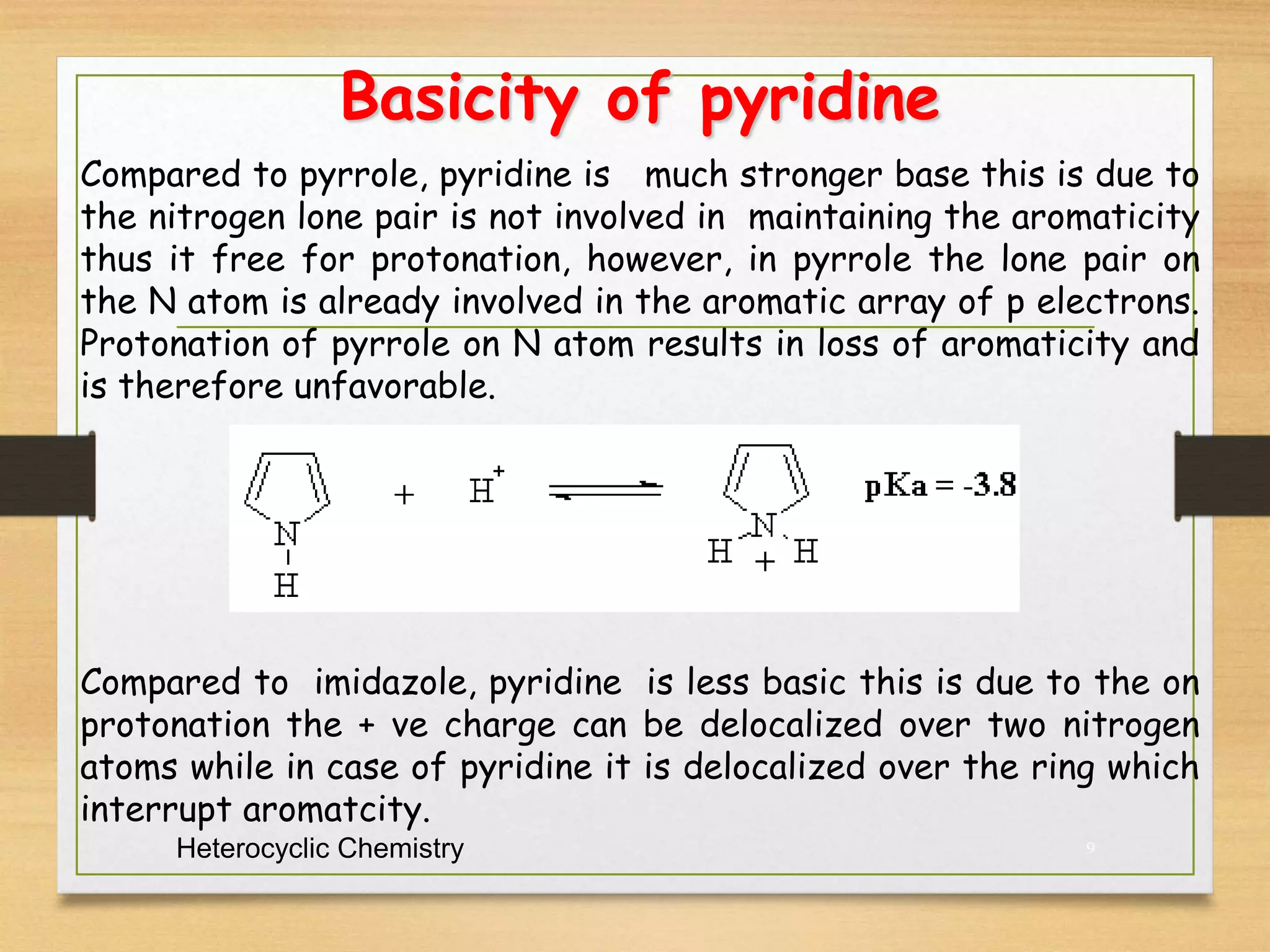
1. Heterocyclic compounds contain ring structures with at least two different elements as members. Pyridine is a six-membered heterocyclic compound containing one nitrogen atom.
