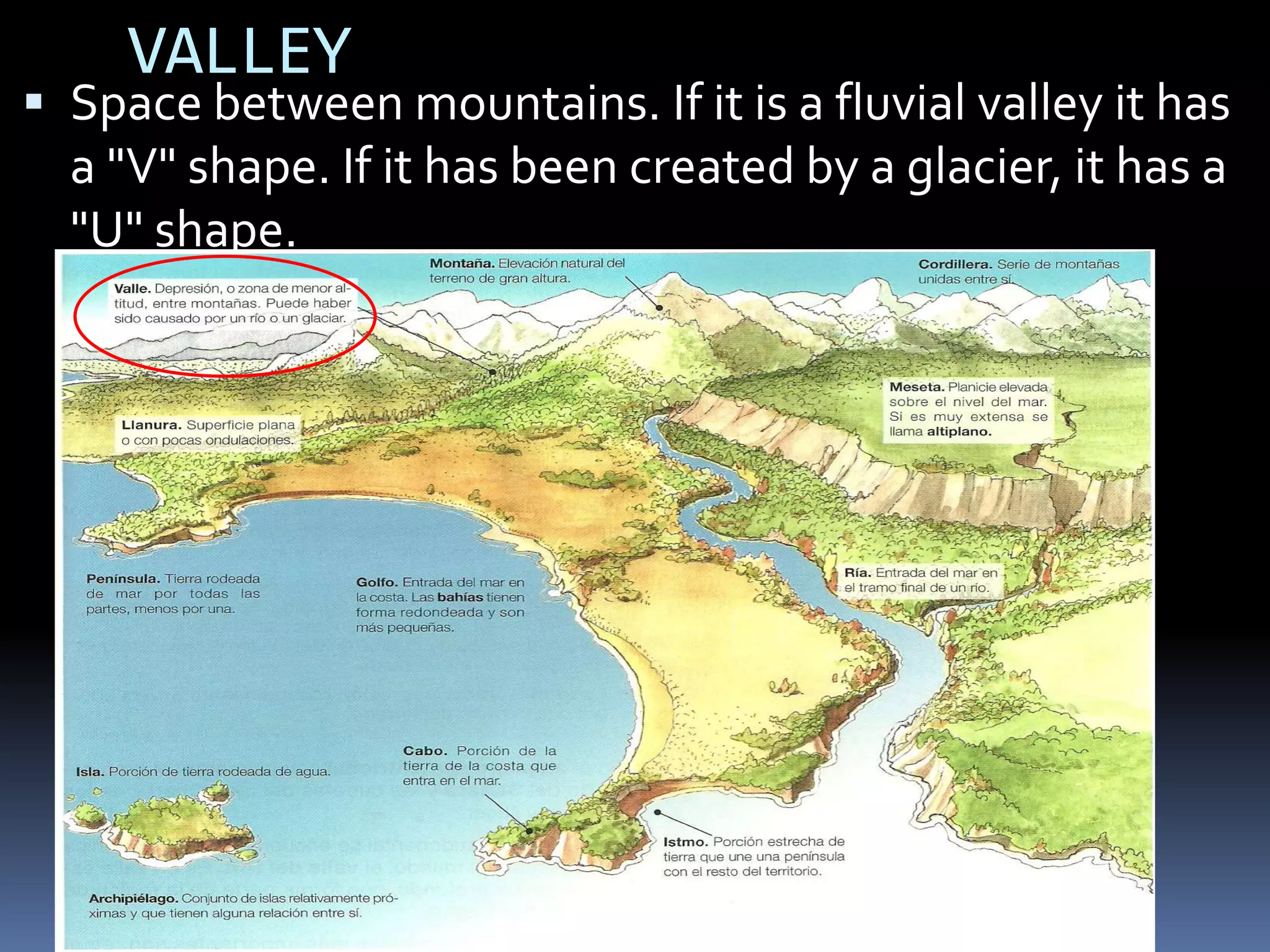
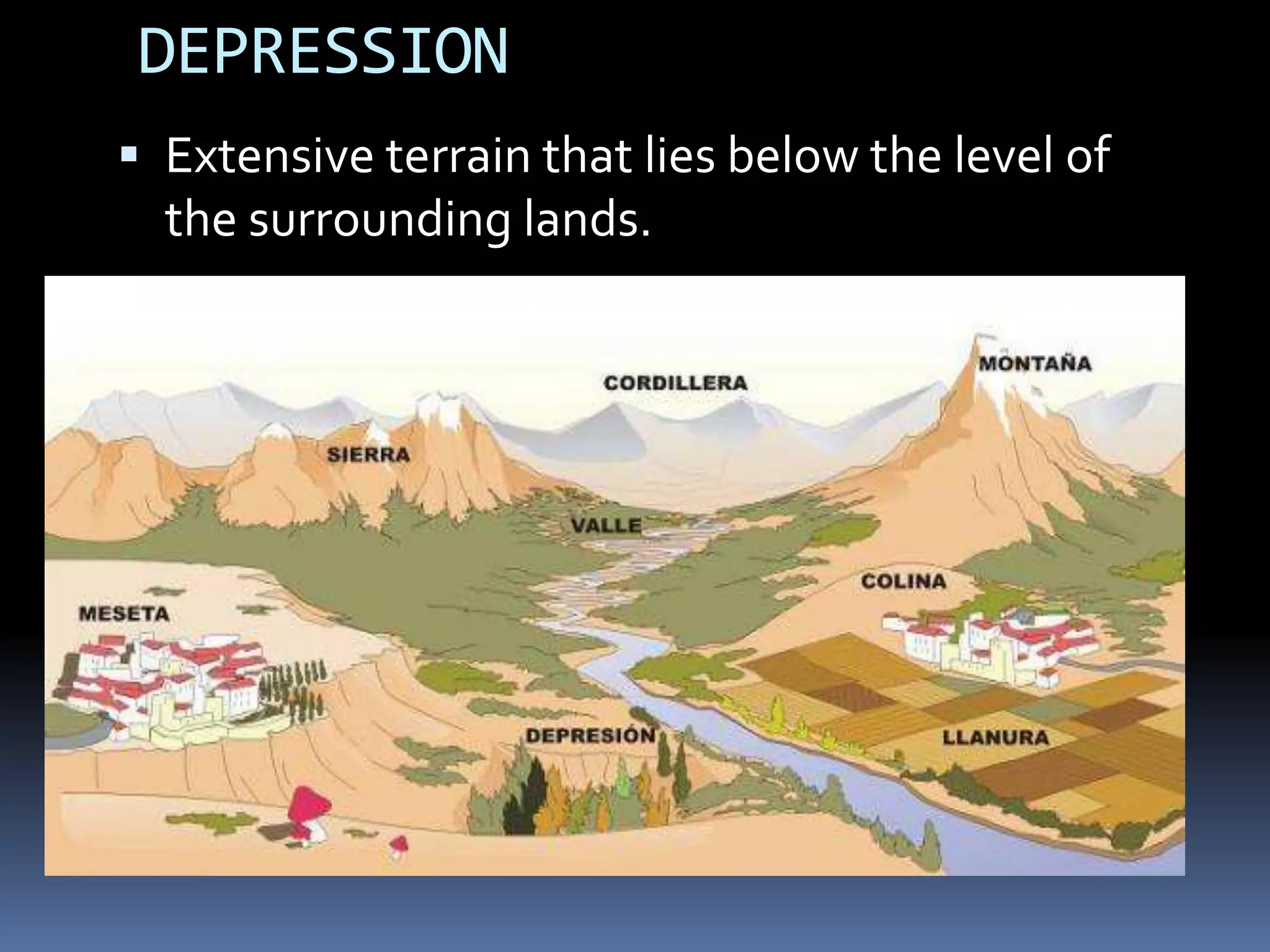
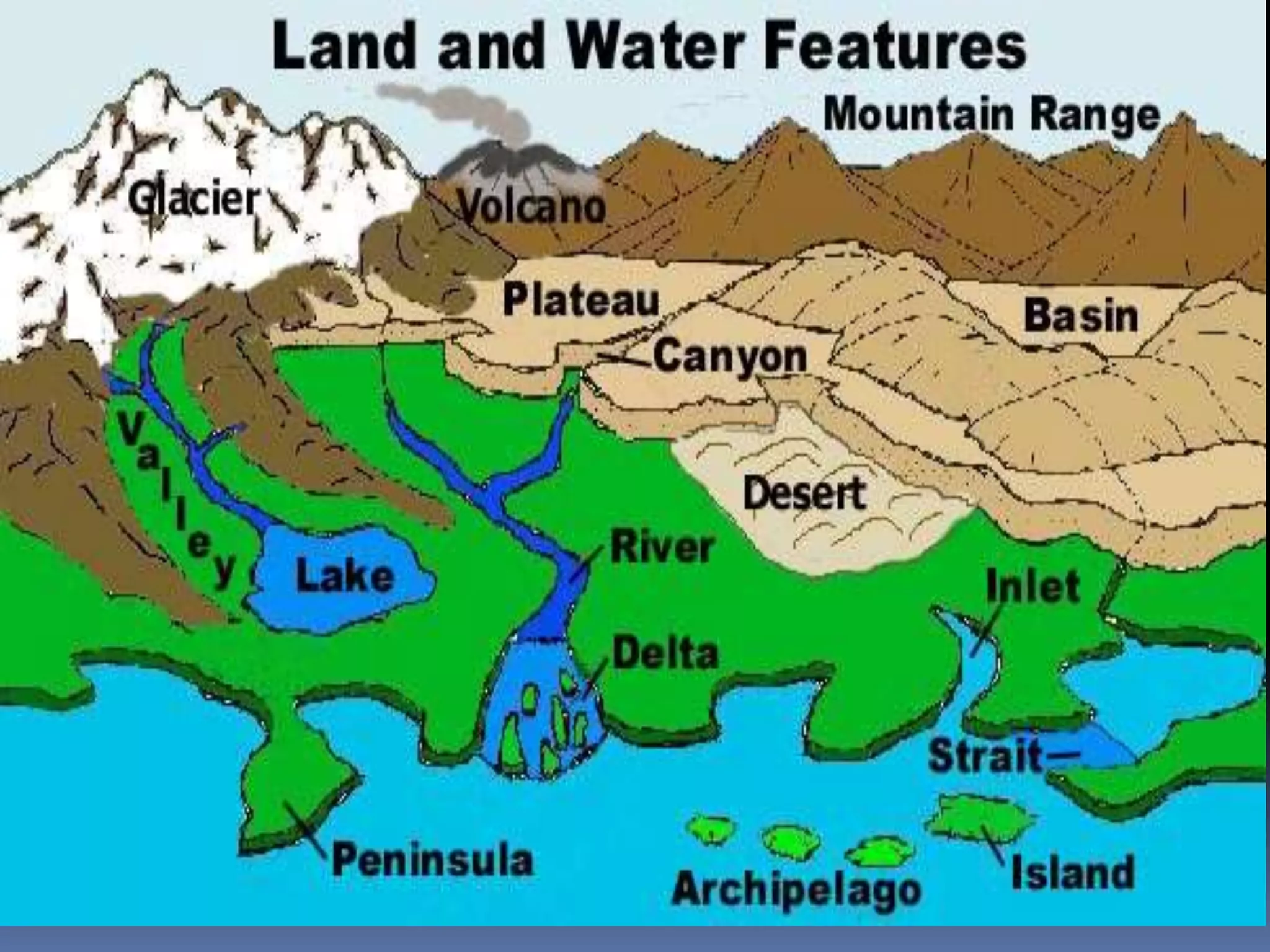
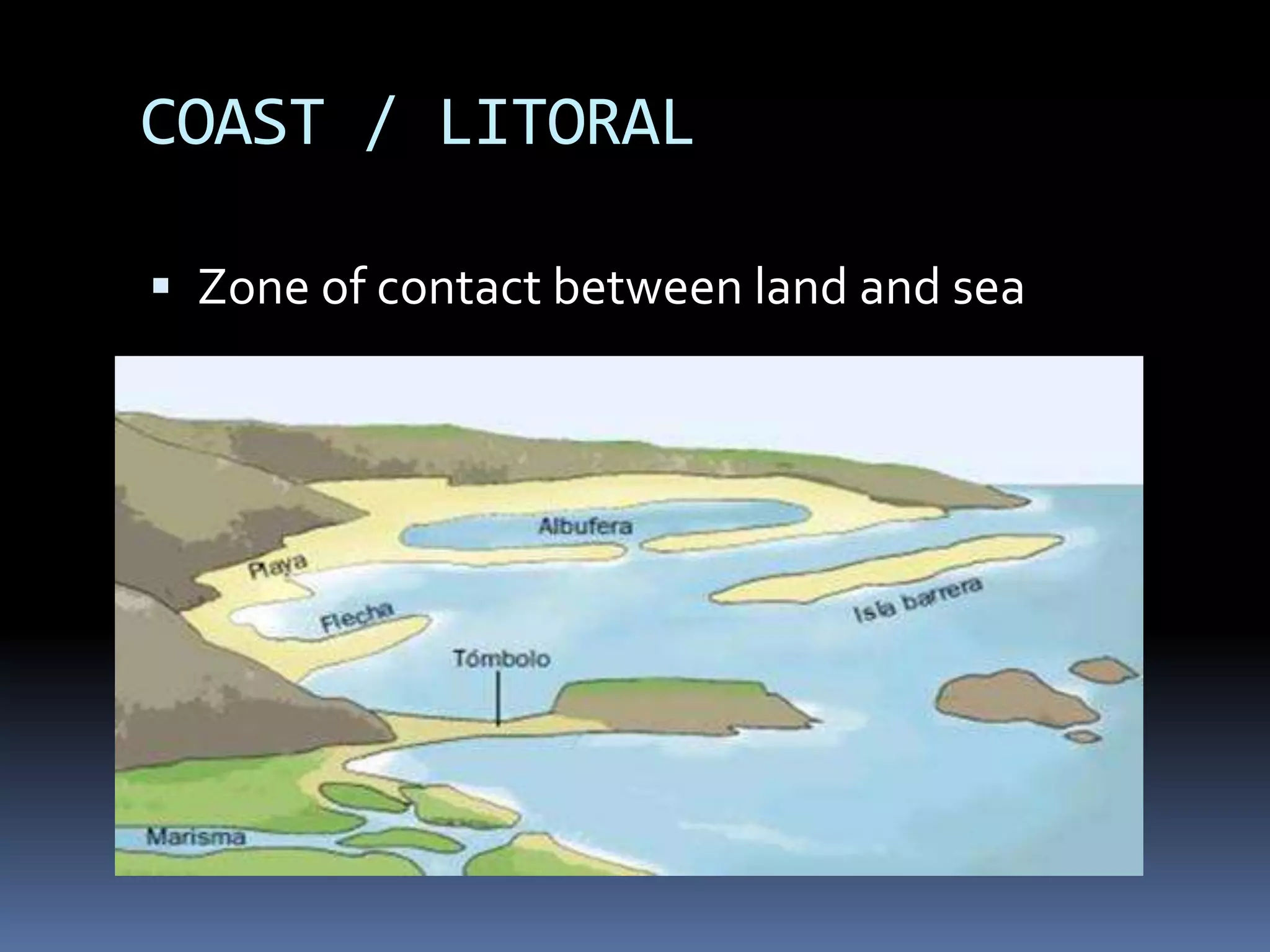
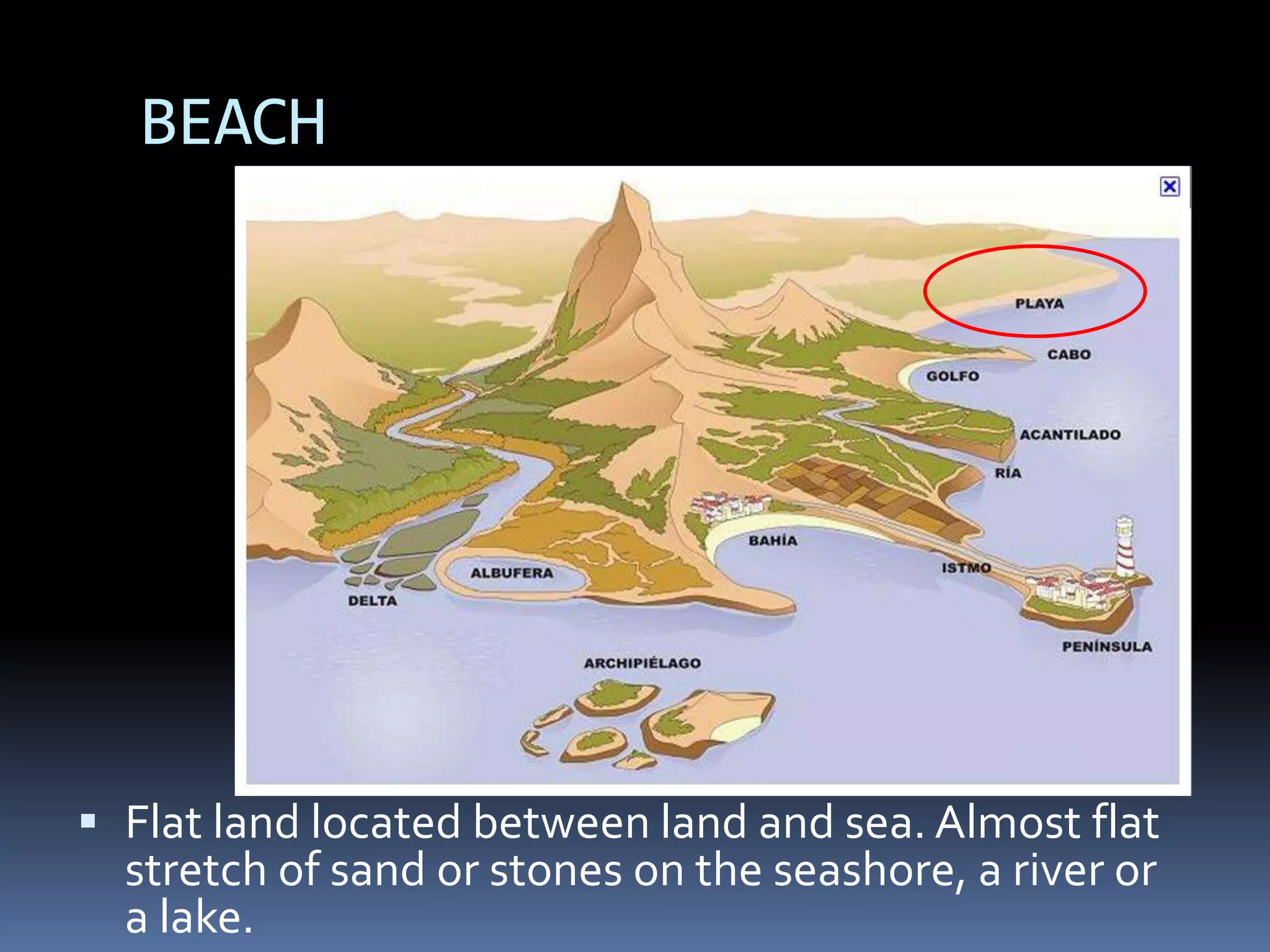
