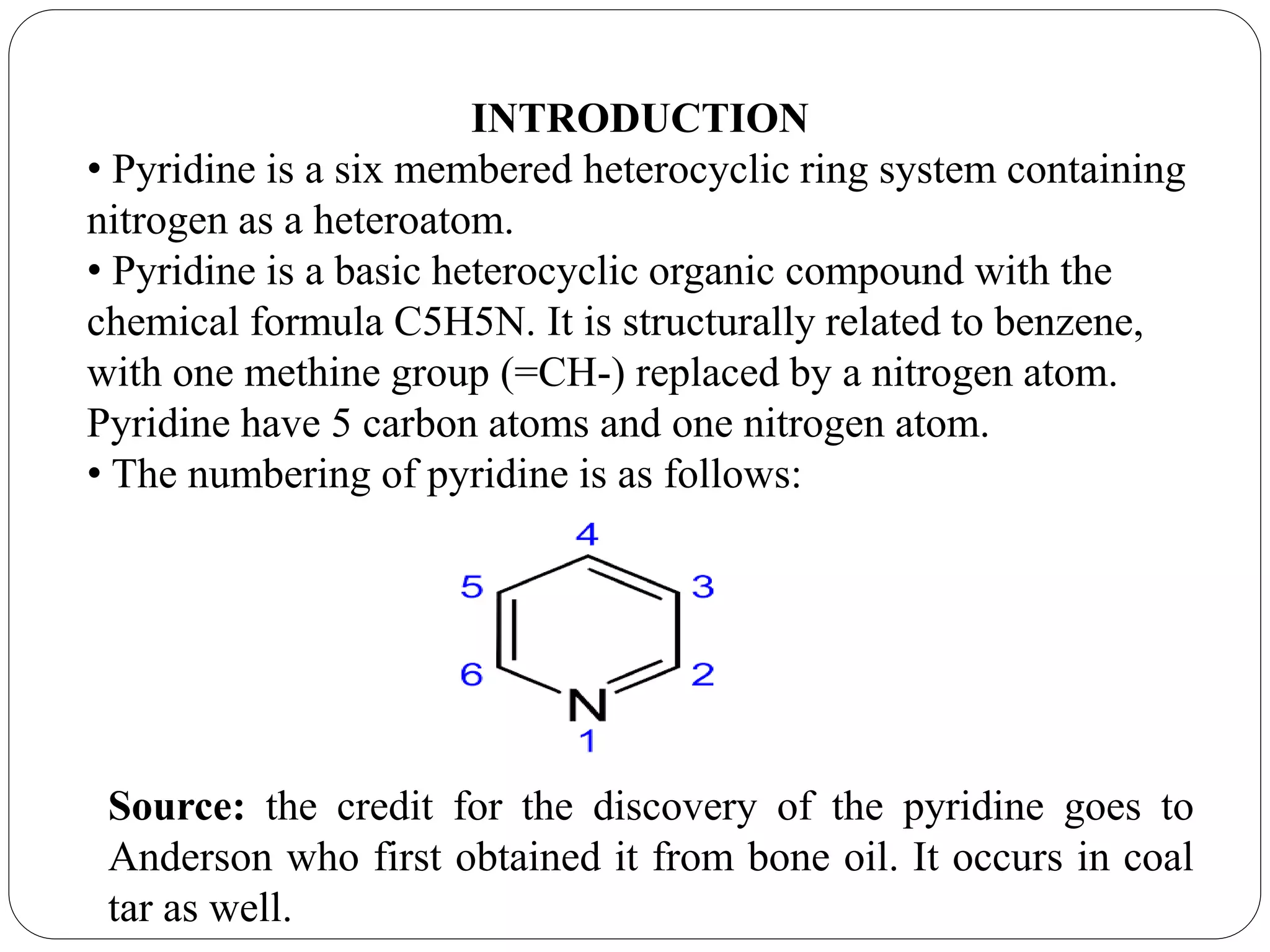
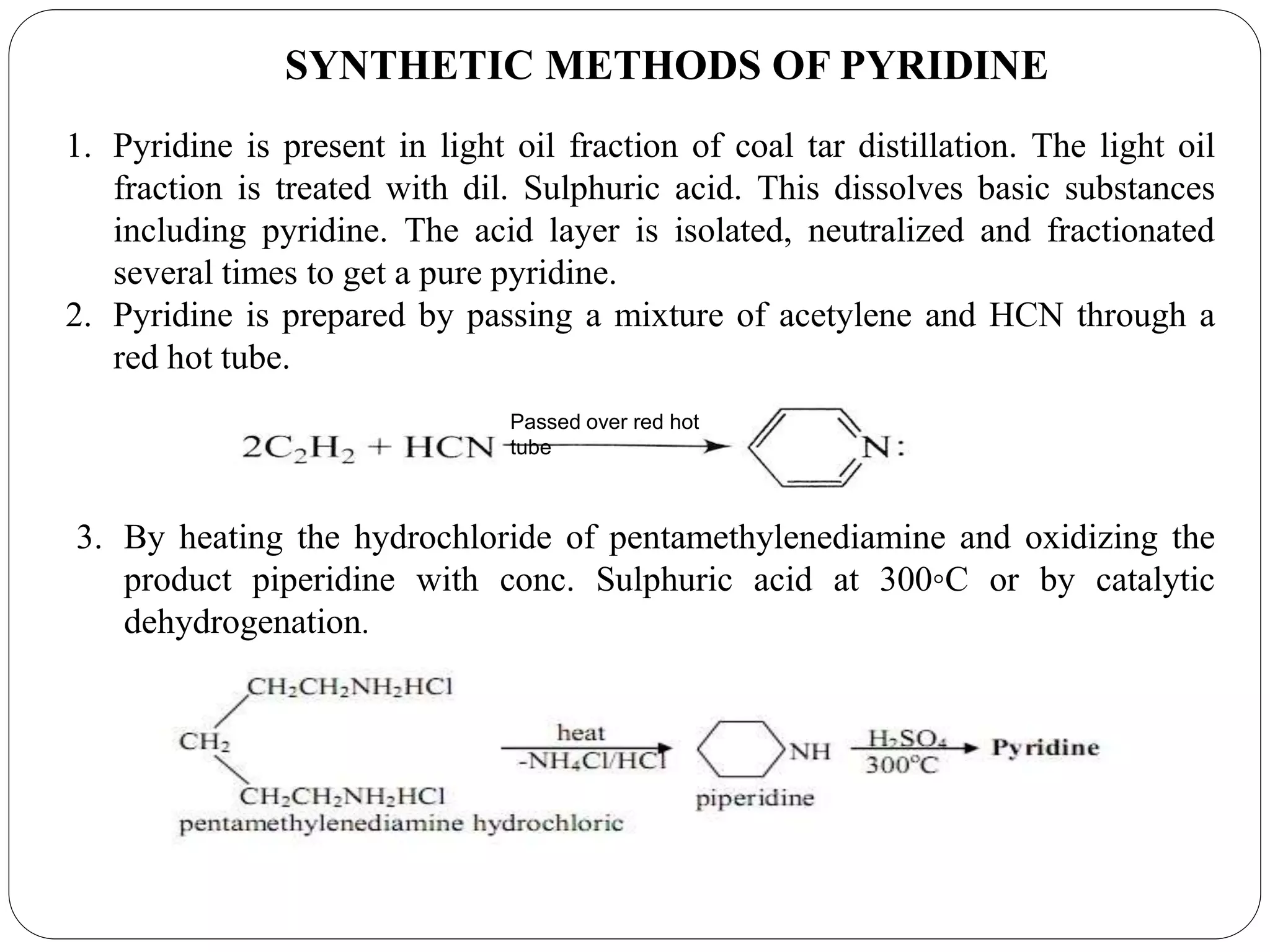
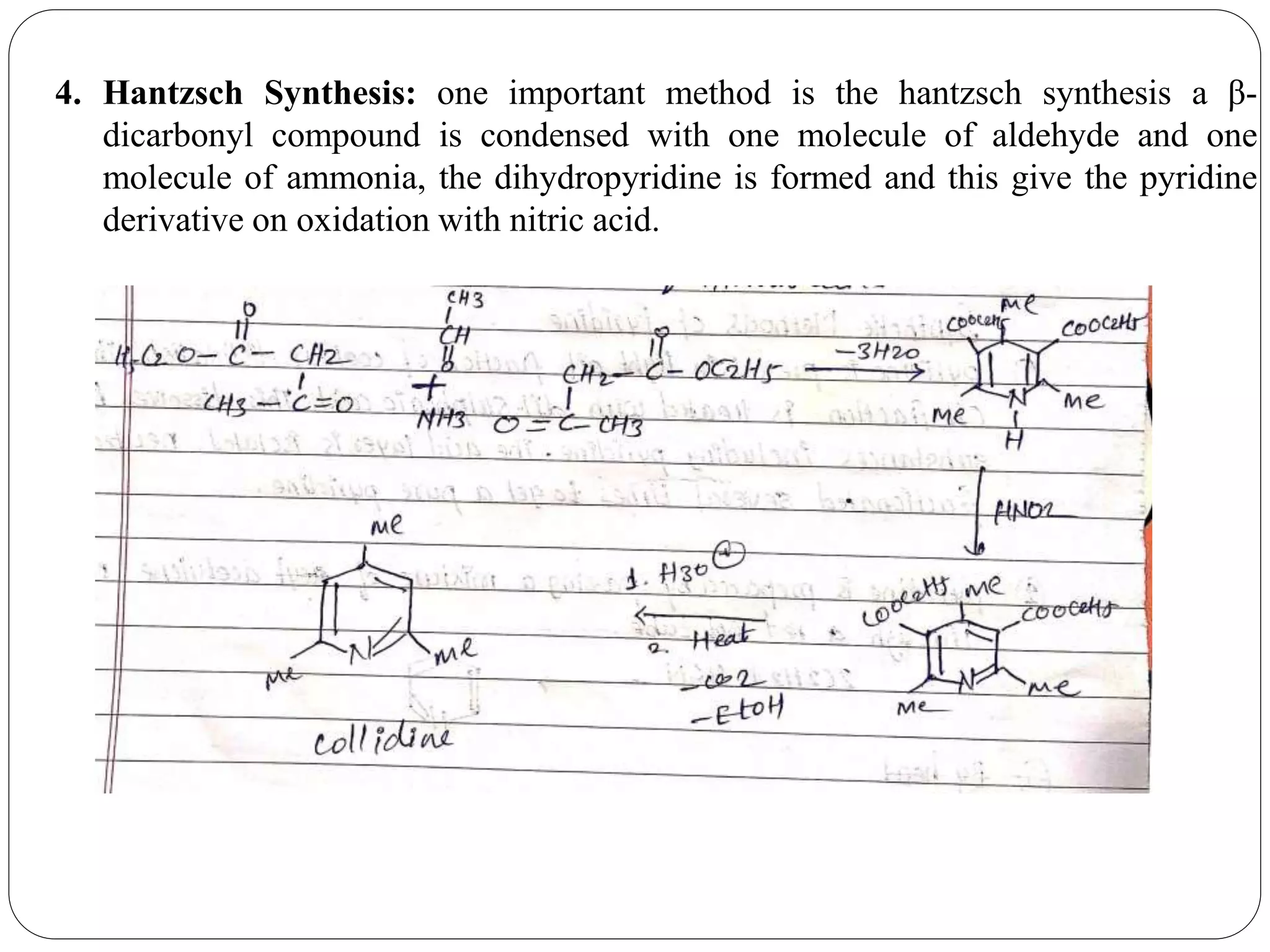
