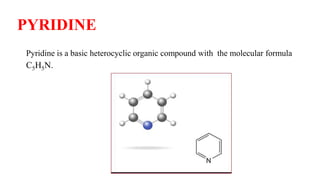
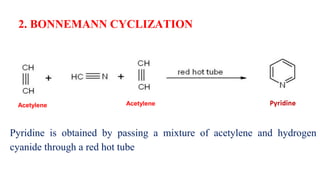
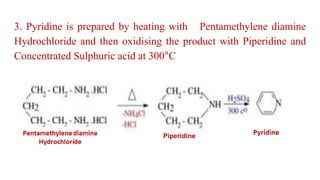
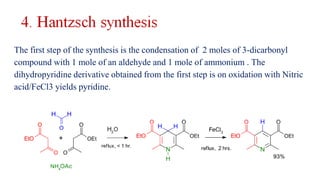
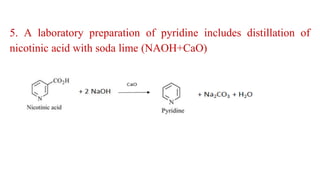
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound (C5H5N) widely used in agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. It is a flammable, weakly alkaline liquid with a distinctive odor and can be isolated from coal tar or synthesized through various methods, including cyclization and laboratory preparation. The document also references key organic chemistry texts for further information.