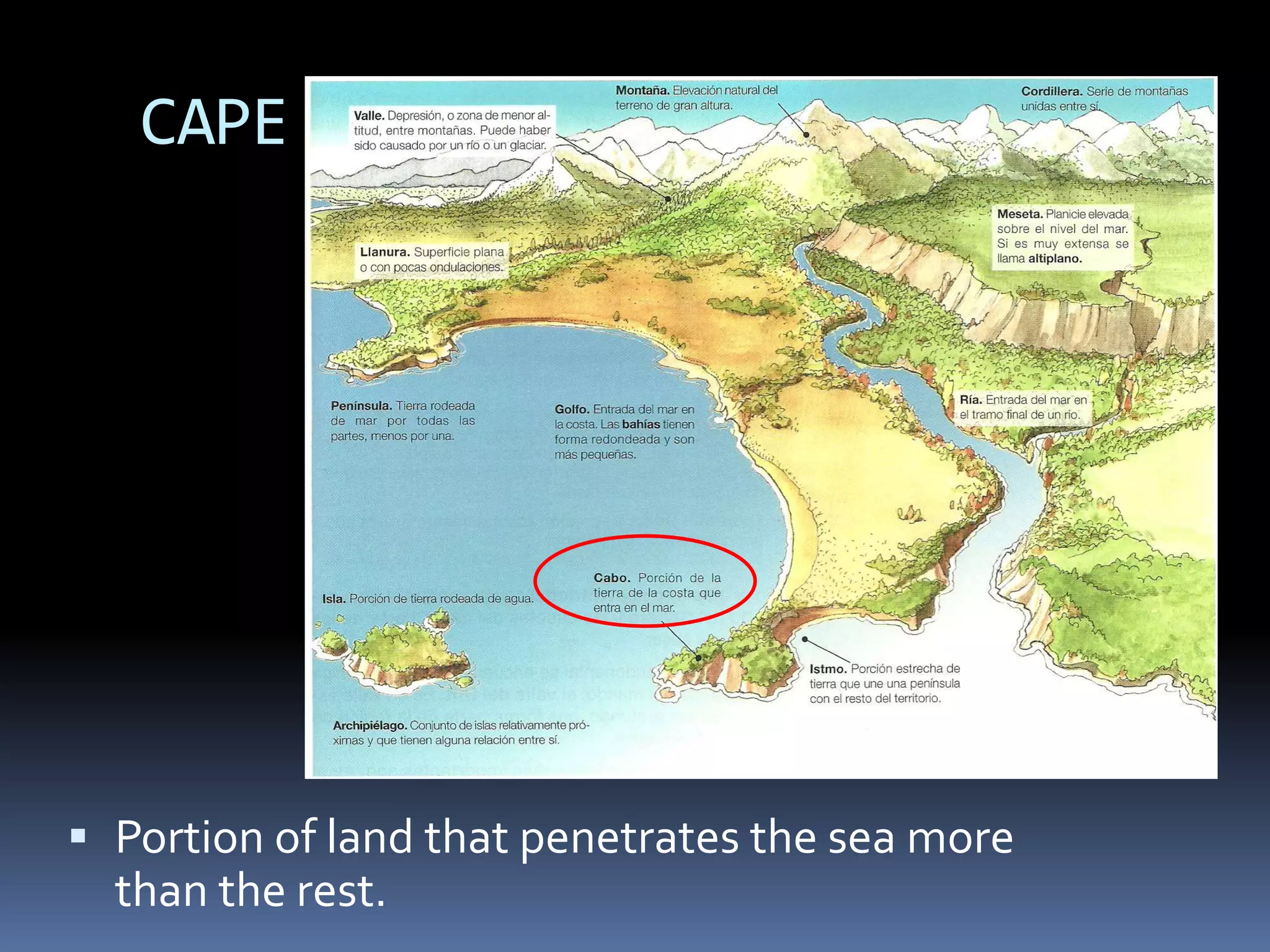
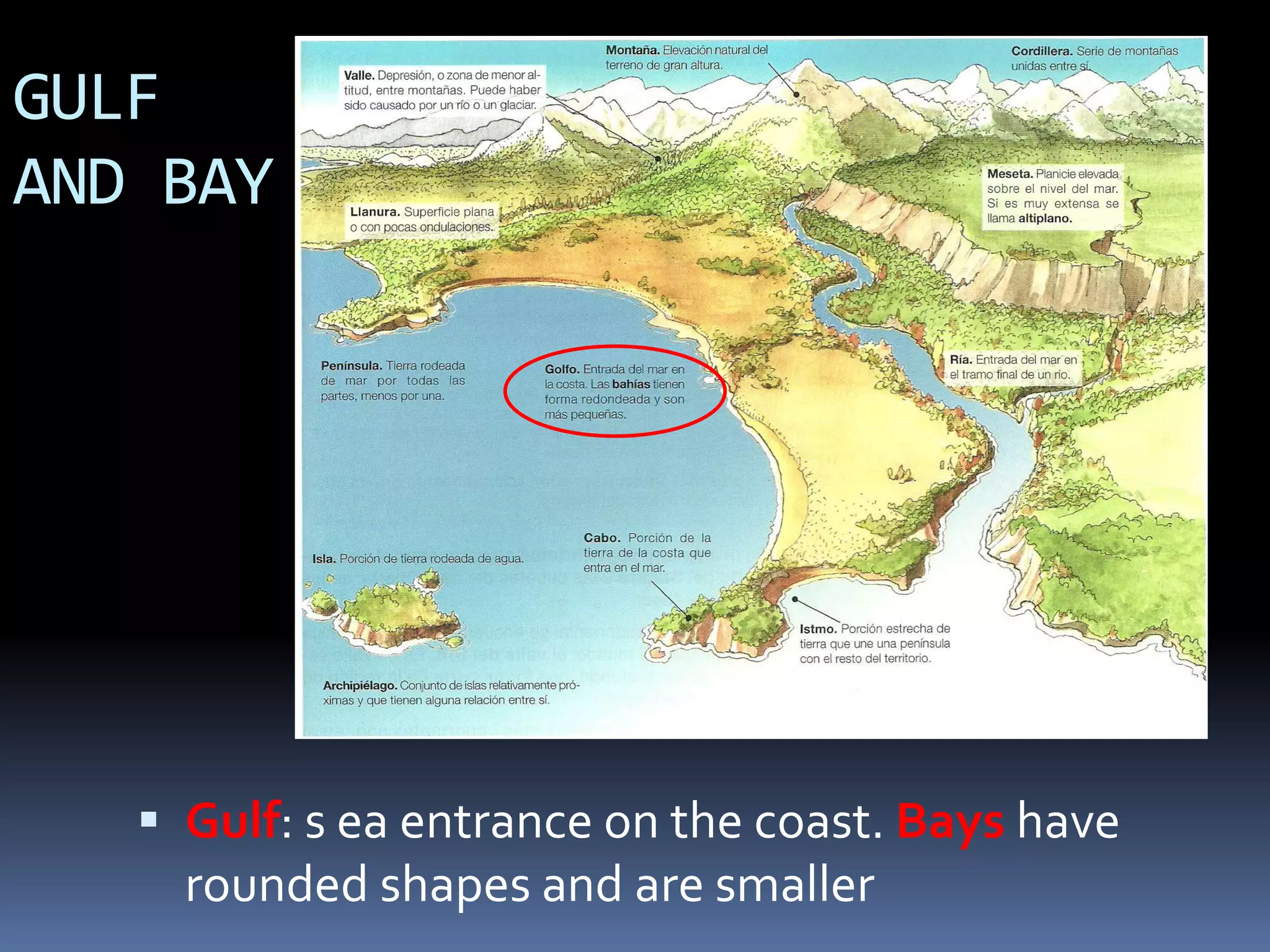
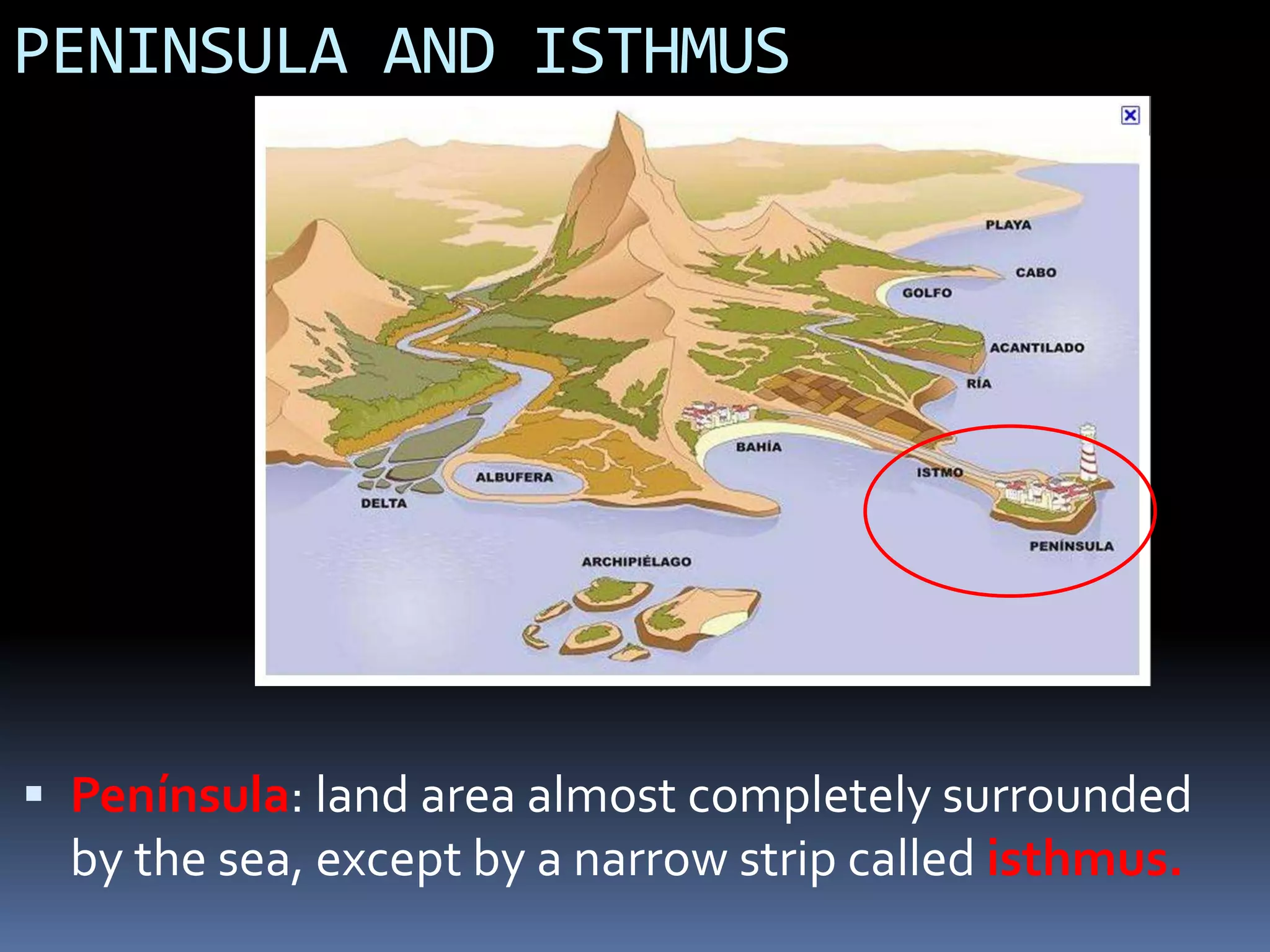
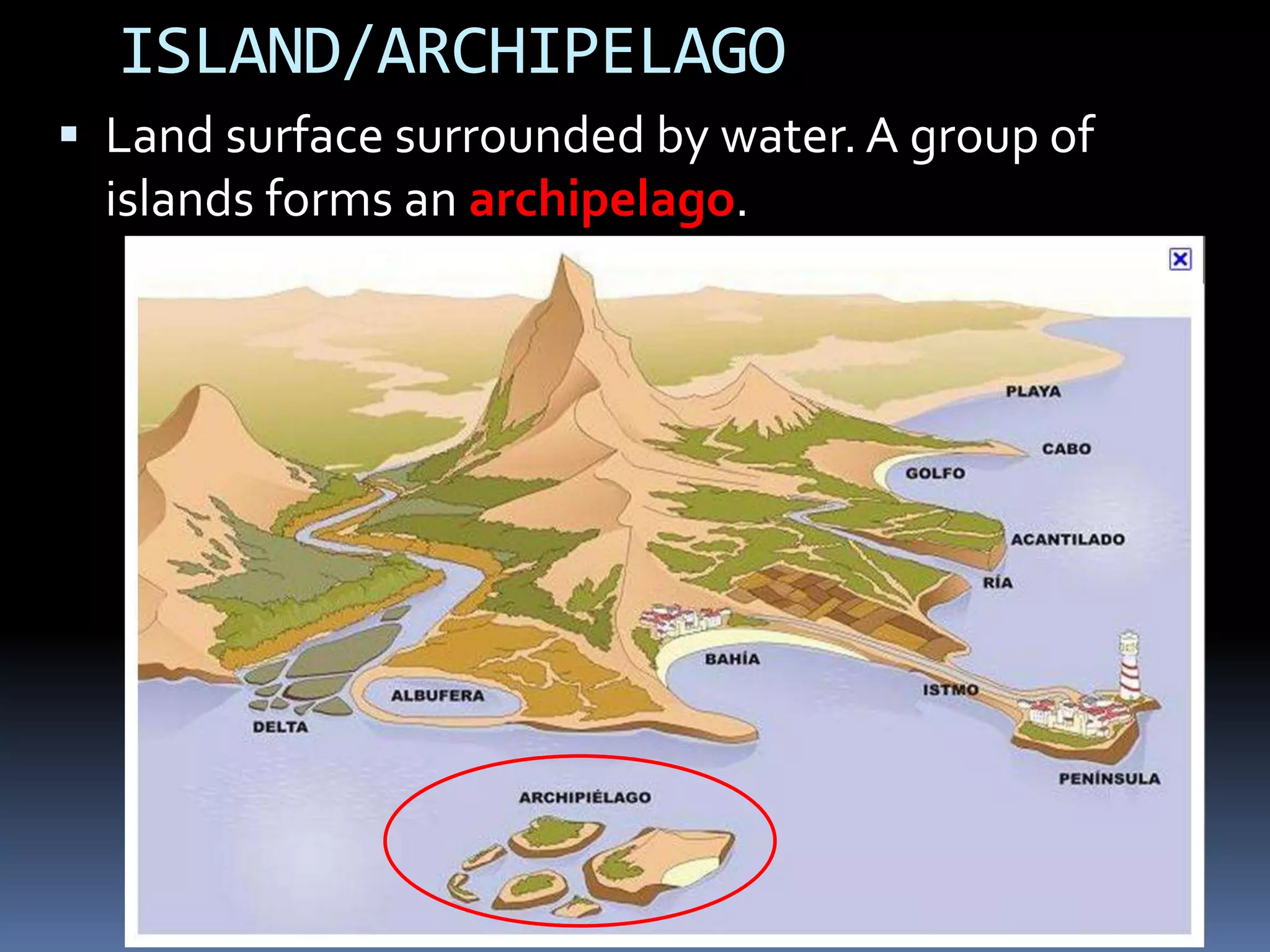
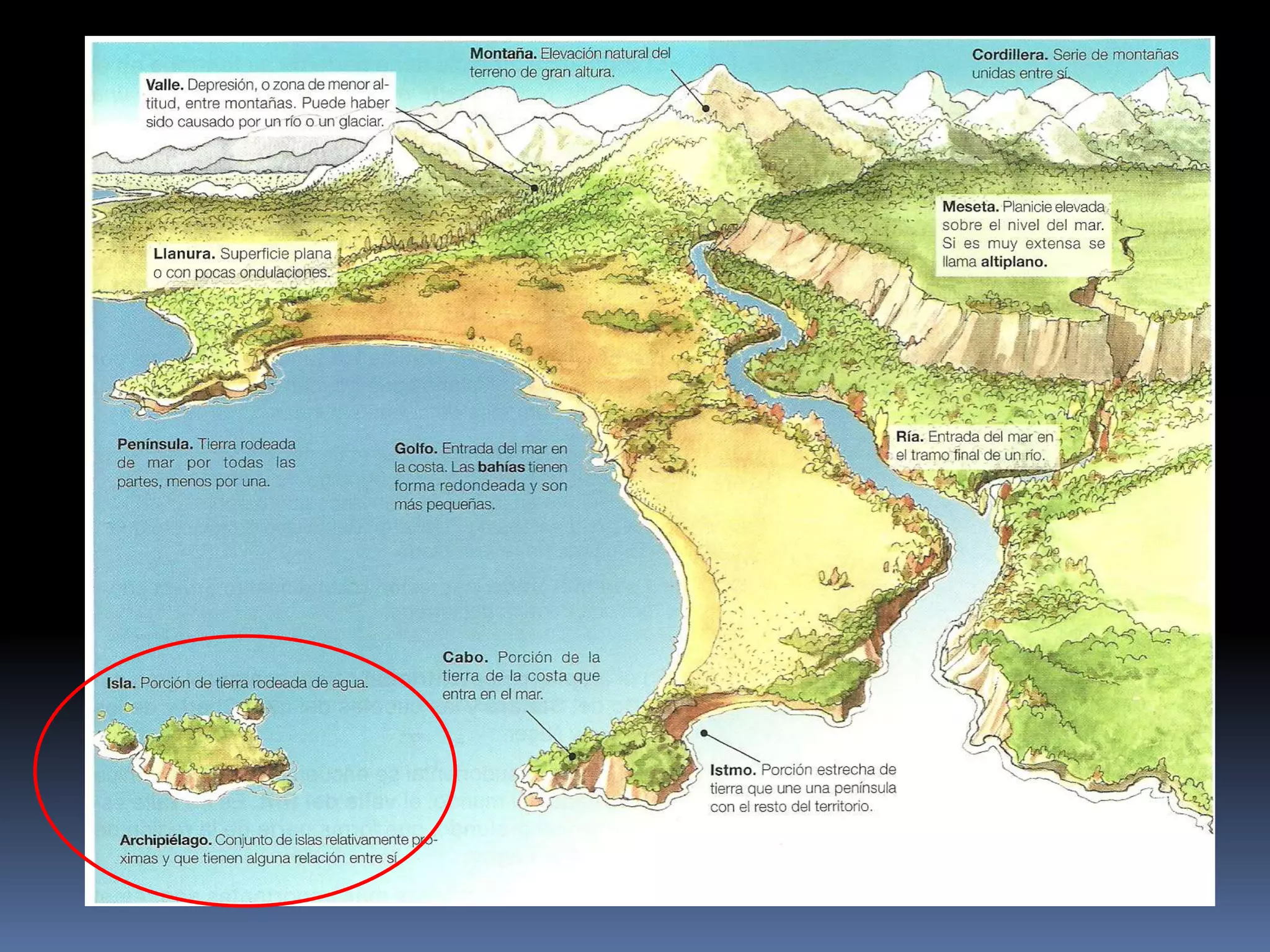
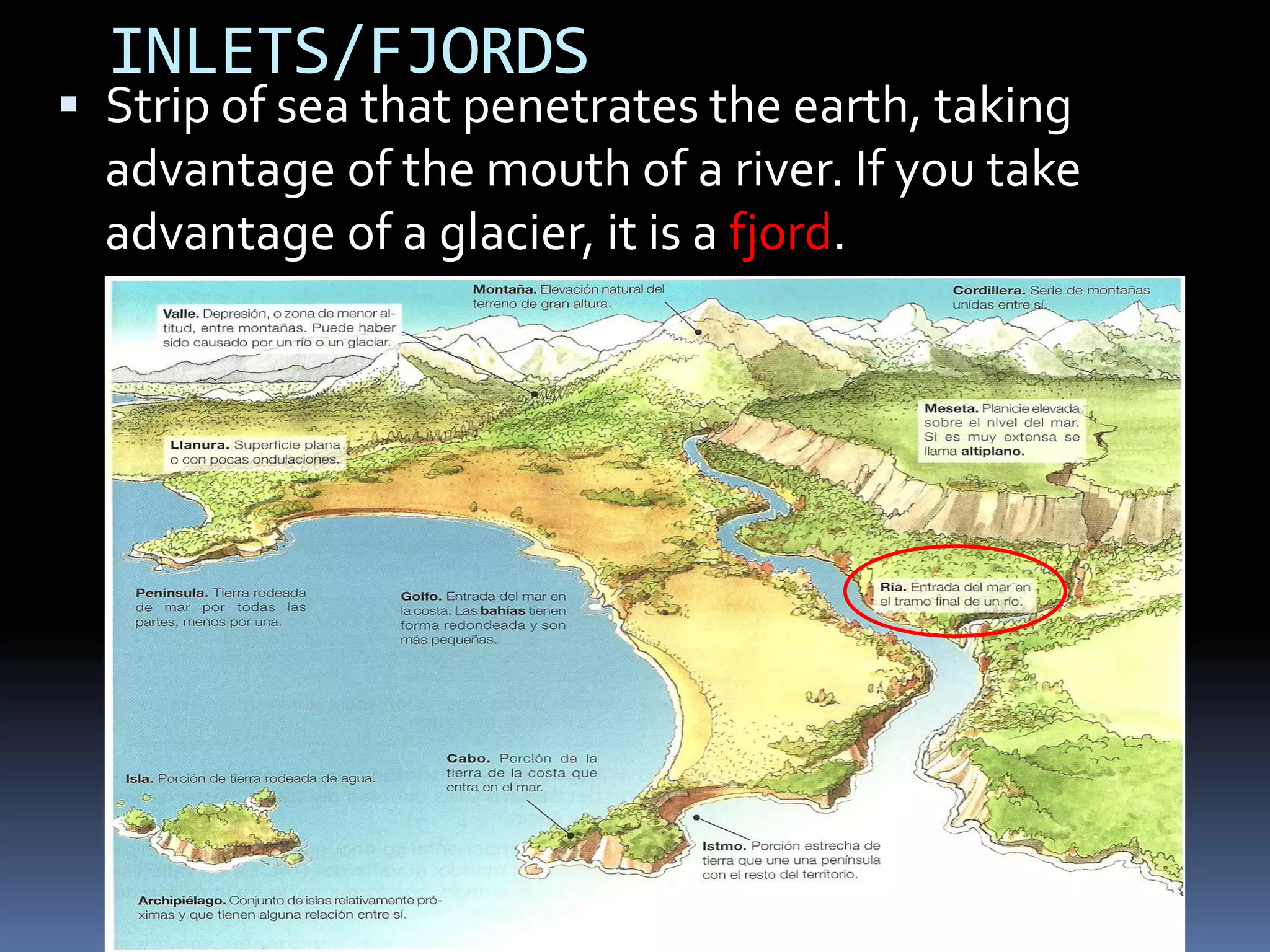