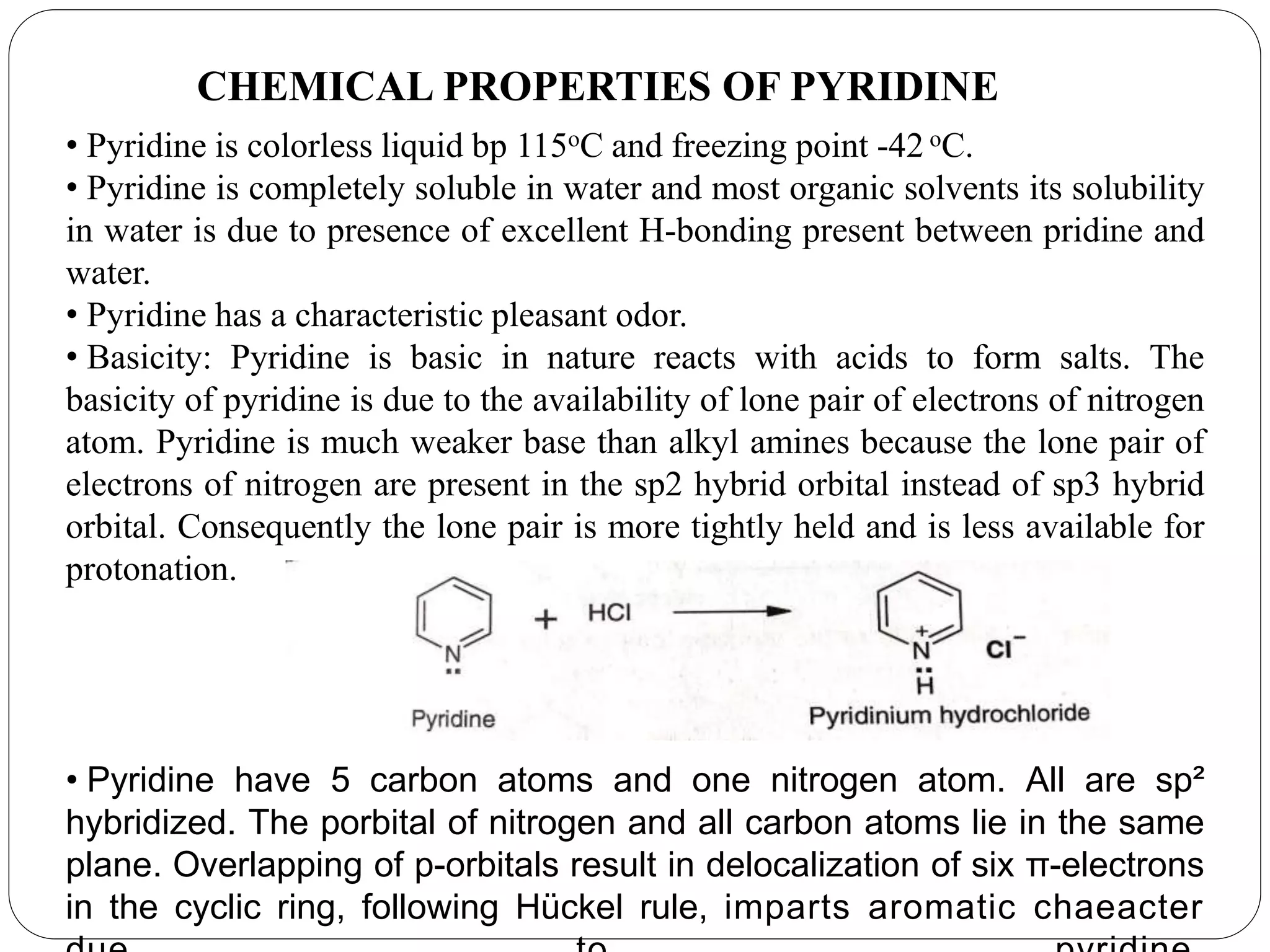
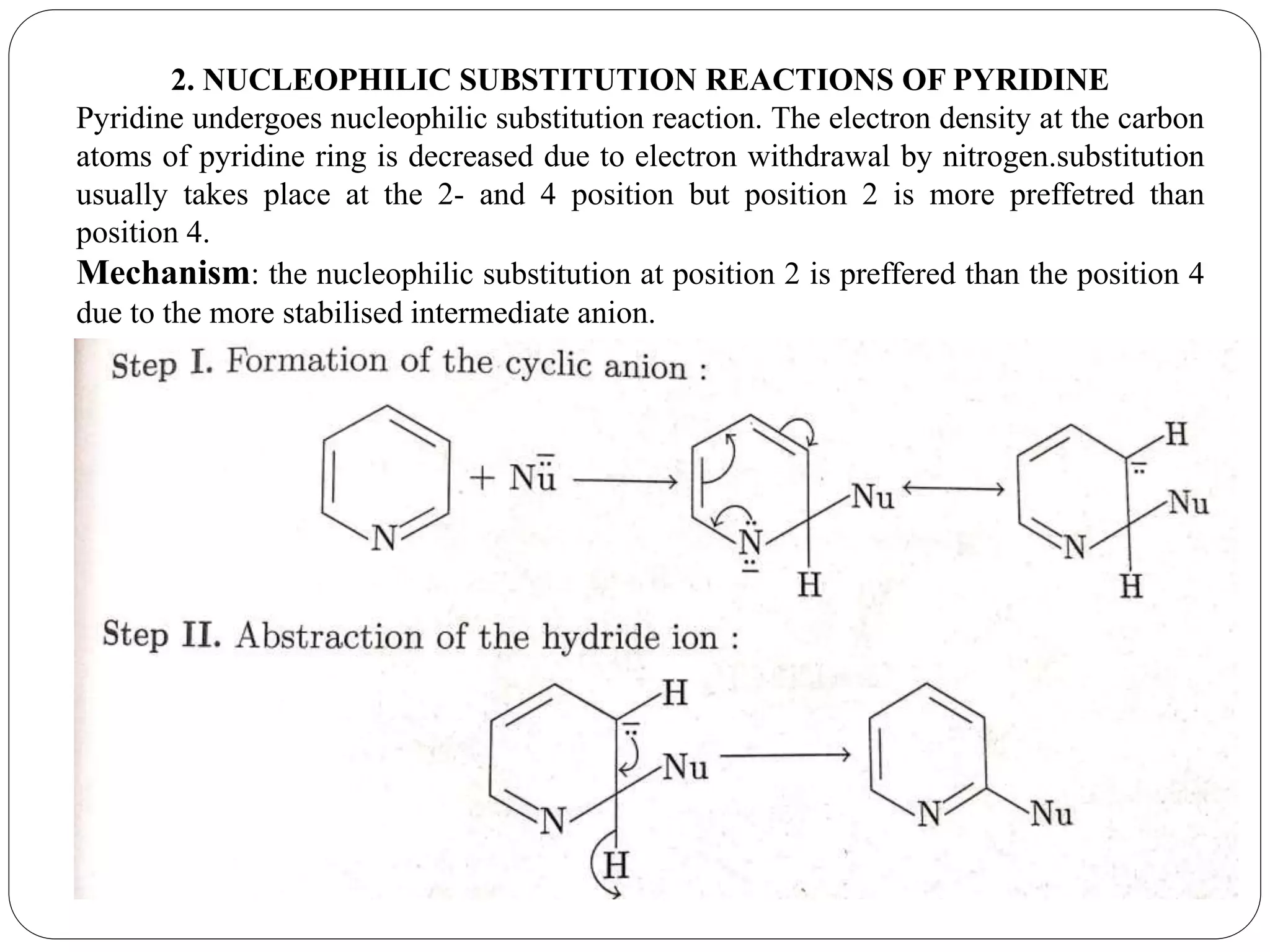
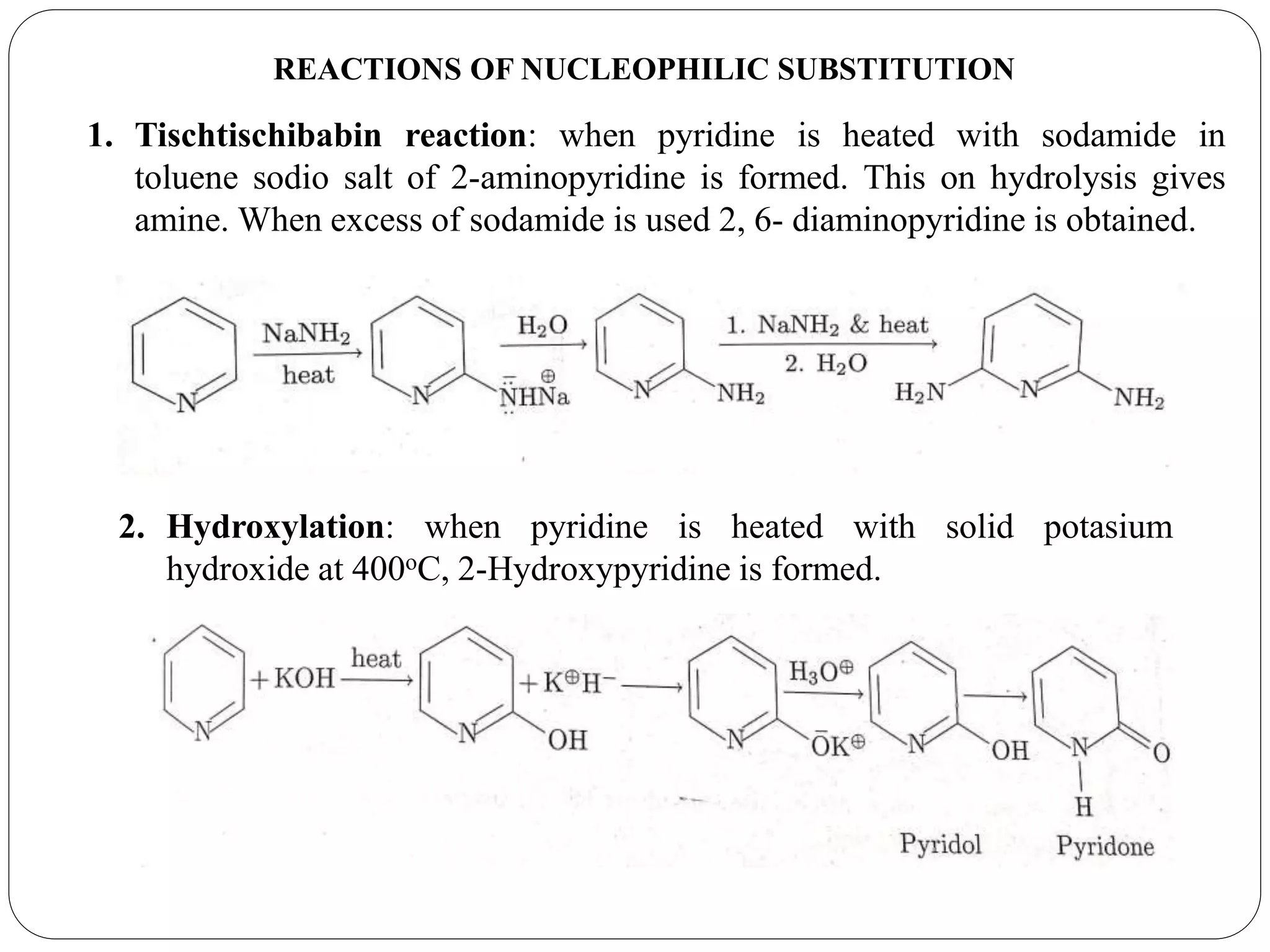
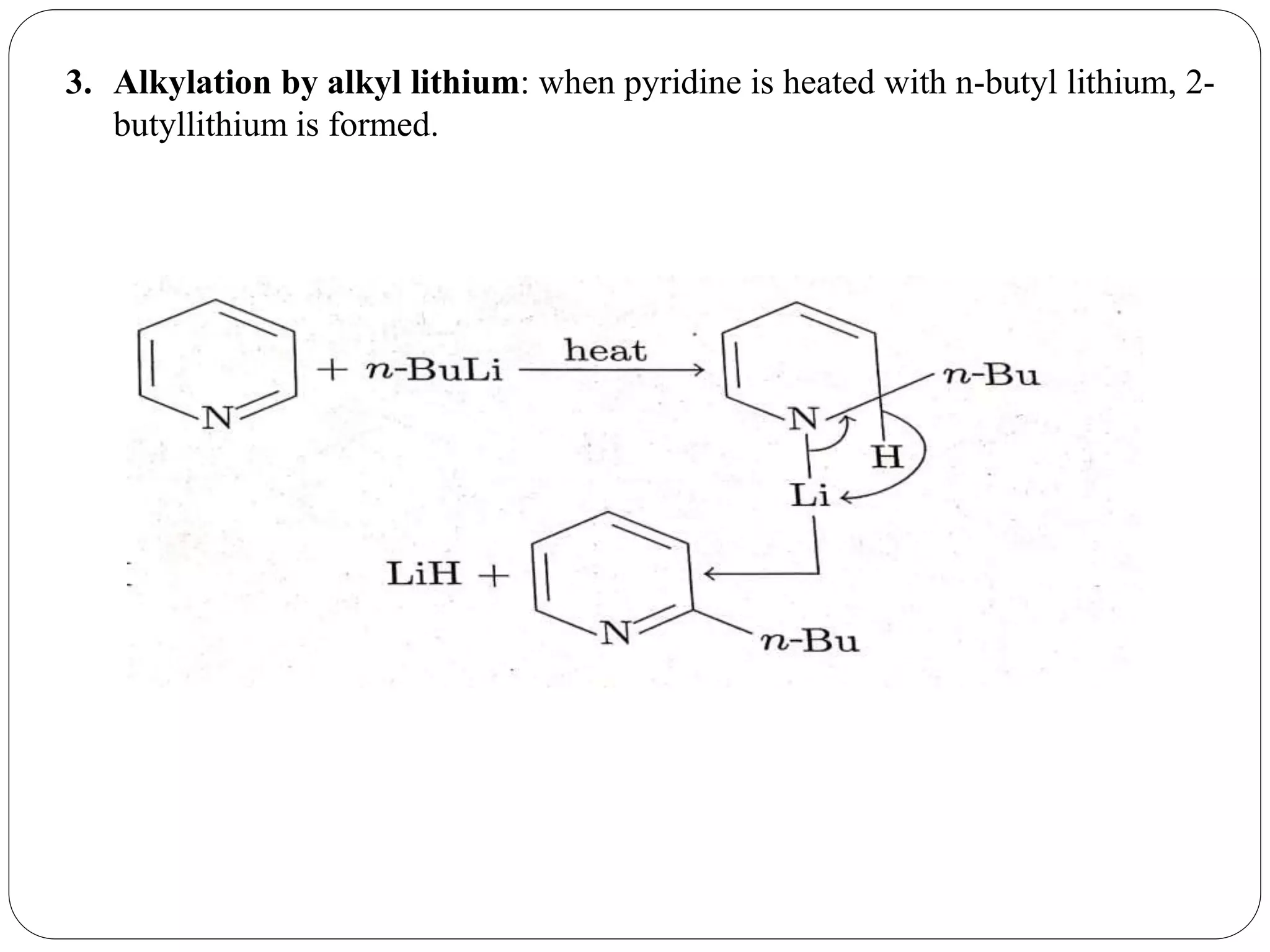