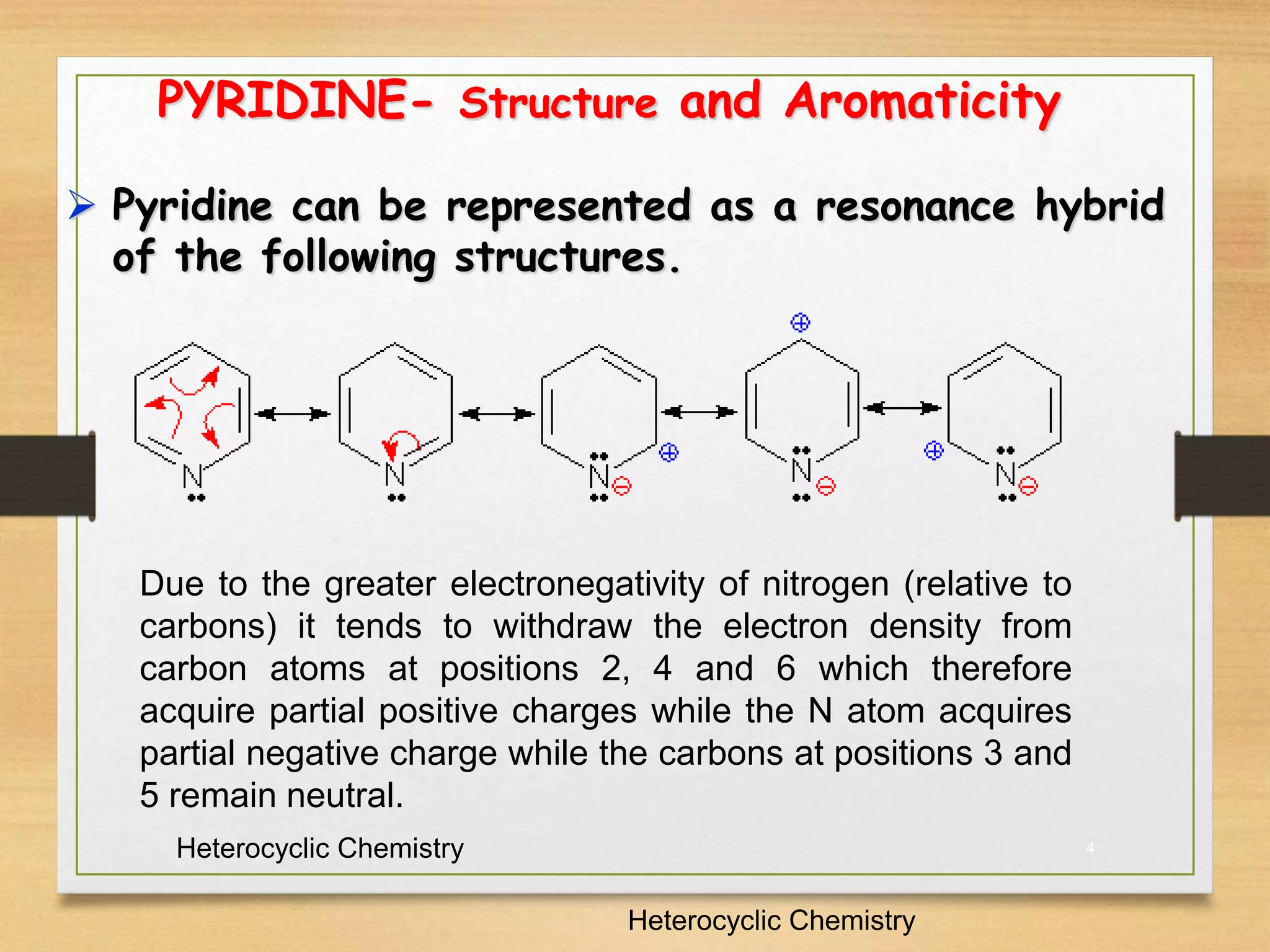
2. Pyridine can be represented by resonance structures with the nitrogen atom withdrawing electron density from certain carbon atoms. It is aromatic but a weaker base than analogous amines due to its sp2 hybridized nitrogen.