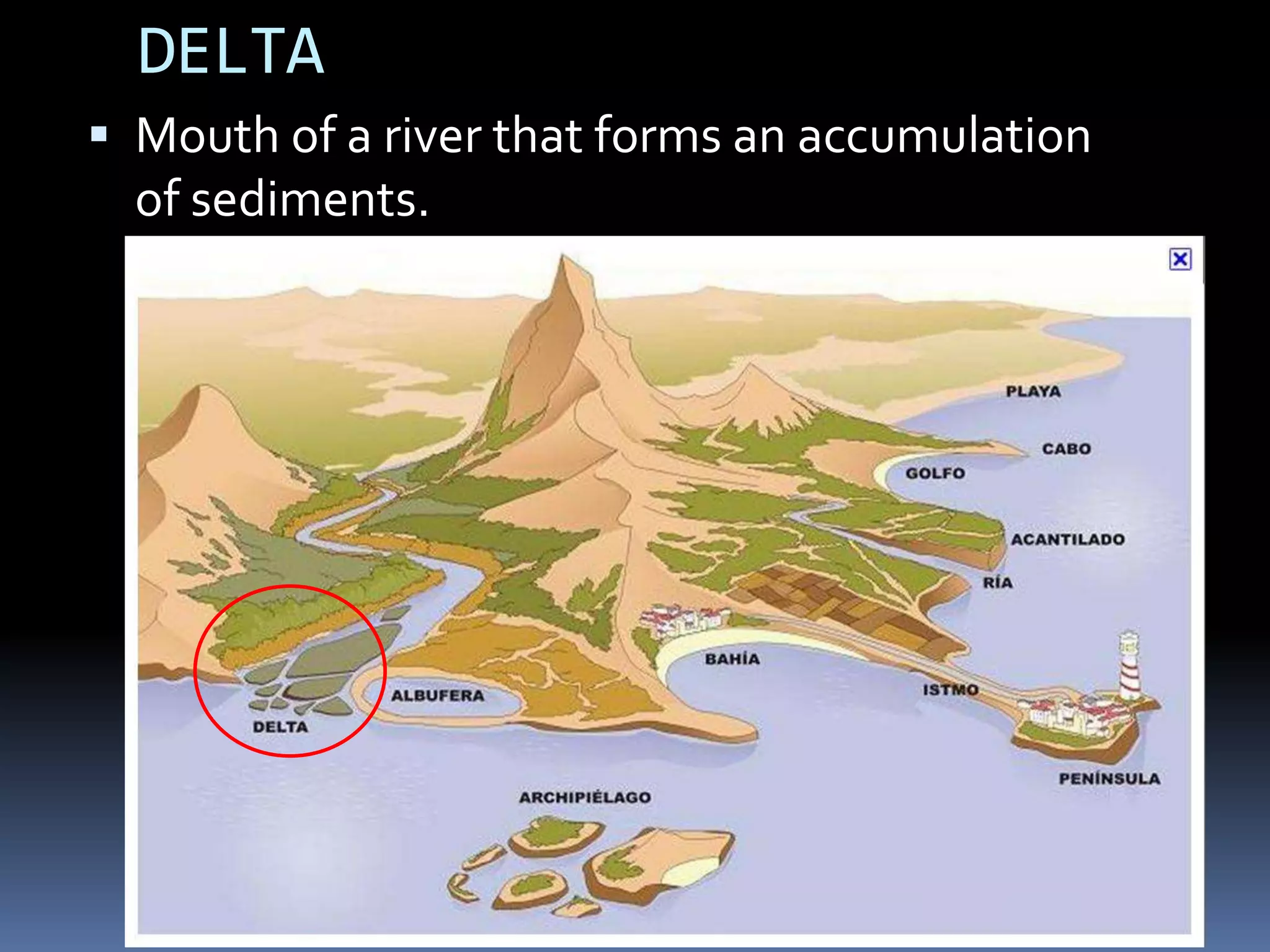
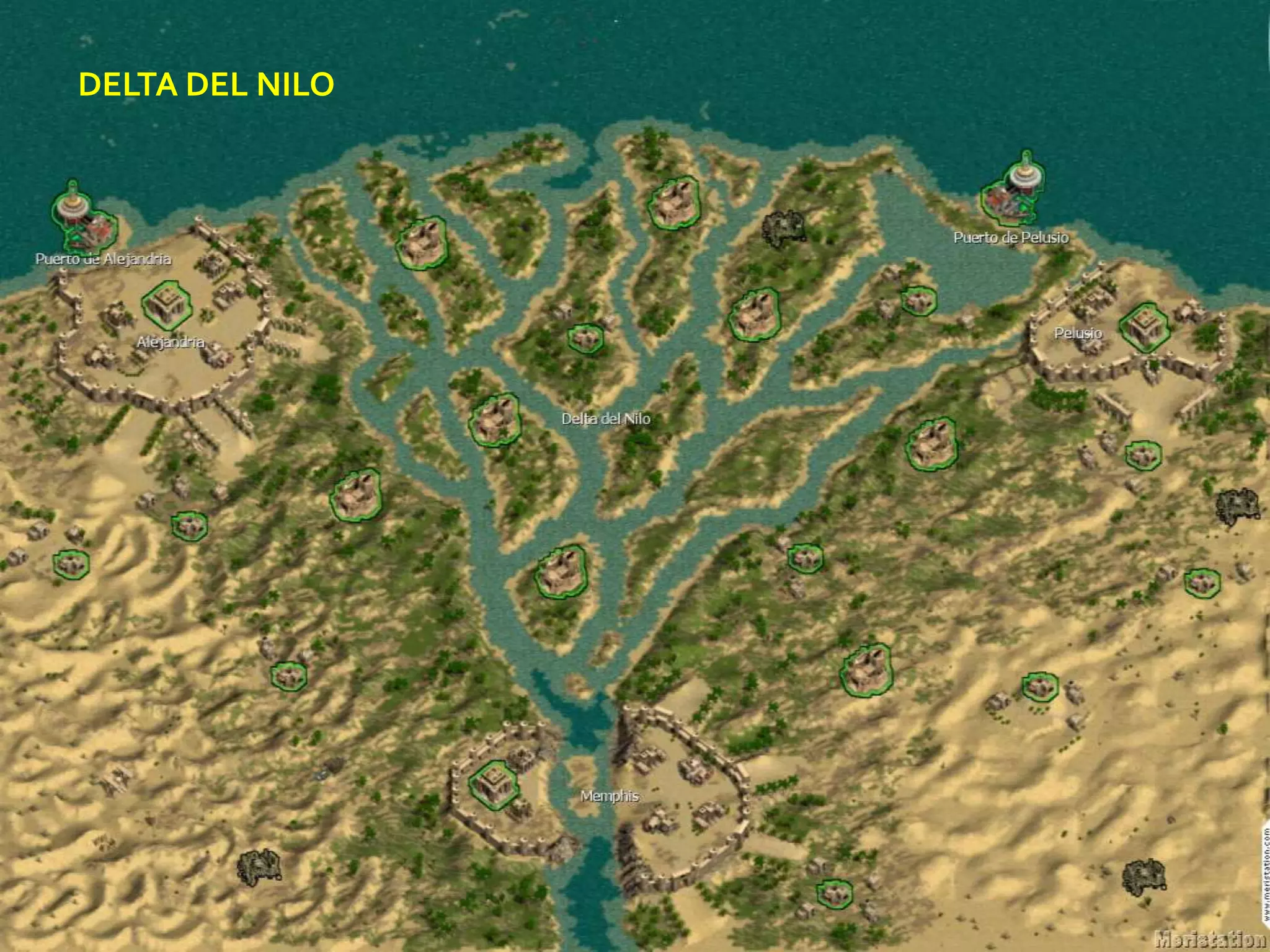
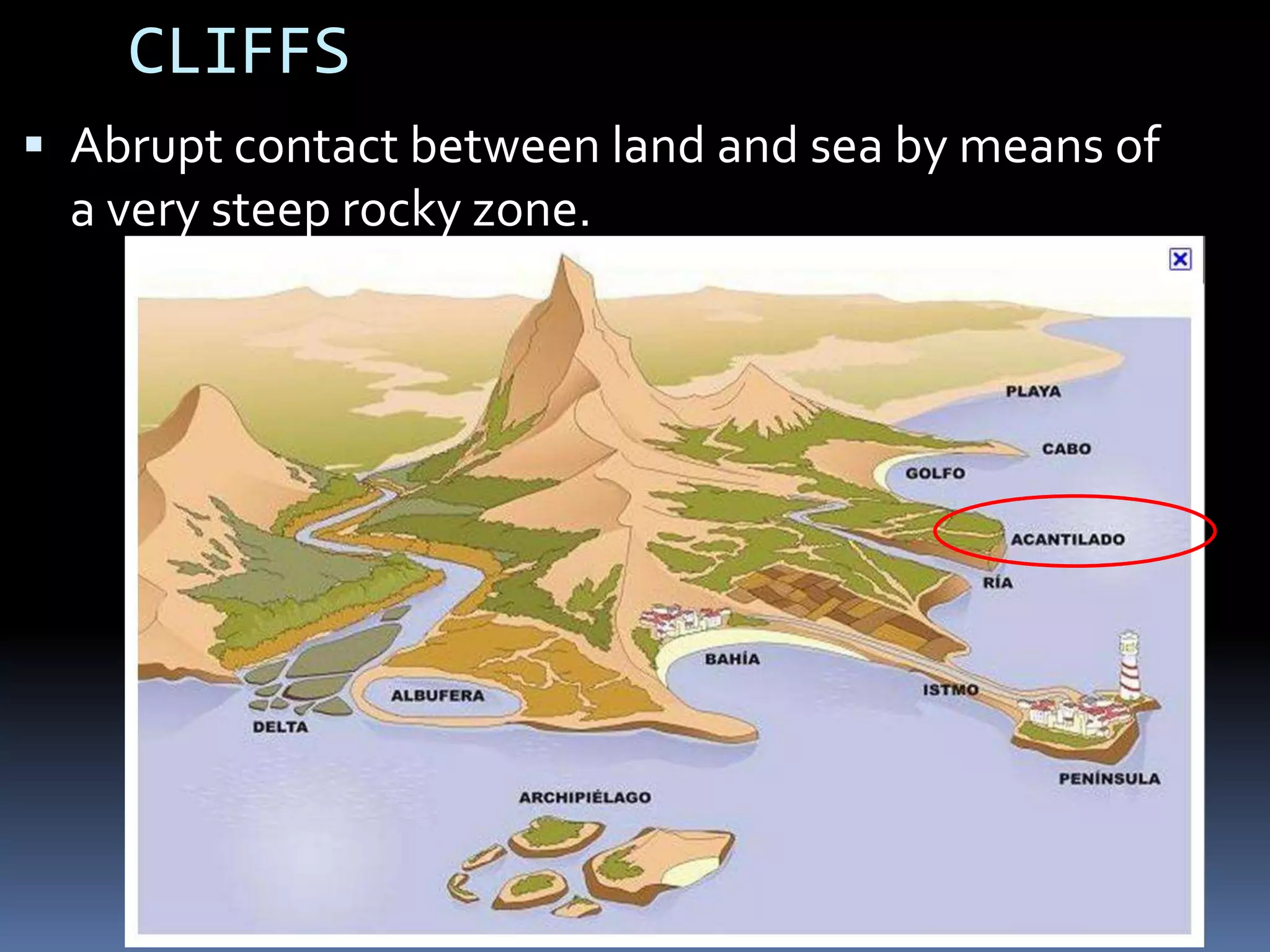
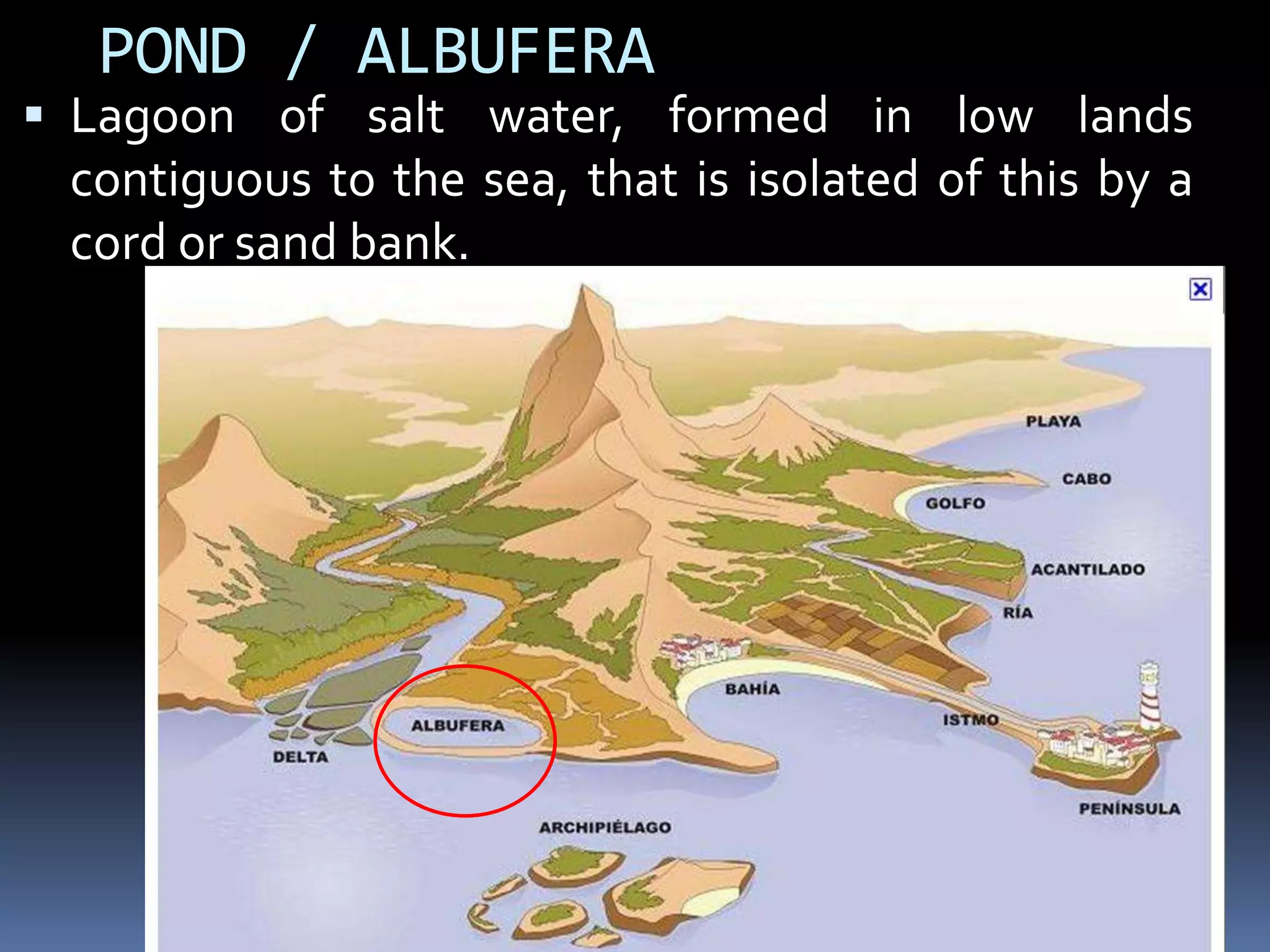
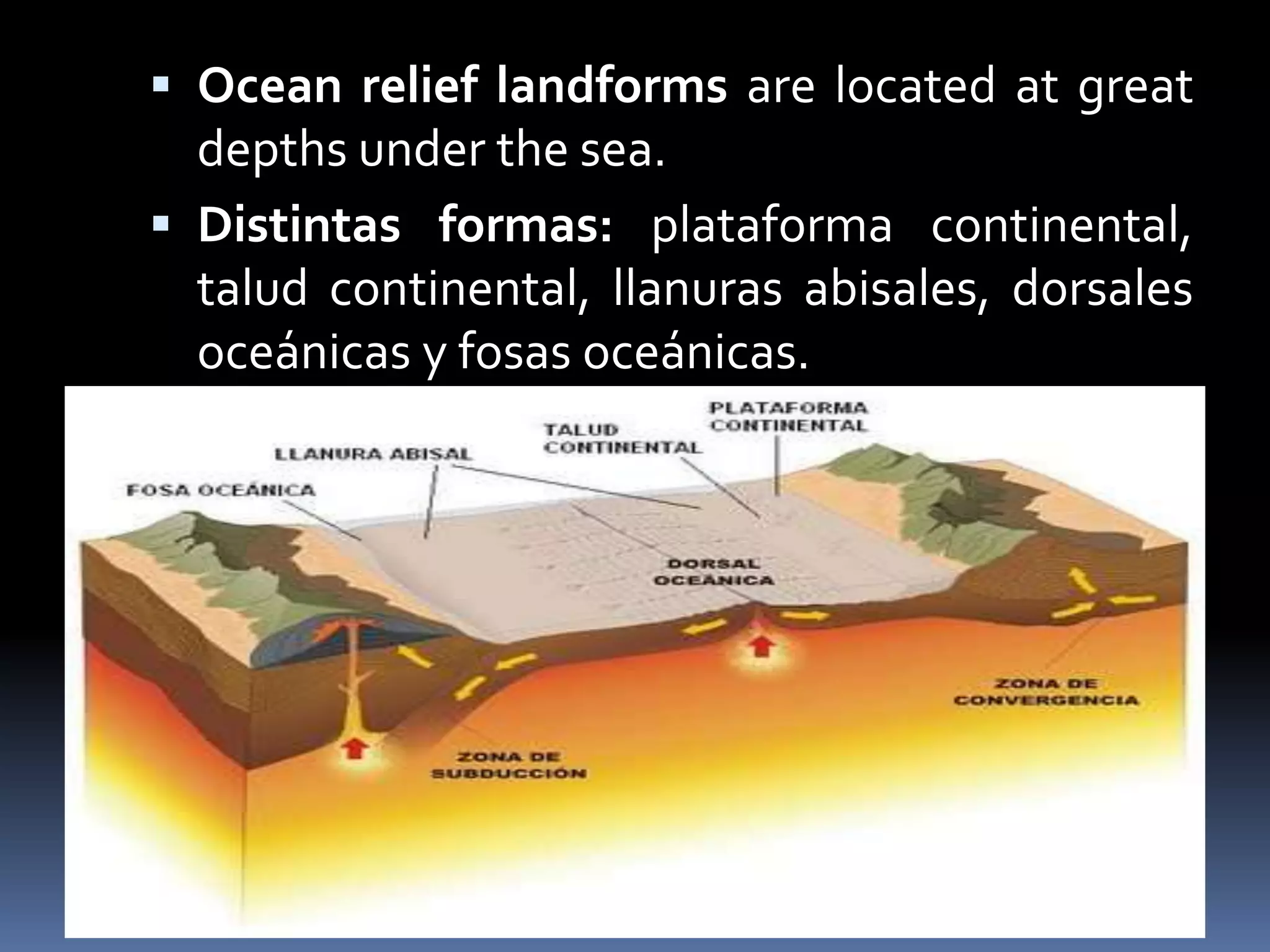
