Embed presentation
Downloaded 142 times

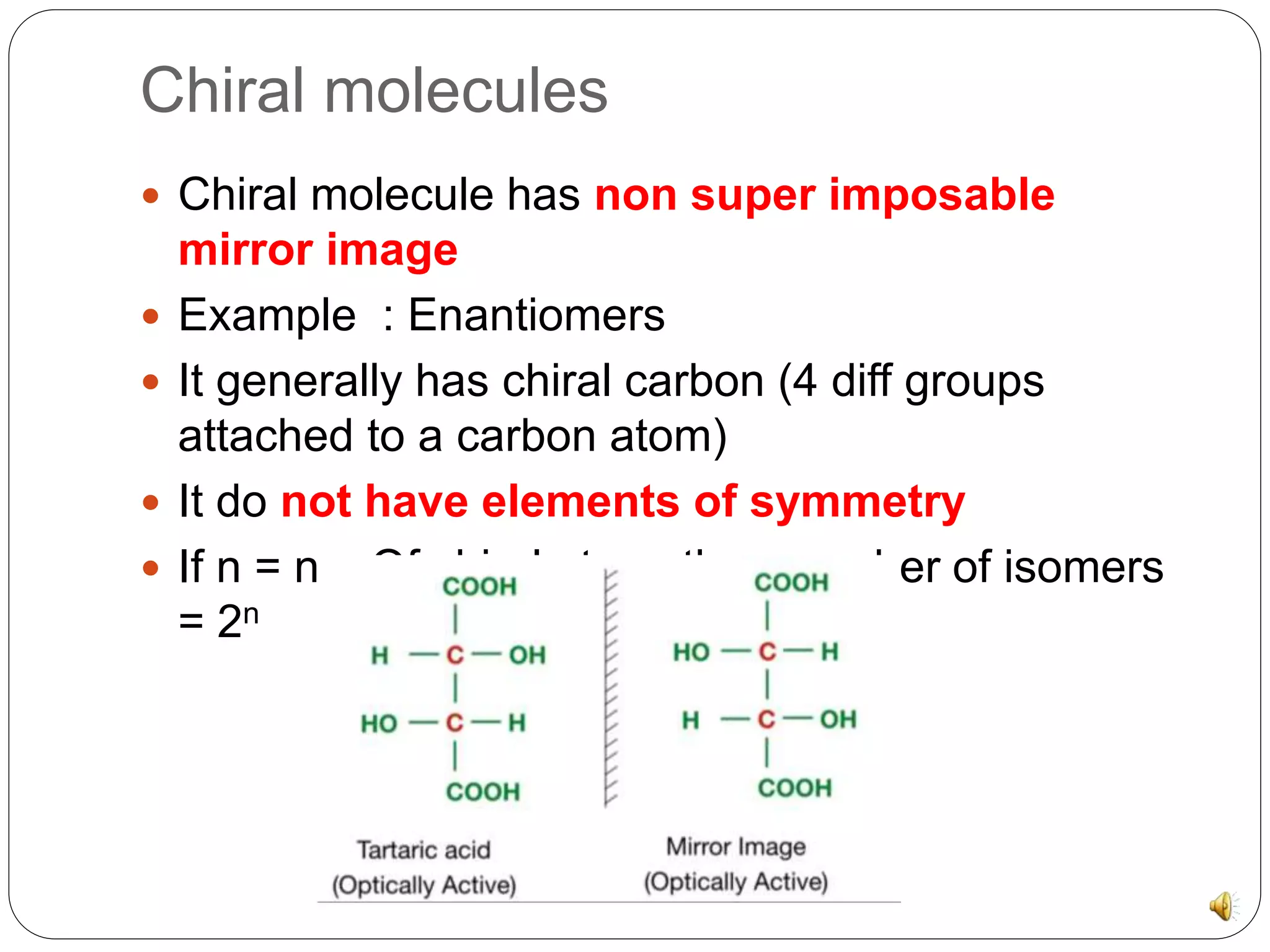
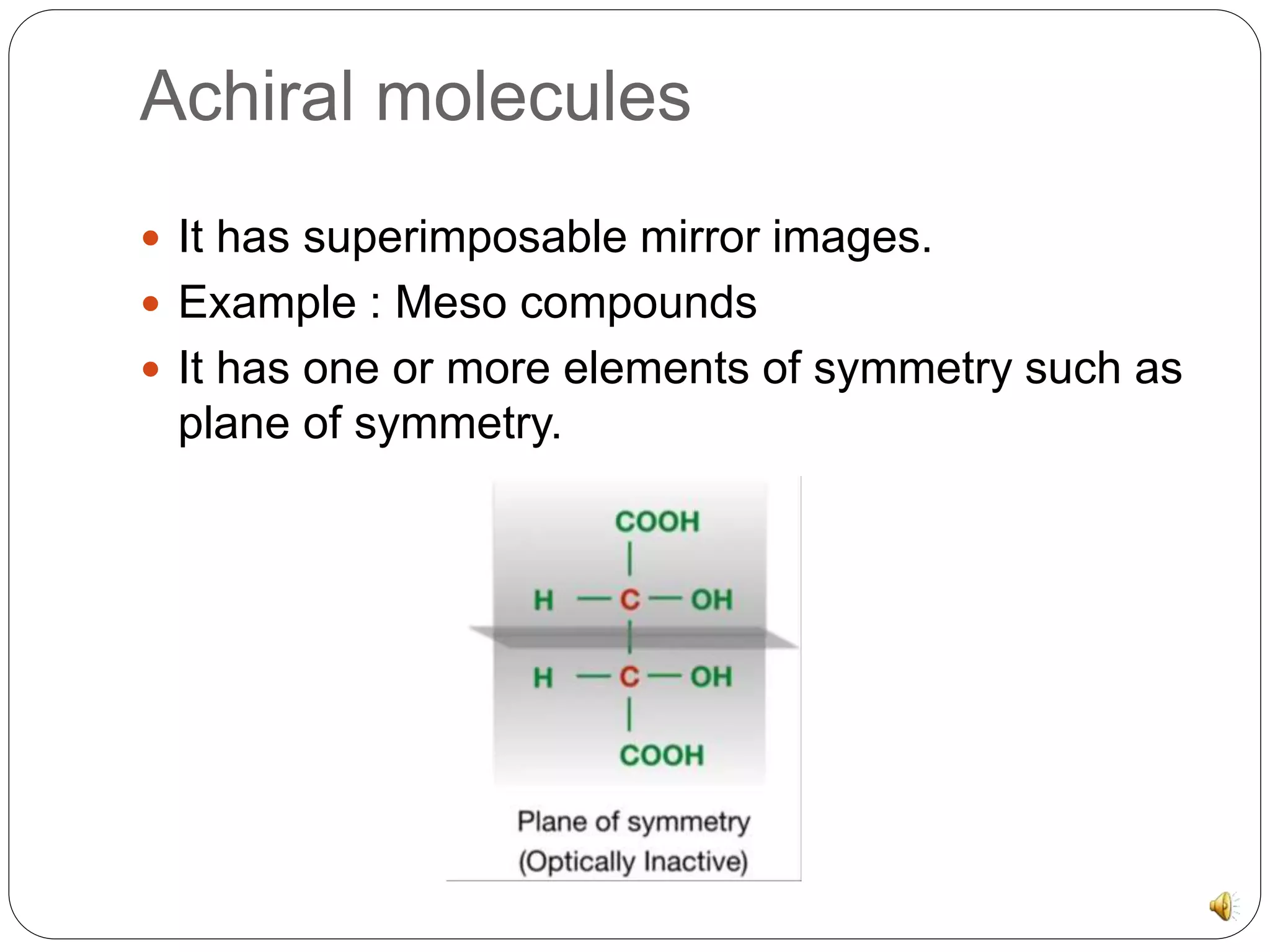


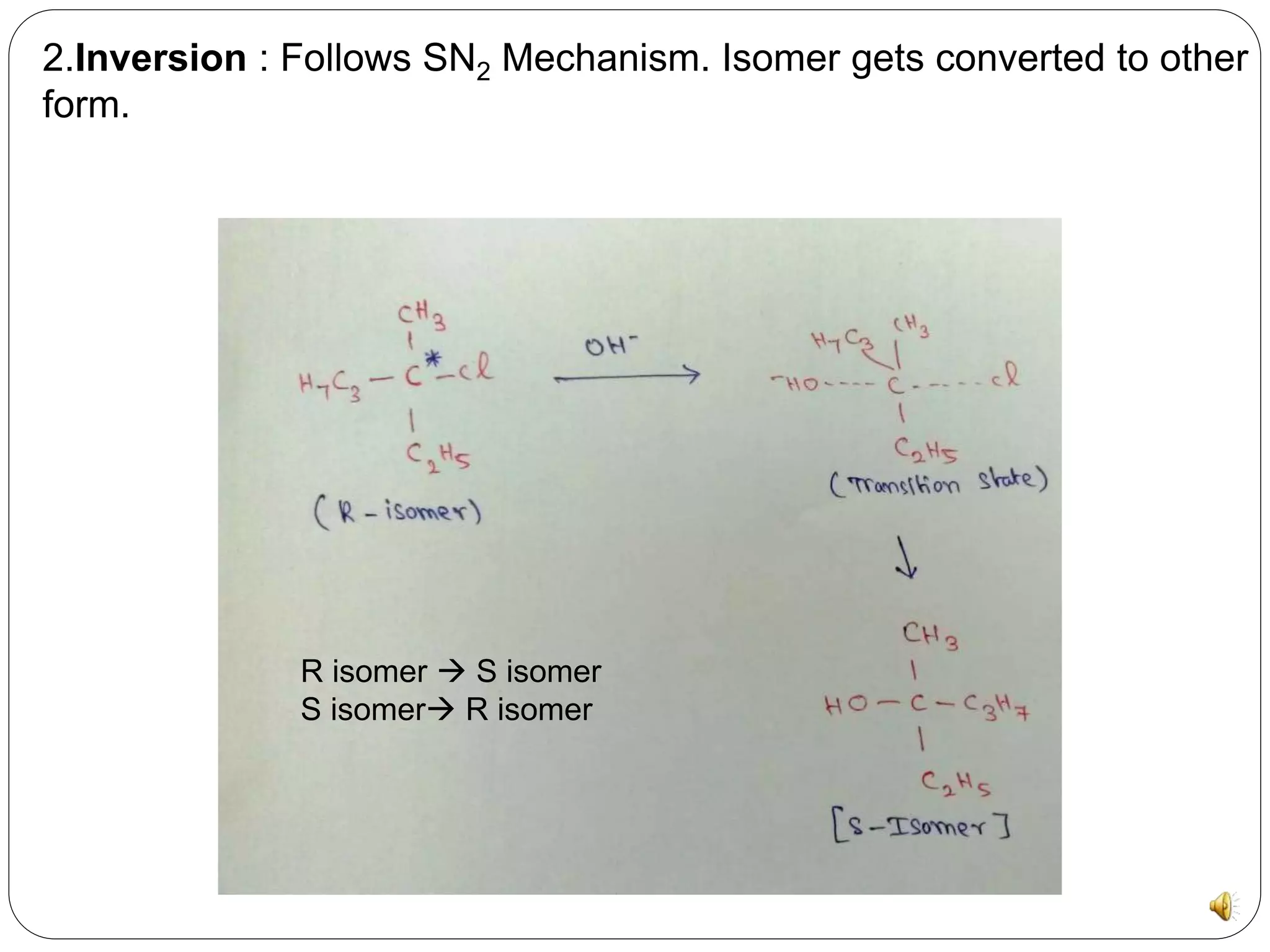



The document discusses chiral molecules and their reactions. Chiral molecules have non-superimposable mirror images due to having four different groups attached to a carbon atom without symmetry. There are three major reactions for chiral molecules: retention, where the configuration of substrate and product remain the same; inversion, where the isomer converts to the other form through an SN2 mechanism; and racemization, where a second chiral center forms diastereomers.








