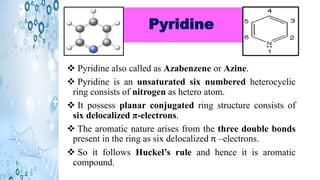
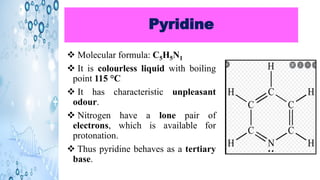
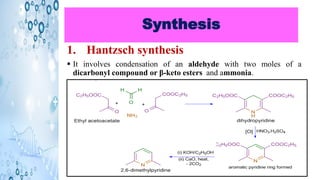
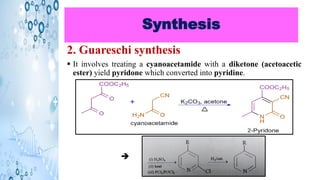
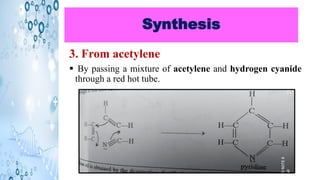
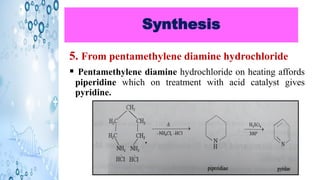
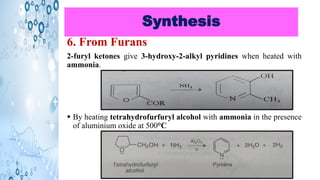
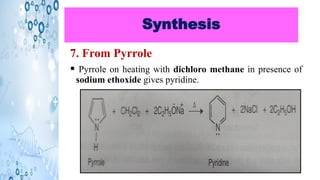
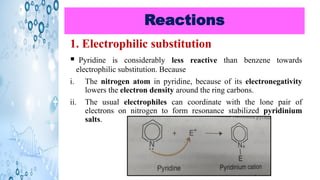
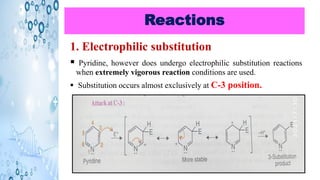
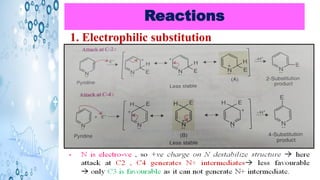
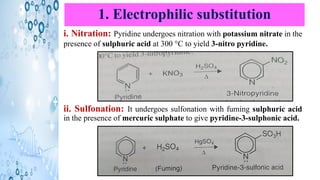
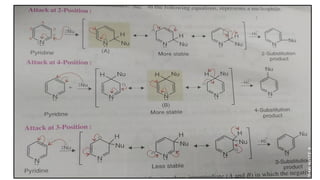
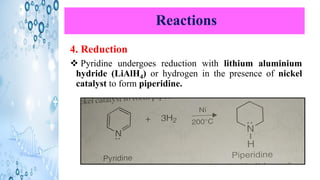
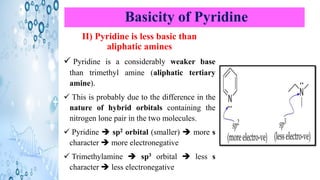
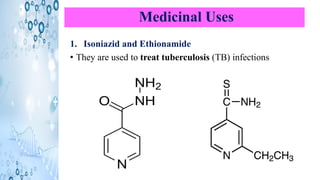
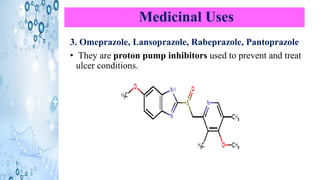
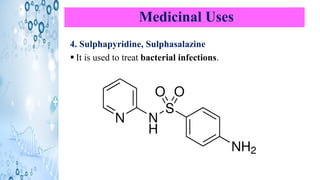
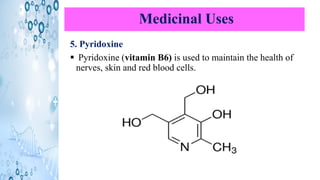
This document discusses the properties and synthesis of pyridine. Pyridine is an aromatic heterocyclic compound containing a six-membered ring with one nitrogen atom. It has a planar structure and is aromatic according to Huckel's rule. Pyridine can be synthesized through several methods including the Hantzsch synthesis and from acetylene. It undergoes electrophilic substitution at the C-3 position and nucleophilic substitution at C-2 or C-4. Pyridine is used as a base in medicines such as isoniazid and omeprazole.