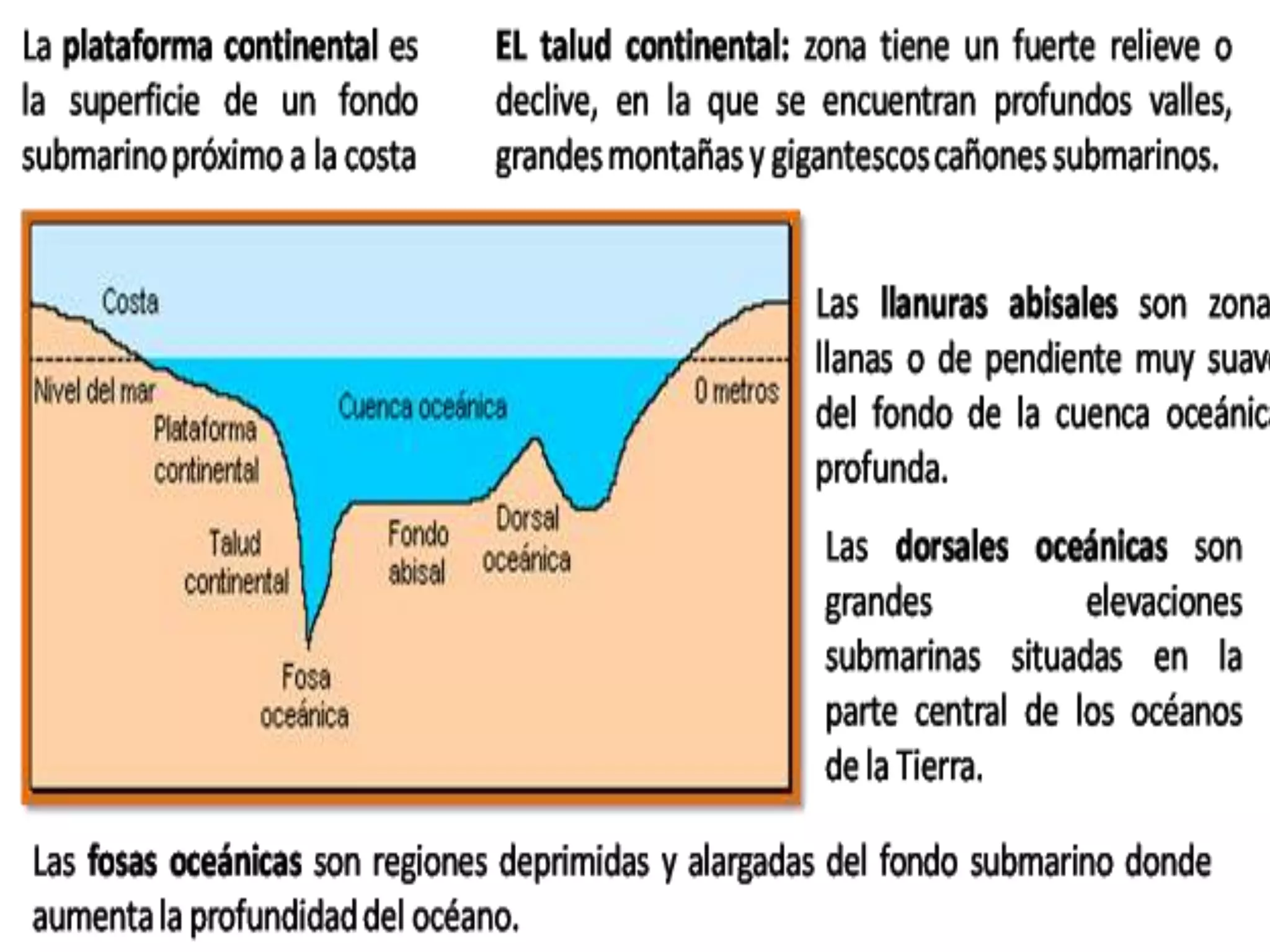
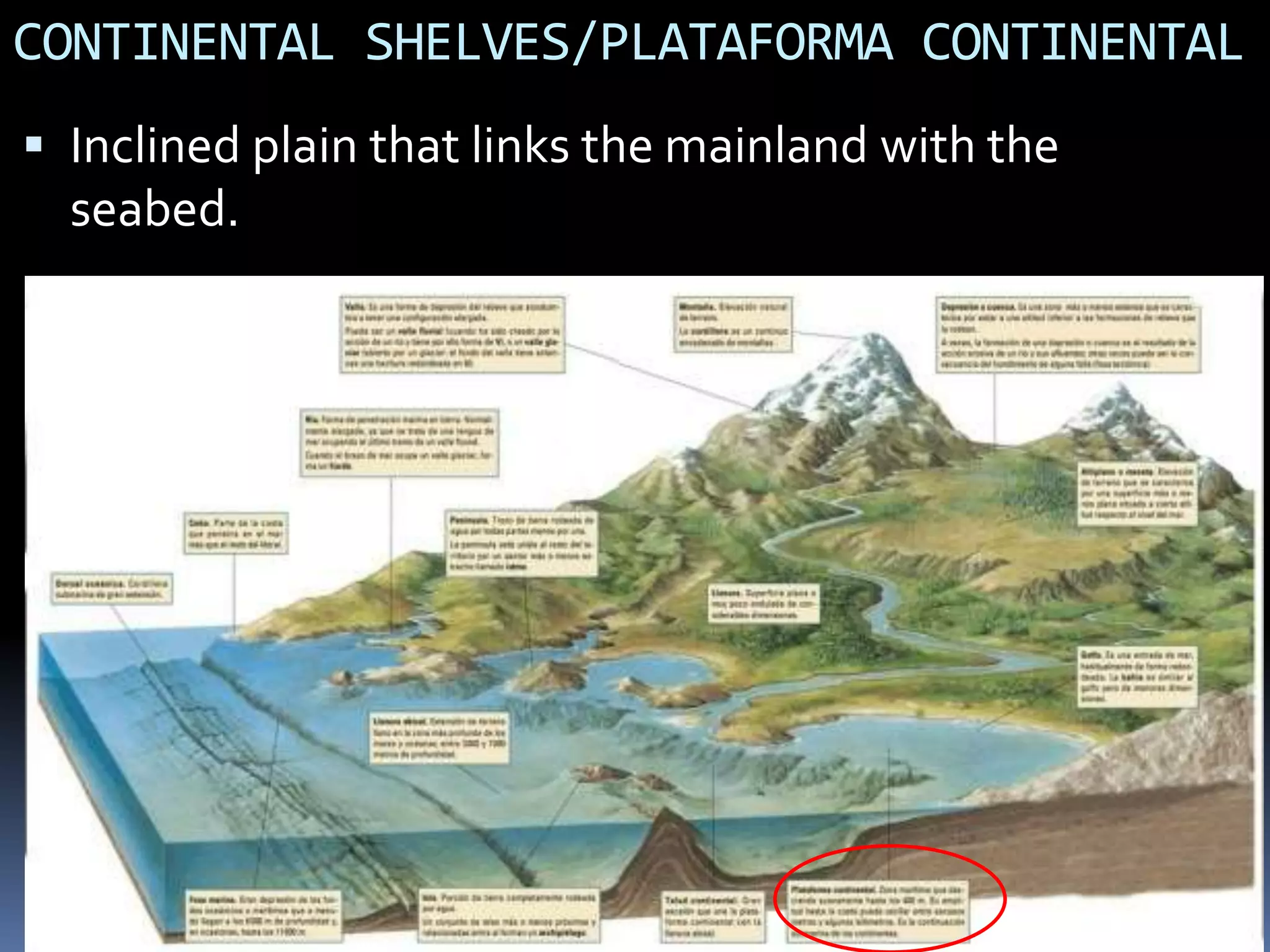
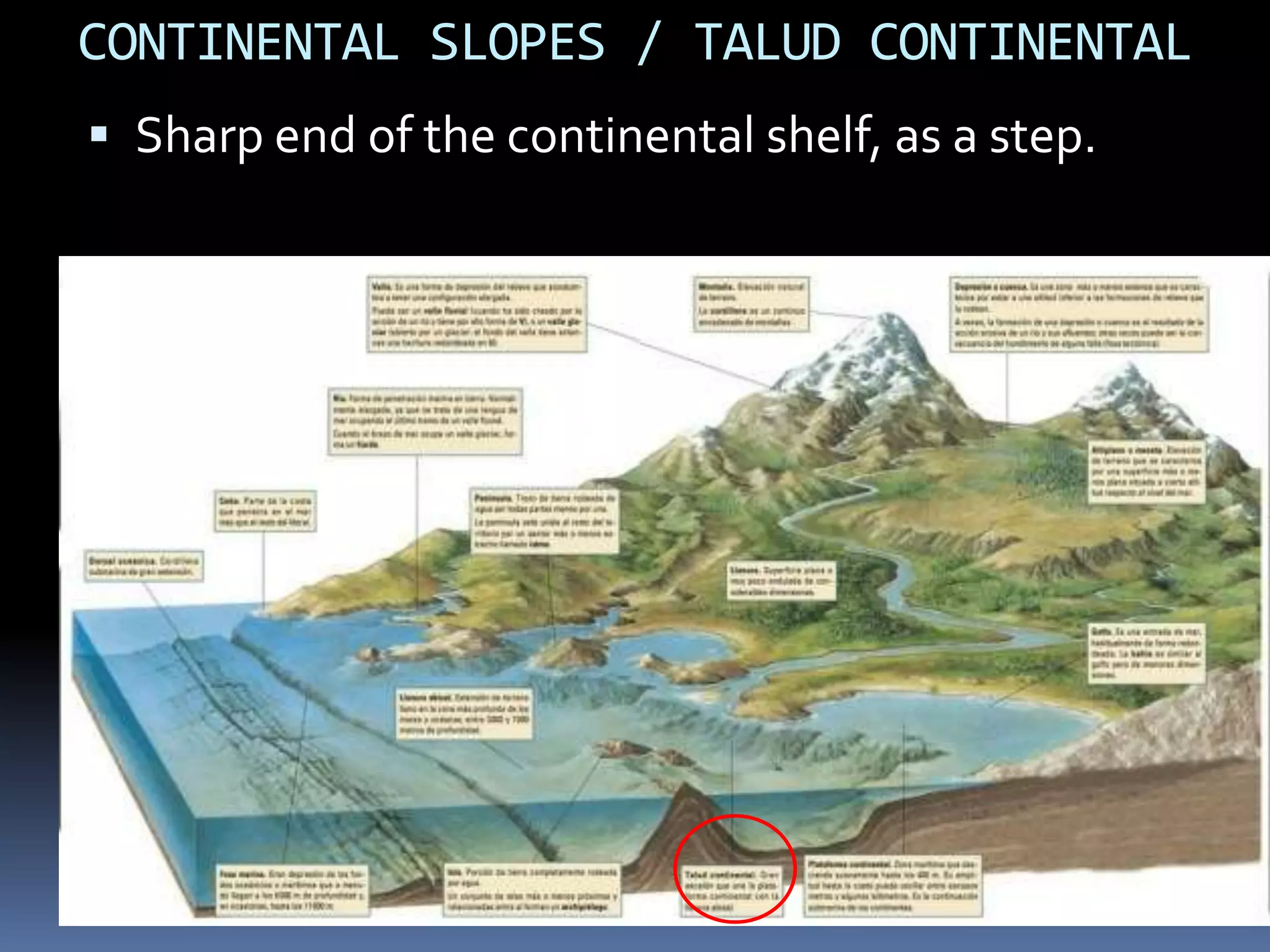
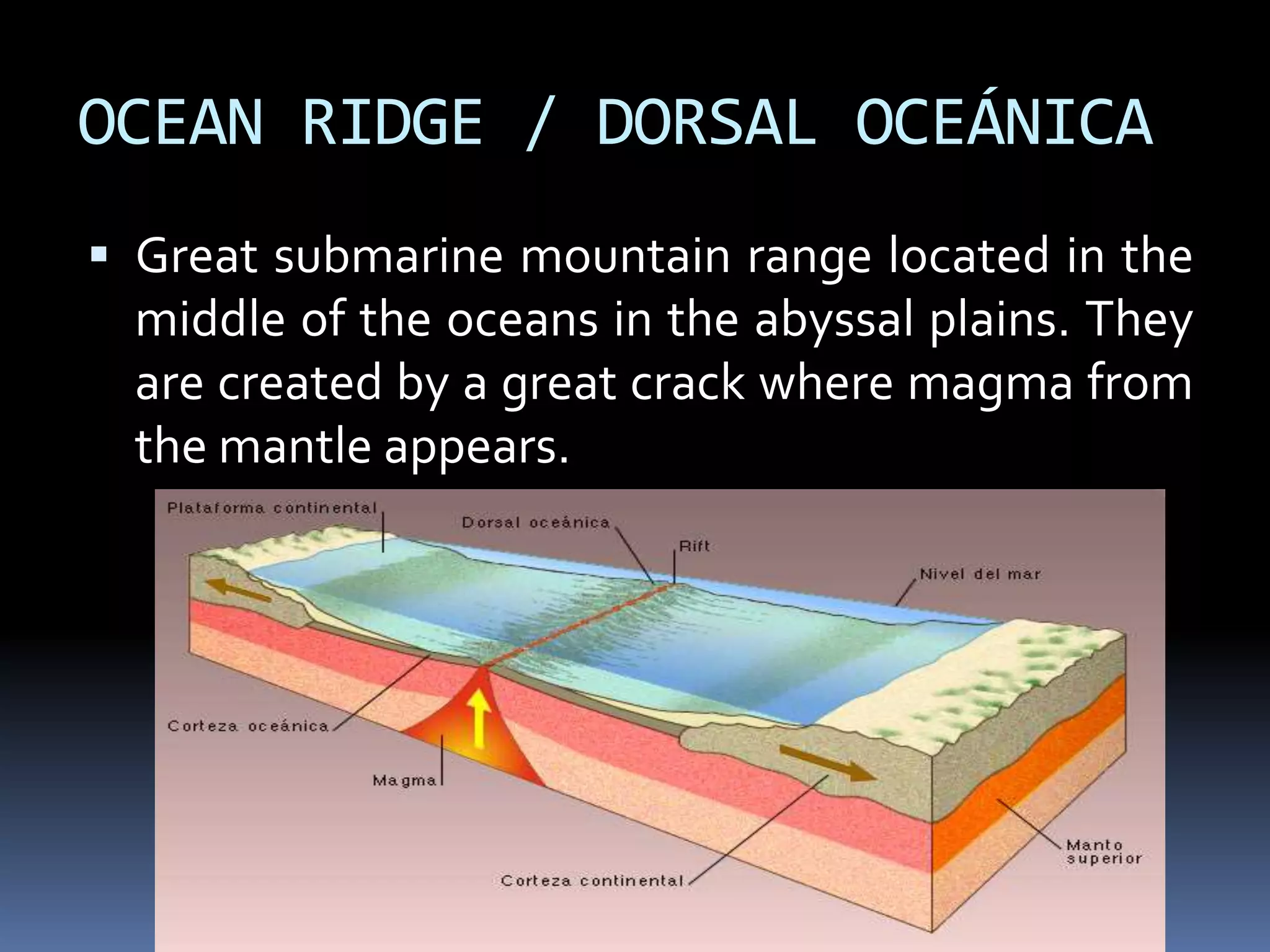
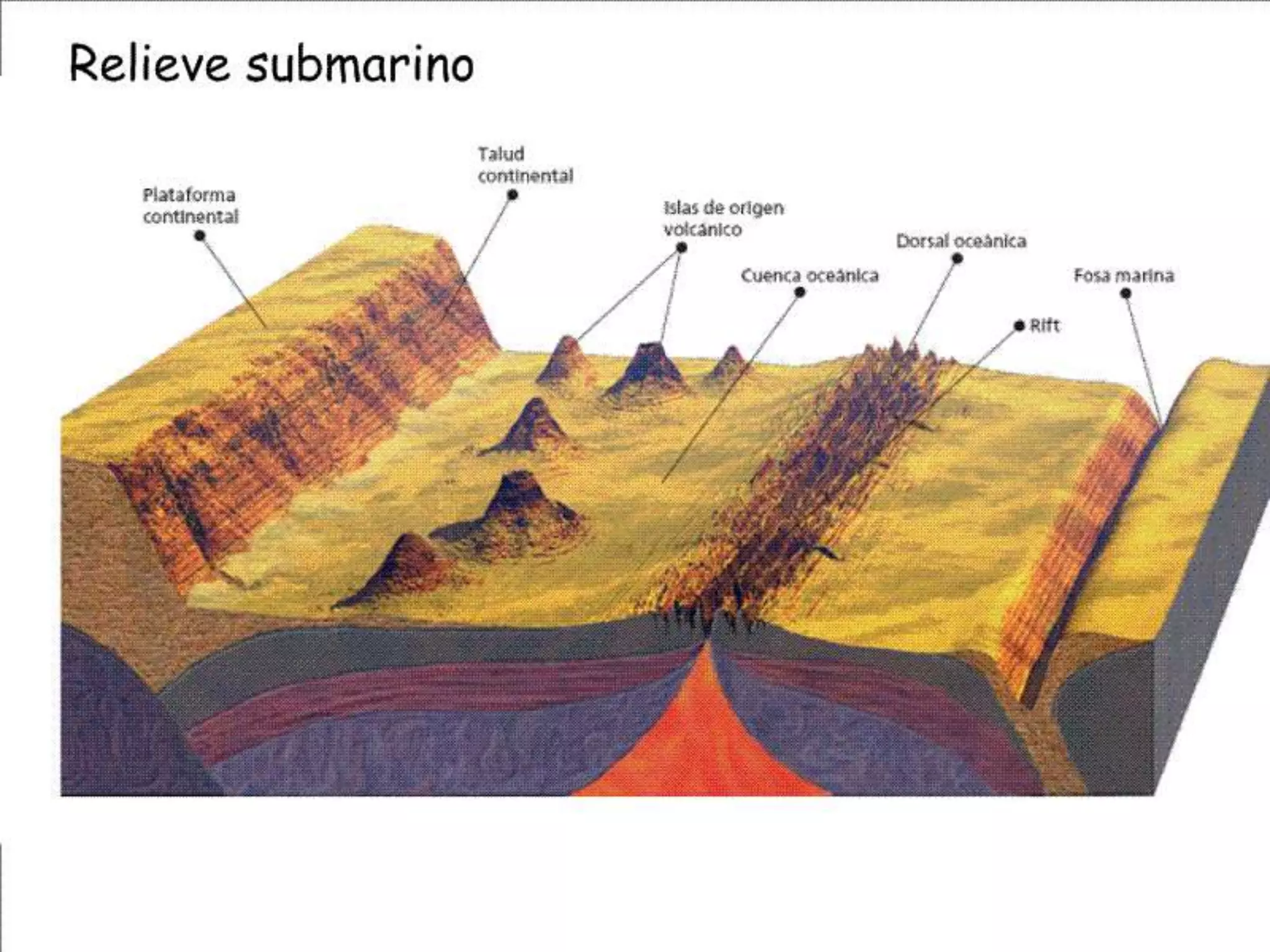
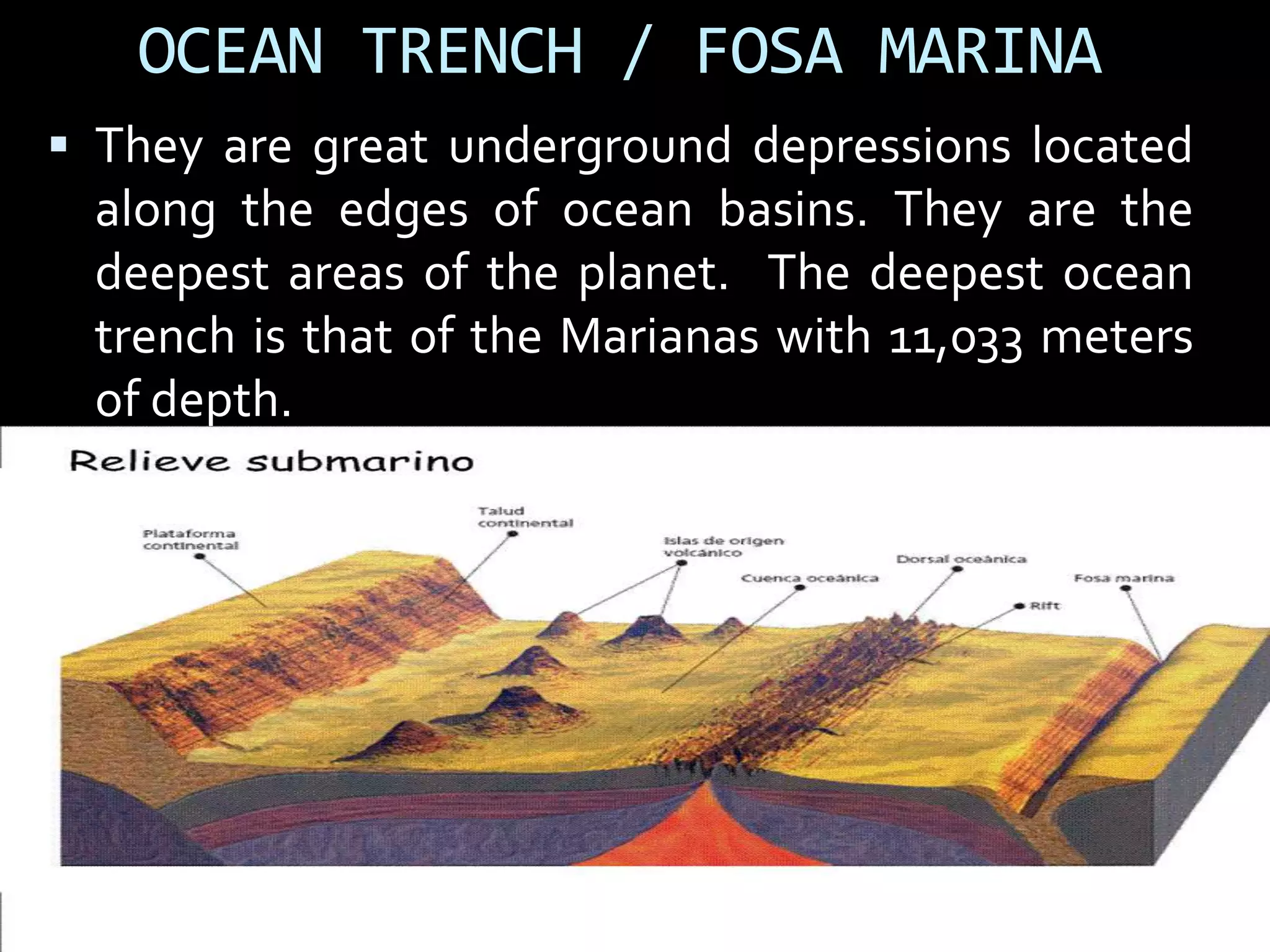
