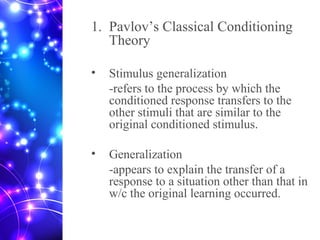
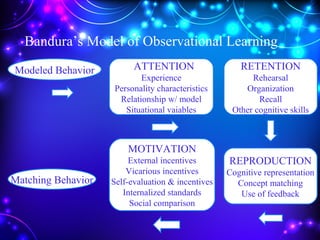
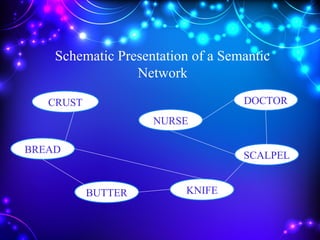
1) The document discusses various theories of learning including behavioral, cognitive, and constructivist theories. Behavioral theories discussed include Pavlov's classical conditioning, Thorndike's law of effect, and Skinner's operant conditioning. Cognitive theories include Bruner's stages of learning and Ausubel's meaningful learning theory.
2) Constructivist theories emphasize that learning involves actively constructing one's own understanding rather than passively receiving information. Constructivists believe learning depends on how information is mentally processed and connected to prior knowledge.
3) For effective learning to occur, instructors should consider students' cognitive development and help students organize new information by relating it to what they already know. Learning involves both individual cognitive processes and