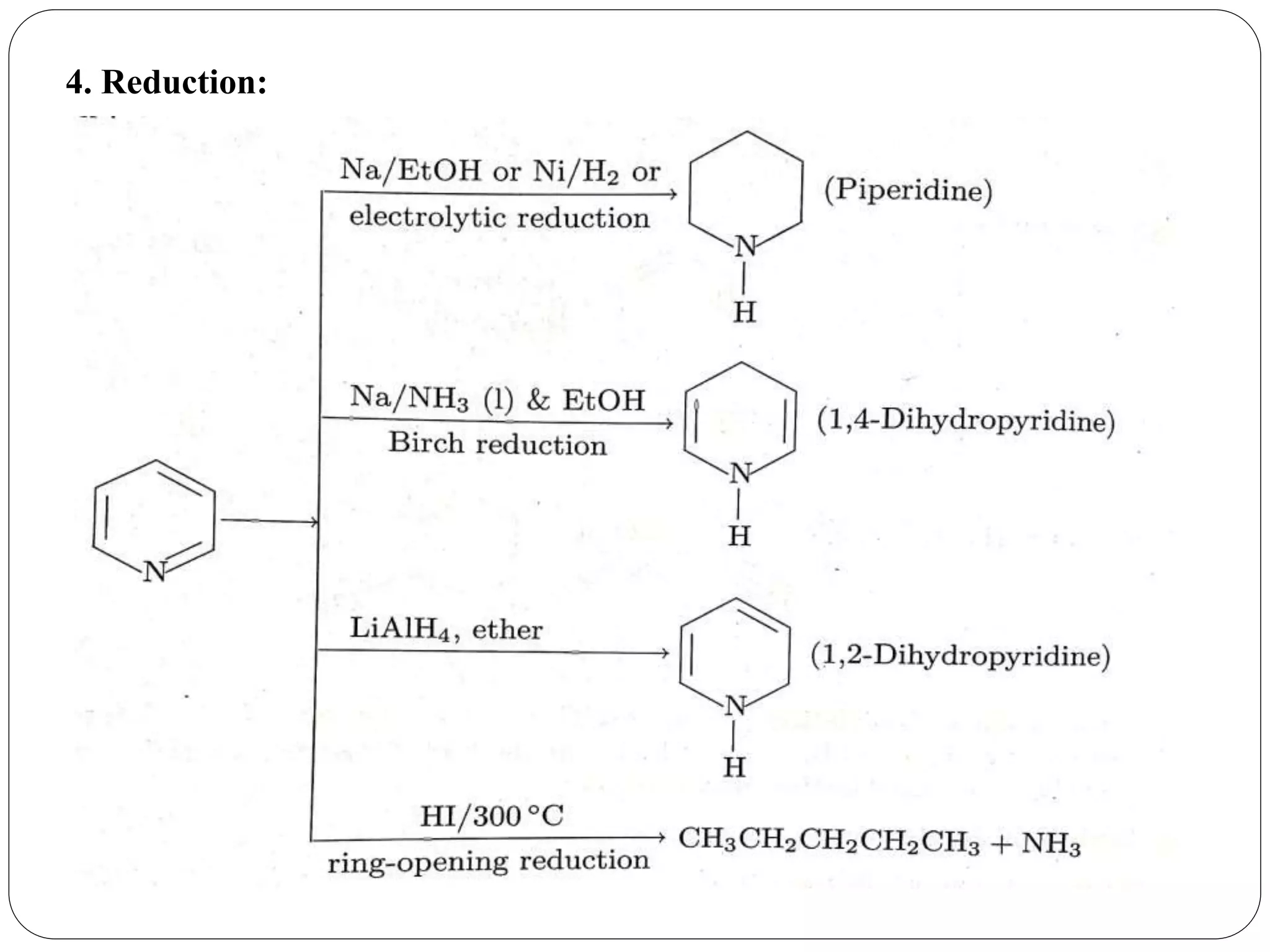
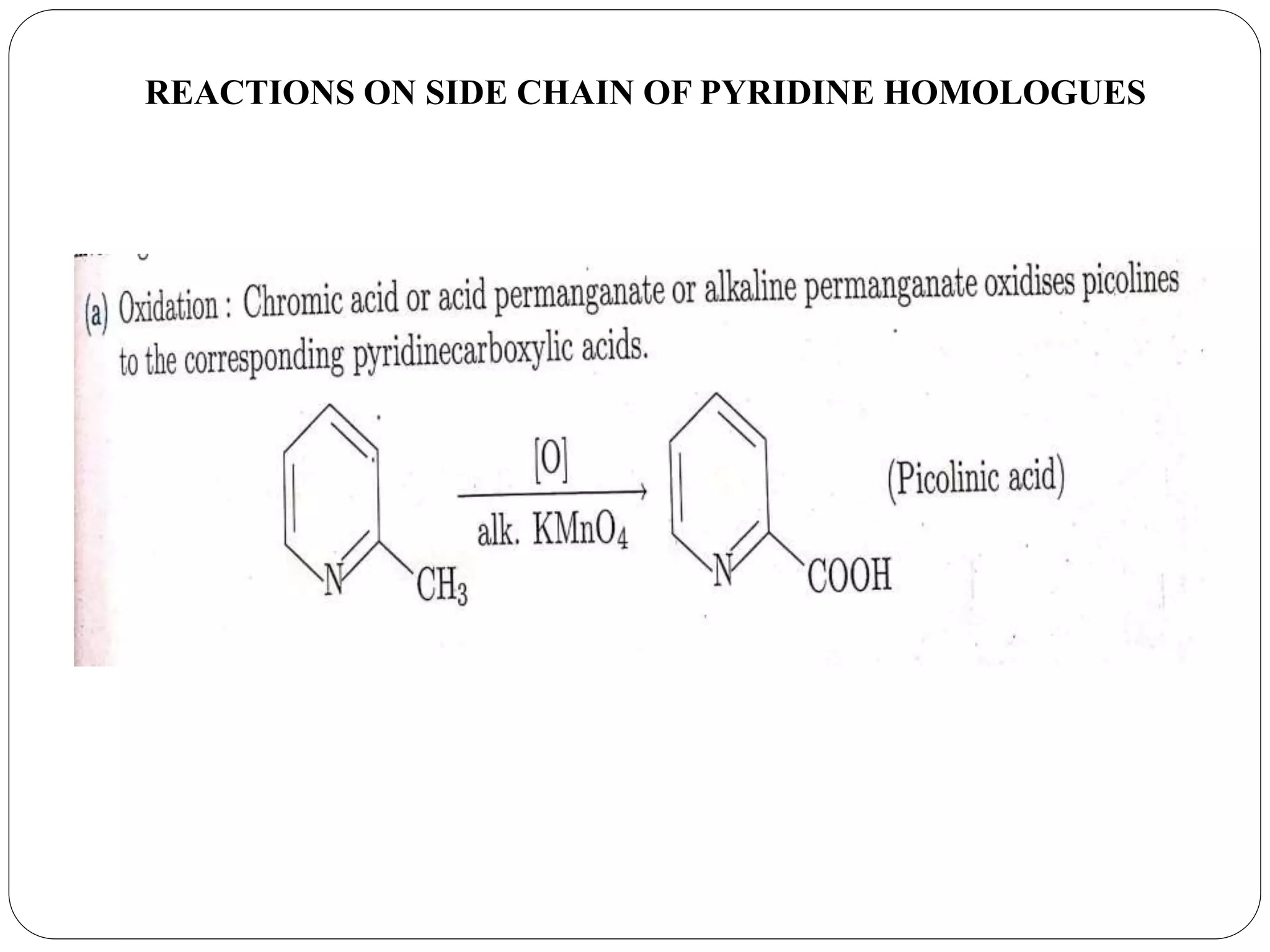
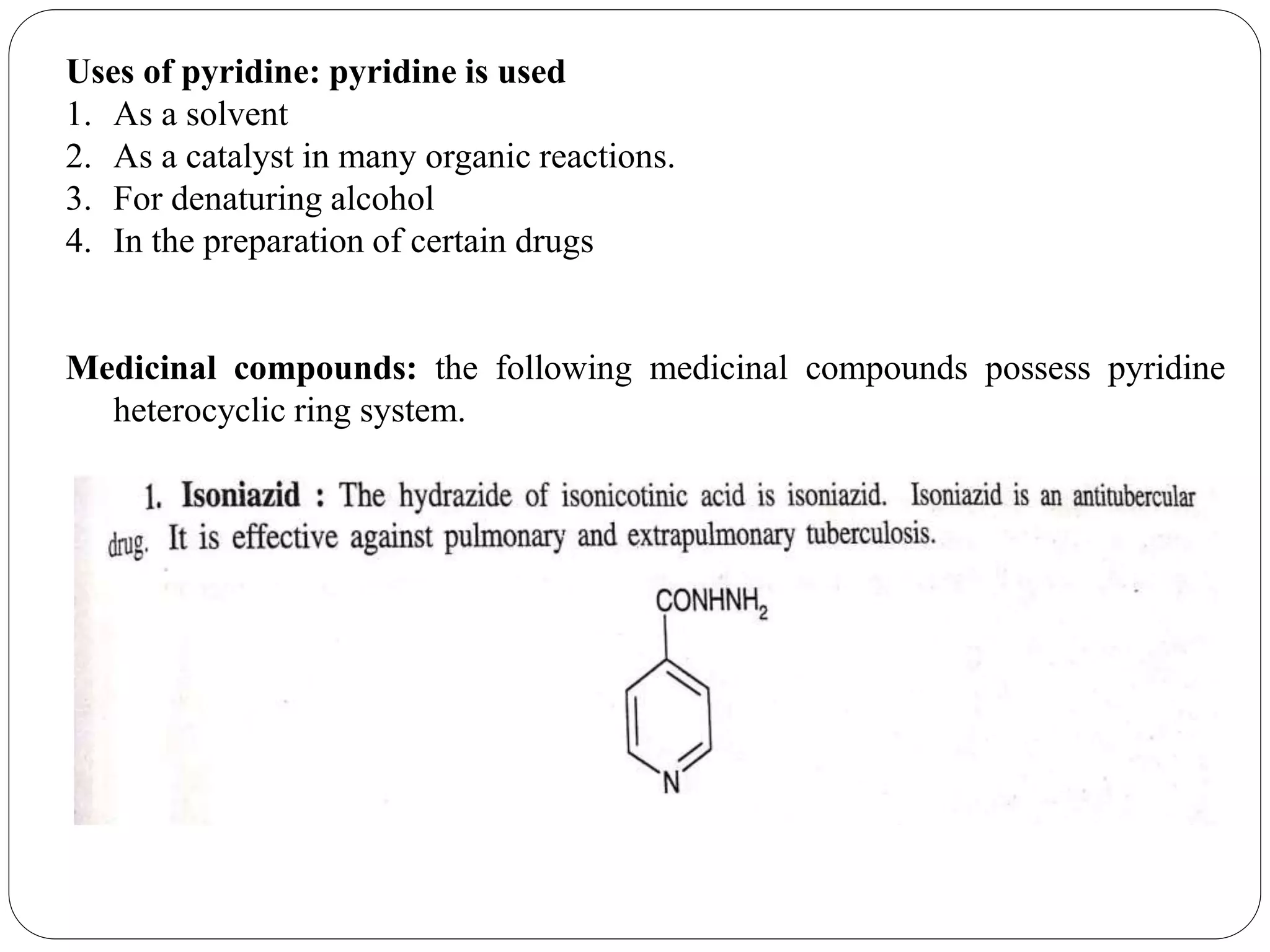