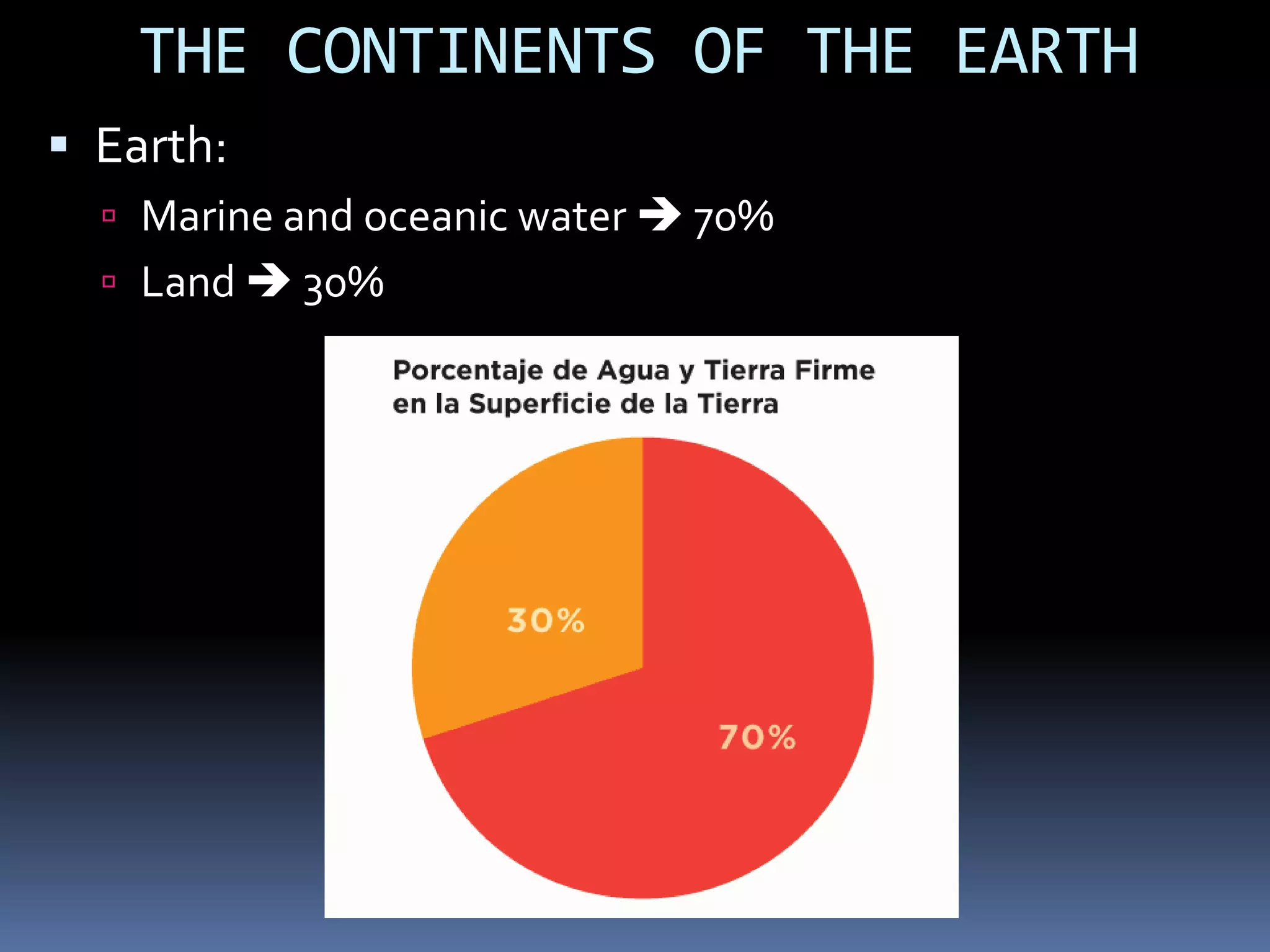
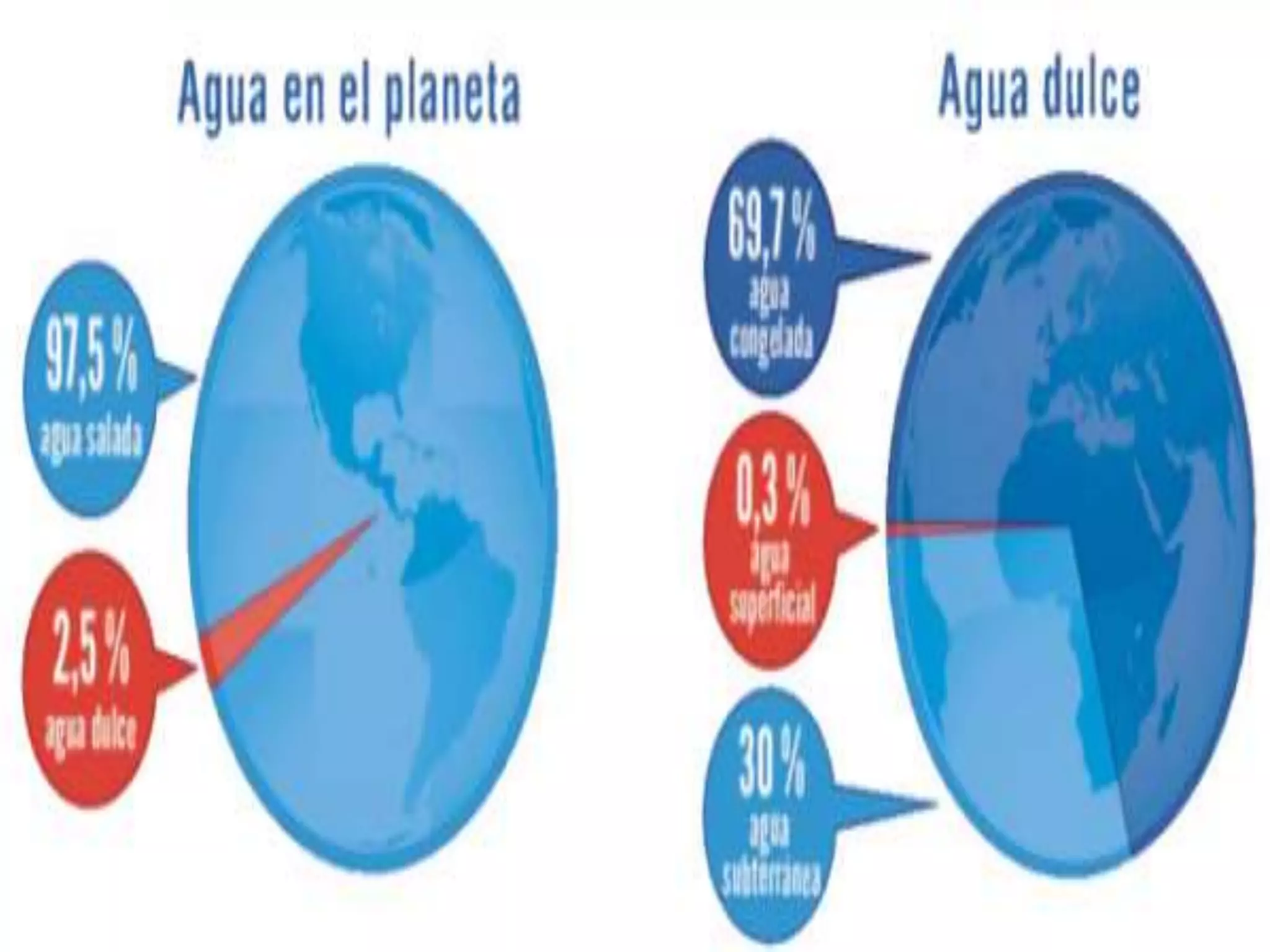
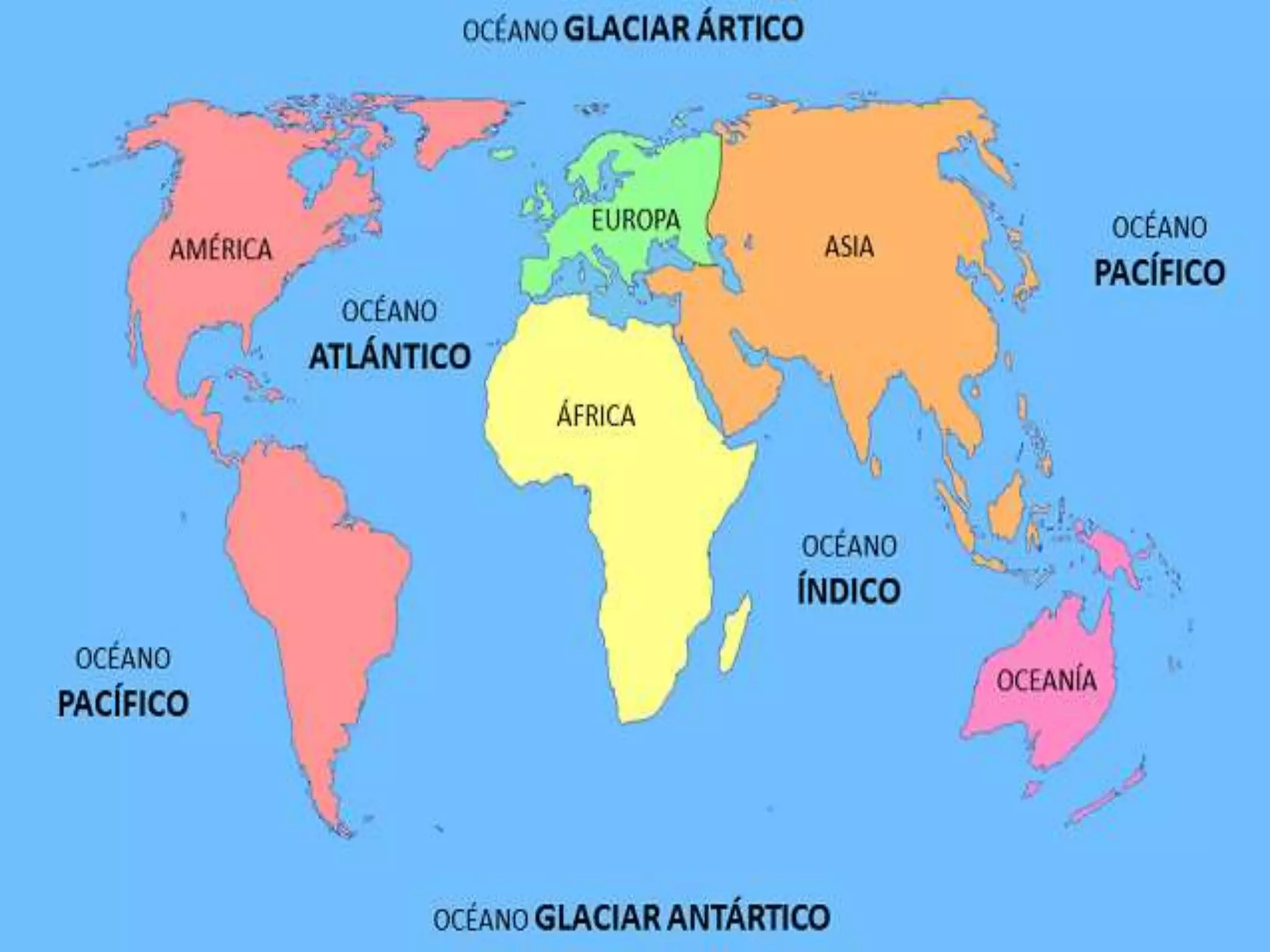
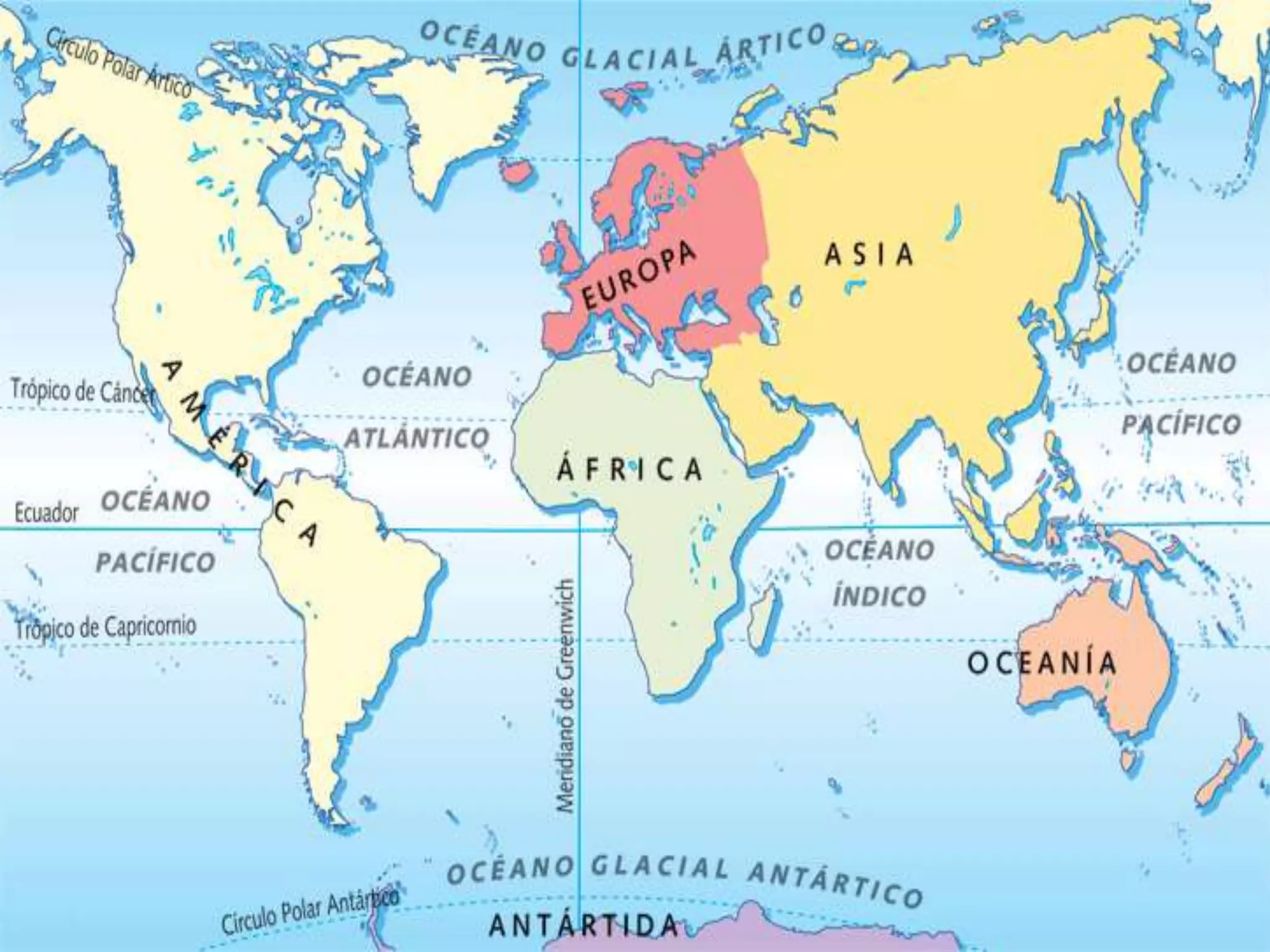
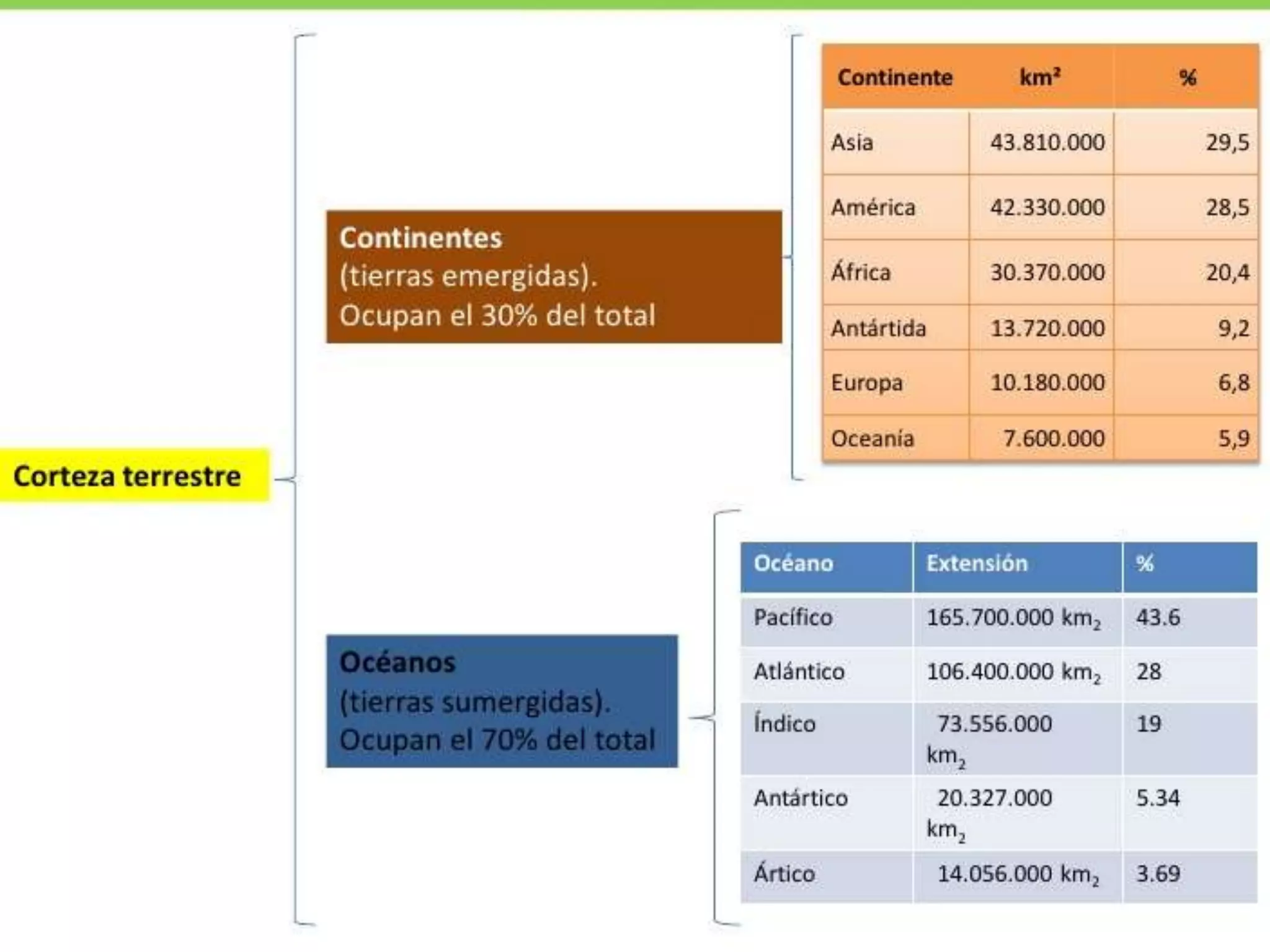
