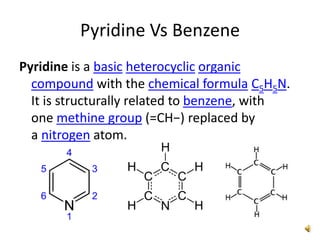
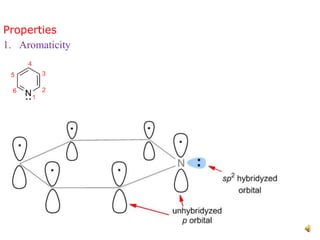
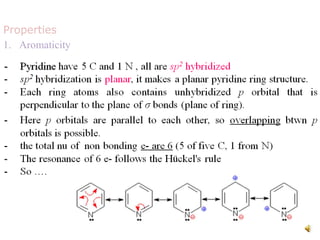
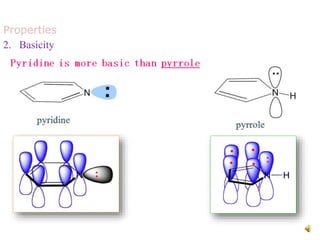
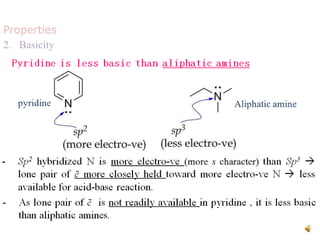
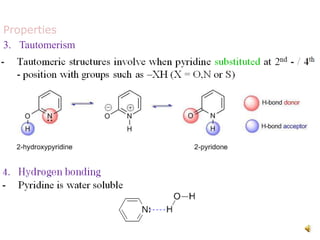
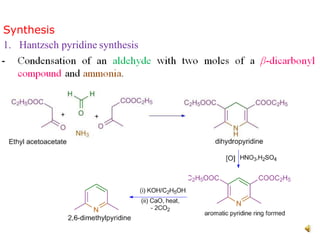
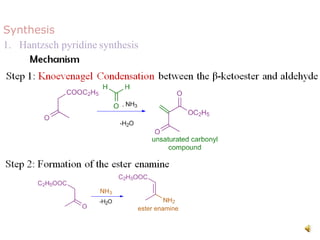
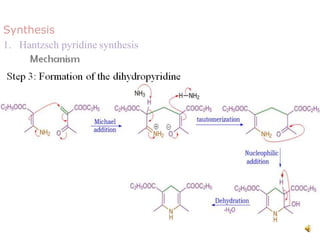
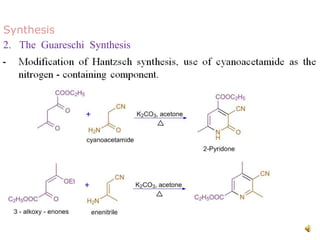
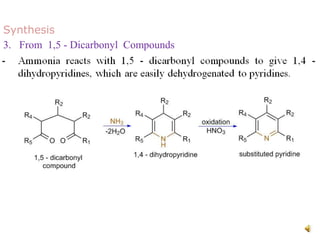
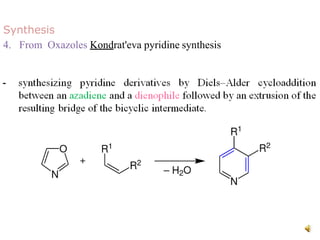
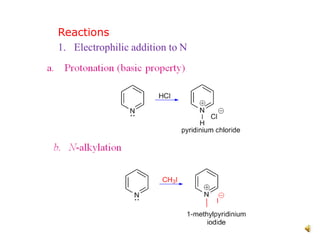
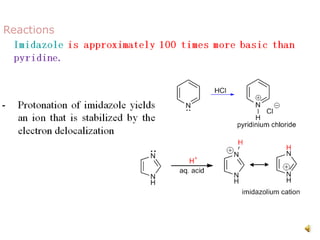
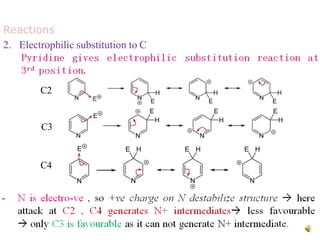
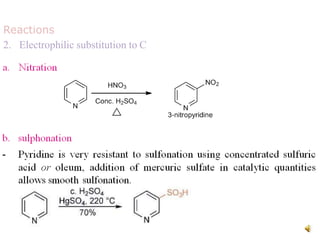
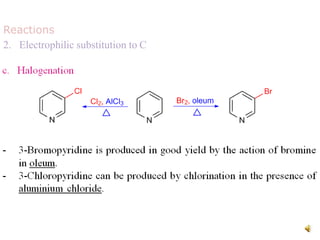
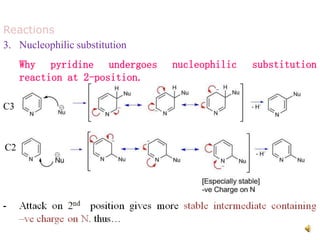
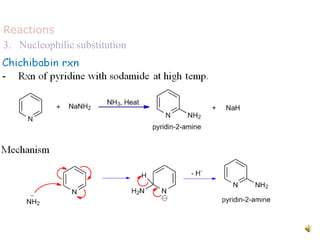
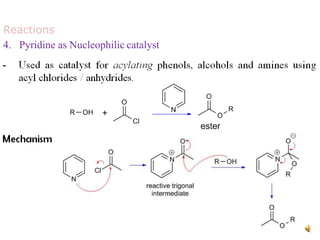
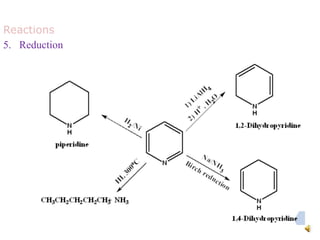
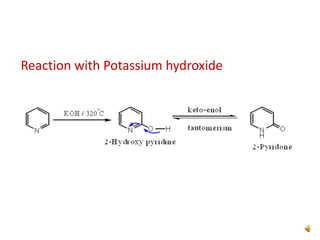
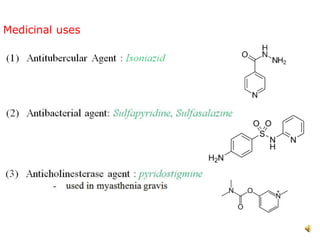
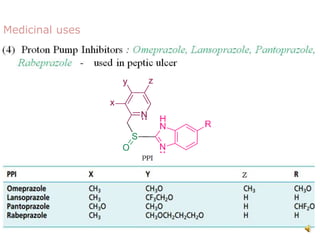
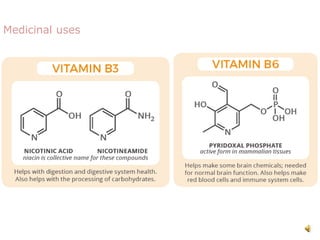
The document discusses pyridine, a basic heterocyclic organic compound related to benzene, detailing its historical discovery, natural occurrence, and commercial extraction from coal tar. It outlines pyridine's physical properties, such as being flammable and having a characteristic unpleasant smell, and it describes several synthesis methods and reactions involving pyridine. Additionally, it notes pyridine's role in everyday products and some medicinal uses.