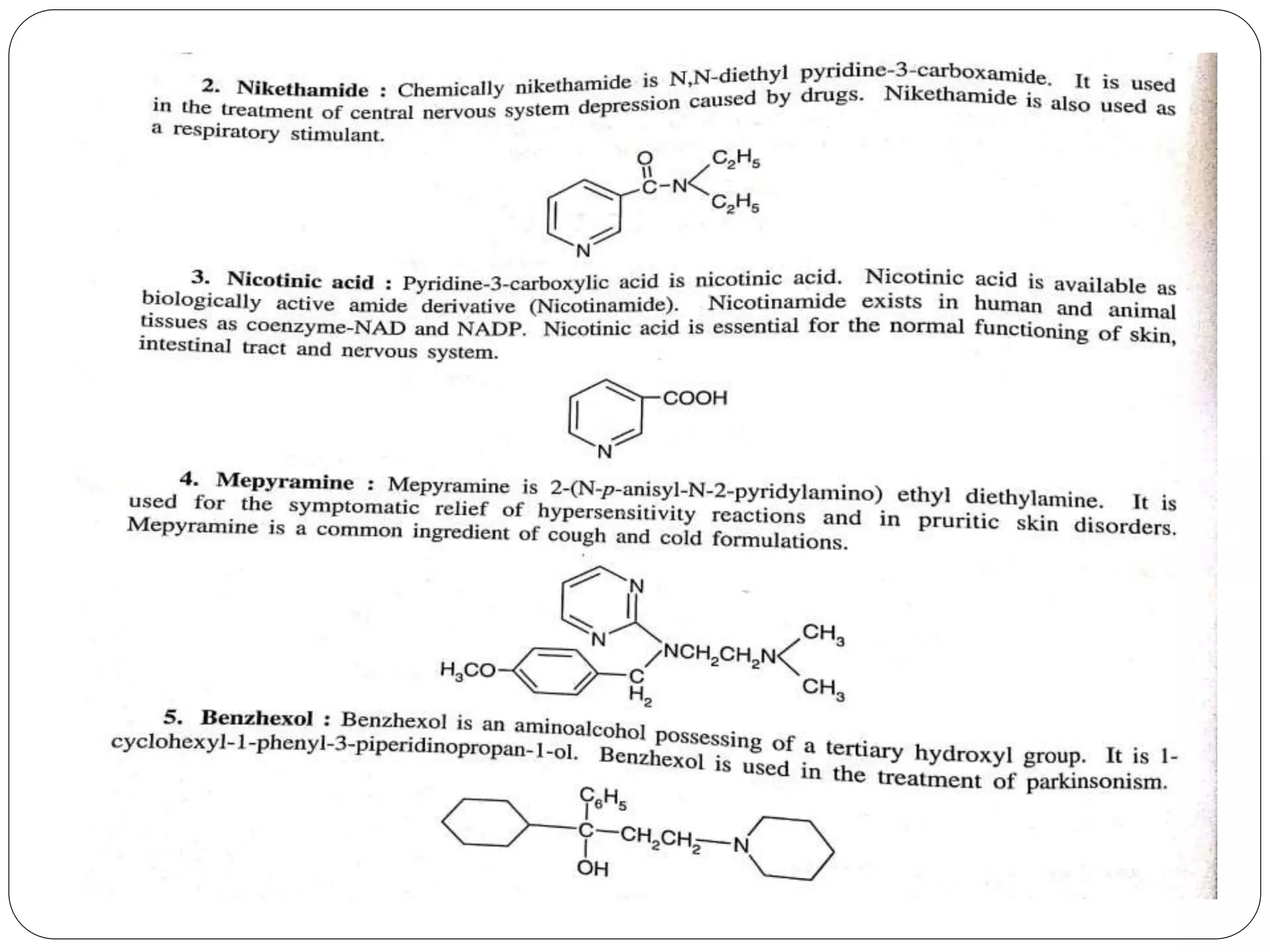
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It has 5 carbon atoms and 1 nitrogen atom arranged in a six-membered aromatic ring. Pyridine can be obtained from coal tar or synthesized by passing acetylene and hydrogen cyanide over a hot tube. It undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution preferably at the carbon-3 position due to stabilization of the intermediate carbocation. Nucleophilic substitution also occurs, preferentially at the carbon-2 position. Pyridine is used as a solvent, in organic reactions, to denature alcohol, and in preparing certain drugs that contain a pyridine ring system.