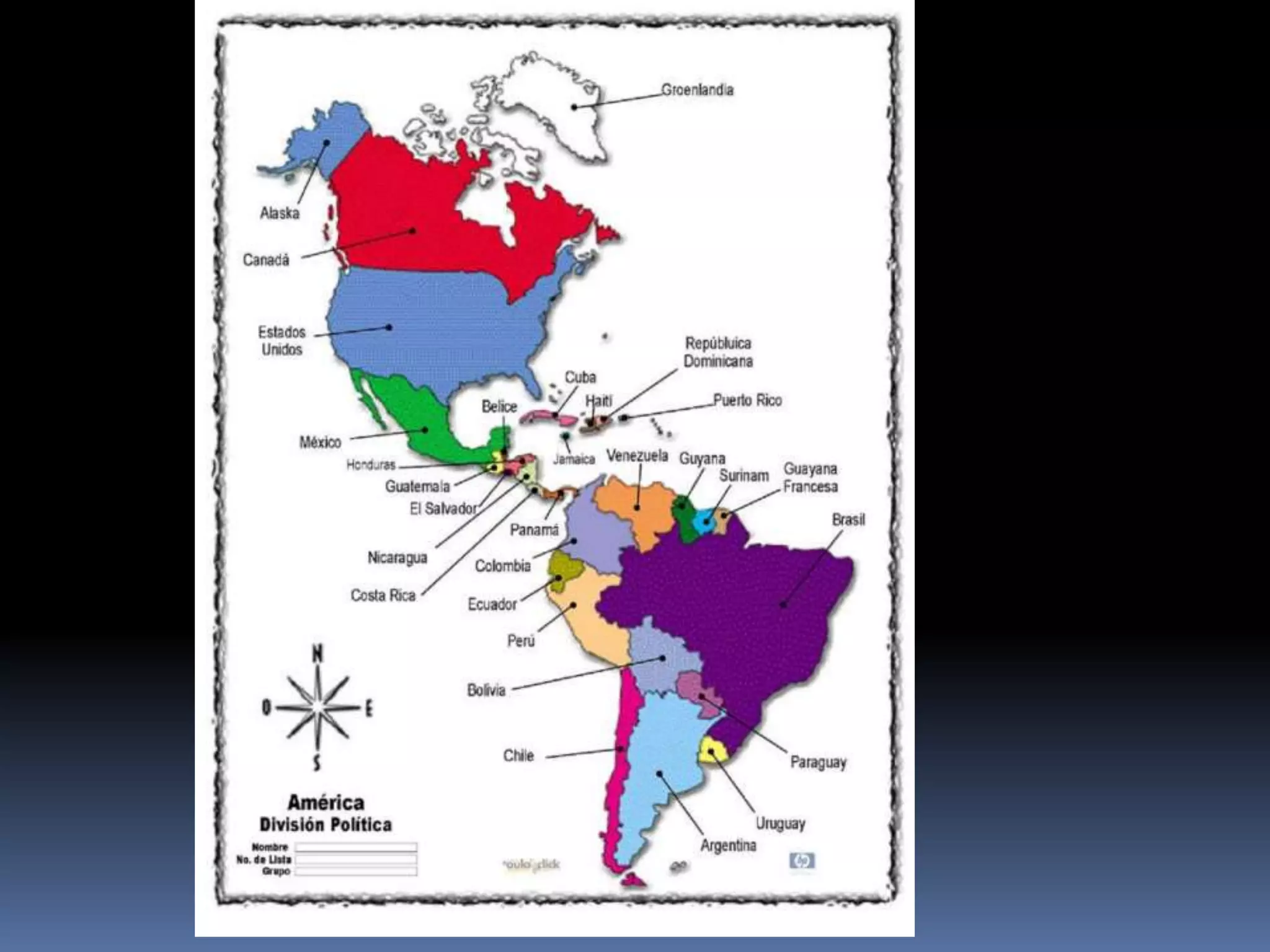
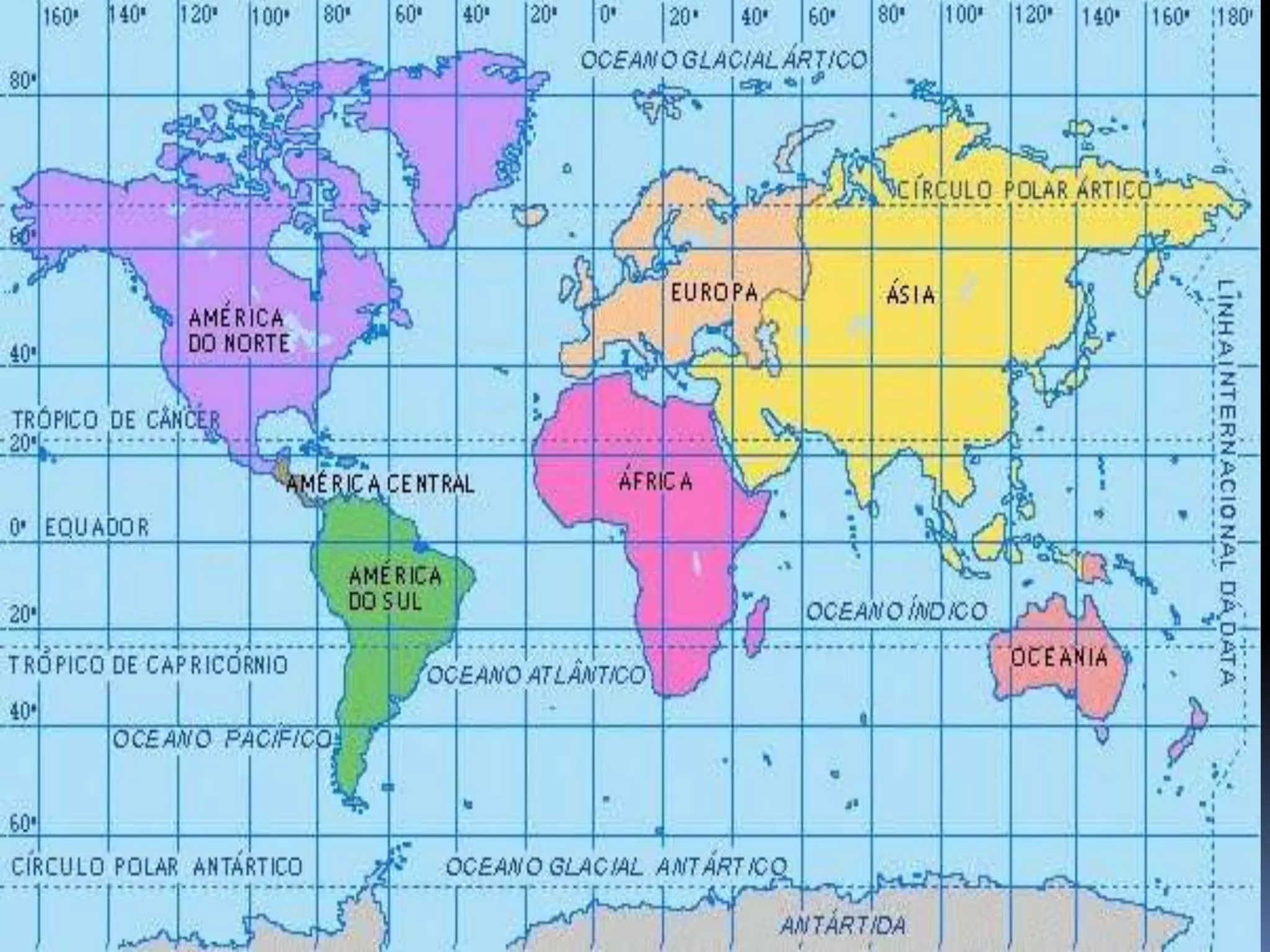
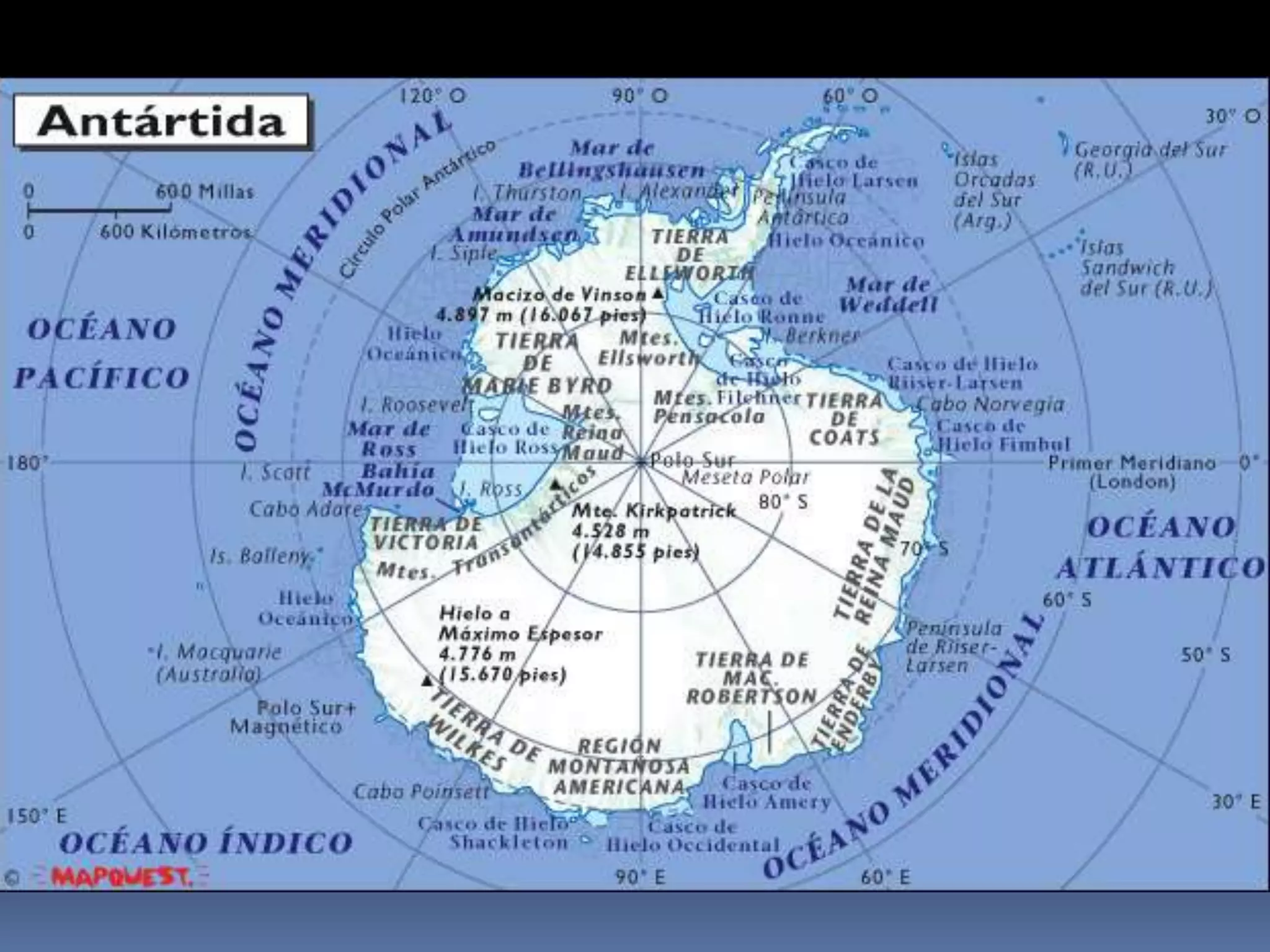
The document discusses the structure and composition of the Earth's interior and surface relief features. It describes the Earth as having a crust, mantle, and core based on its composition. The crust and upper mantle make up the lithosphere which is divided into tectonic plates. Plate tectonics and the actions of external erosional forces shape the Earth's surface relief features such as mountains, plains, and coastal landforms. Volcanic activity, folding, and faulting create different types of mountains during plate collisions and movements.