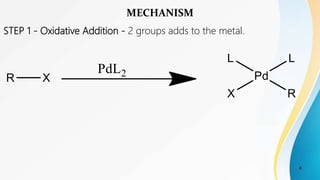
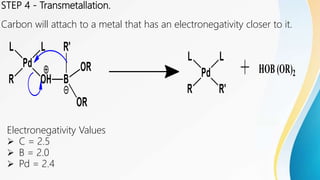
The Suzuki reaction is a palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction between boronic acids or esters with organic halides, triflates, or other boron-containing compounds. This reaction occurs under basic conditions and leads to the formation of carbon-carbon single bonds, typically between an aryl or vinyl group and another aryl or vinyl group. It is commonly used to synthesize biaryl compounds. The reaction proceeds through oxidative addition, transmetallation, and reductive elimination steps. Key advantages are mild reaction conditions and availability of boronic acids. The Suzuki reaction has applications in synthesizing pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and natural products.

![Suzuki reaction is the Pd catalysed cross coupling reaction[1]
between the boronic / organoboronic acids / organoboranes with
organic halides[2], triflates, etc under basic conditions[3] which leads
to the formation of carbon carbon single bonds.[4]
This reaction is commonly used for synthesising biaryl
compounds.
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suzukireaction-190218212358/85/Suzuki-reaction-2-320.jpg)







![• Xenbucin 1, an analgesic drug, was synthesized in 4 steps using two
different routes. The biaryl fragment could successfully be produced
via a Pd/C catalysed Suzuki coupling [5]
12
SYNTHETIC APPLICATIONS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suzukireaction-190218212358/85/Suzuki-reaction-12-320.jpg)
![• Boscalid, a fungicide is prepared via Suzuki reaction.[6]
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suzukireaction-190218212358/85/Suzuki-reaction-13-320.jpg)
![• In Valsartan, the biaryls can easily be prepared by this reaction. [6]
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suzukireaction-190218212358/85/Suzuki-reaction-14-320.jpg)
![• The formal total synthesis of Oximidine by G.A.Molander et al. was
done by using this reaction. [4]
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suzukireaction-190218212358/85/Suzuki-reaction-15-320.jpg)


![REFERENCE
1. Jie Jack Li; Name Reactions: A Collection of Detailed Mechanisms and
Synthetic Applications Fifth Edition; Springer Science & Business Media,
30-Jan-2014; Page no. 544
2. Benny K G Theng; Clay Mineral Catalysis of Organic Reactions; CRC
Press, 27-Jul-2018; Page No.2016
3. Ranjit S. Dhillon; Hydroboration and Organic Synthesis : 9-Borabicclo
[3.3.1] nonane (9-BBN); Springer Science & Business Media; 01 - May -
2007; Page No. 523
4. Laszlo Kurti, Barbara Czako; Strategic Applications of Named Reactions
in Organic Synthesis; Elsevier, 29-Apr-2005; Page no. 37
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suzukireaction-190218212358/85/Suzuki-reaction-18-320.jpg)

