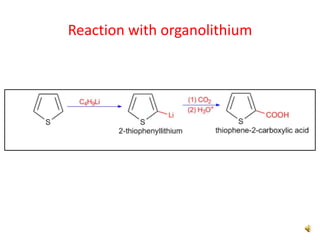
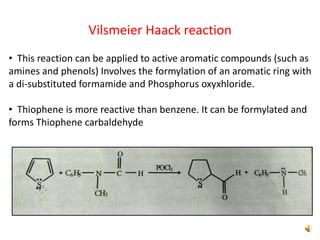
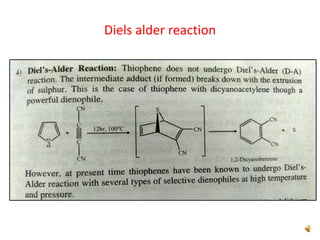
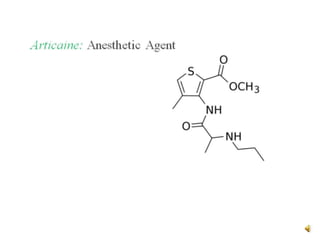
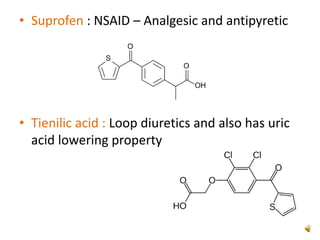
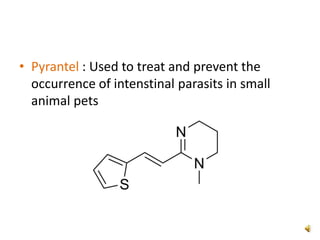
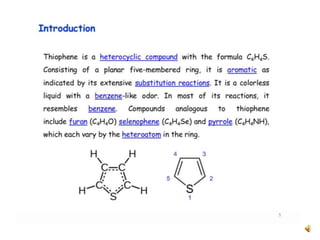
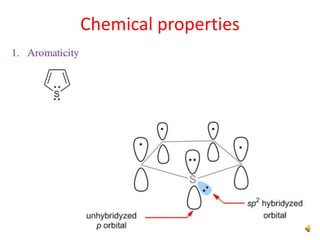
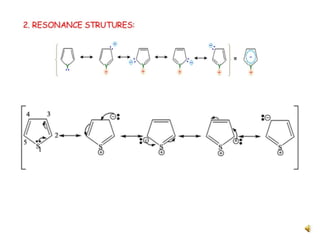
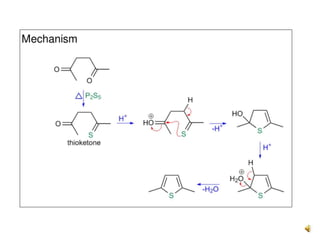
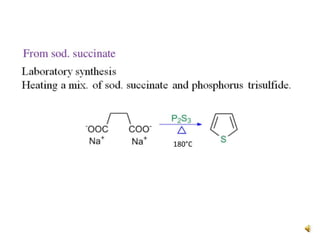
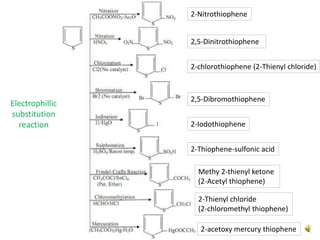
Thiophene, discovered by Viktor Meyer in 1882 as a benzene contaminant, is a toxic, flammable liquid with applications in various pharmaceutical compounds due to its bioisosterism with benzene. Its unique properties allow for various chemical reactions and medicinal uses, exhibiting activities such as anti-microbial and anti-cancer effects. Thiophene derivatives are significant in medicinal chemistry for their diverse biological activities and therapeutic profiles.


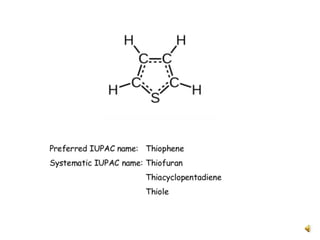






![Reduction
[O]
Tetramethylene
sulphone](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heterocyciccompound-thiophene-200619051047/85/Heterocycic-compound-Thiophene-20-320.jpg)