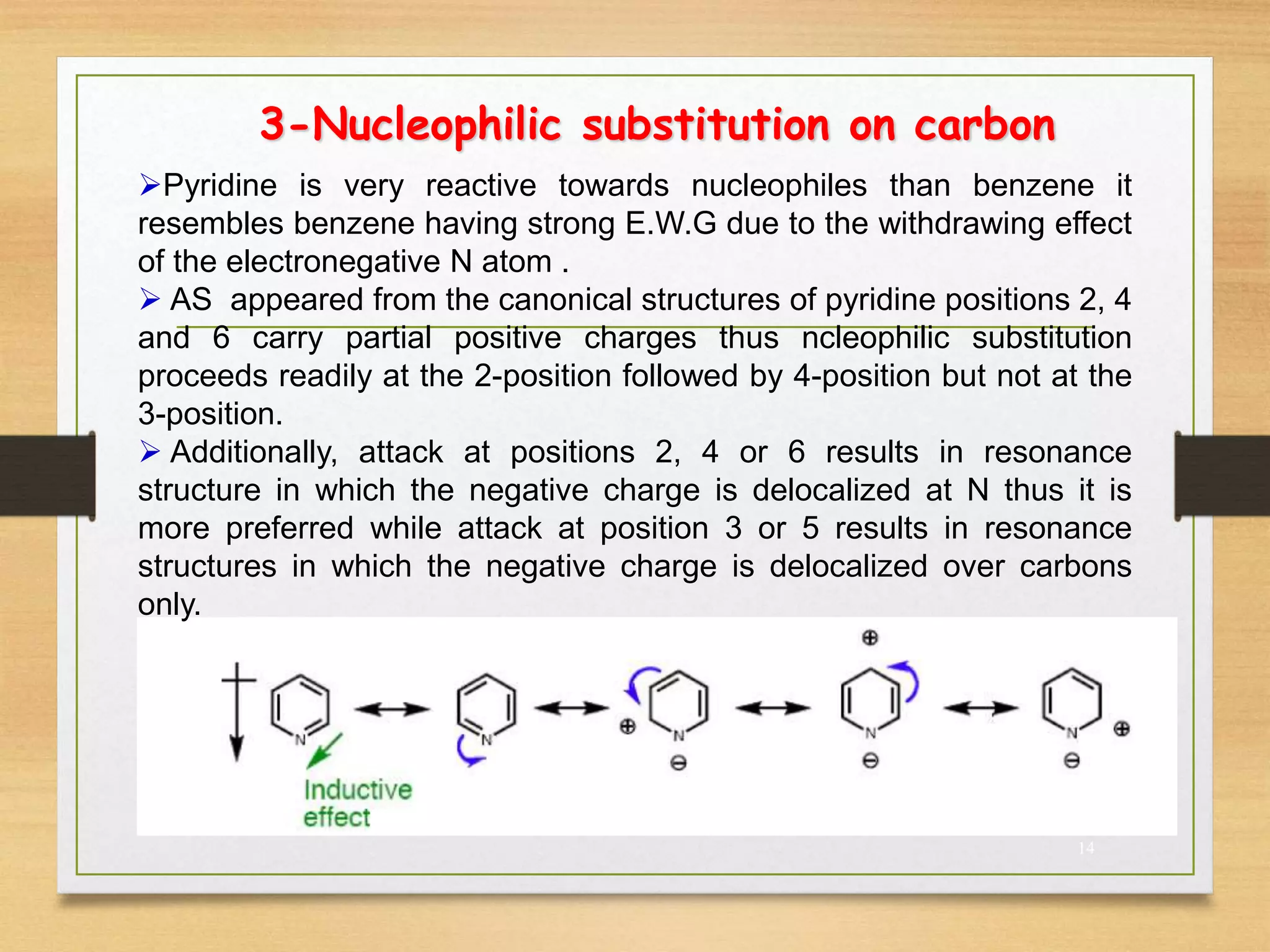
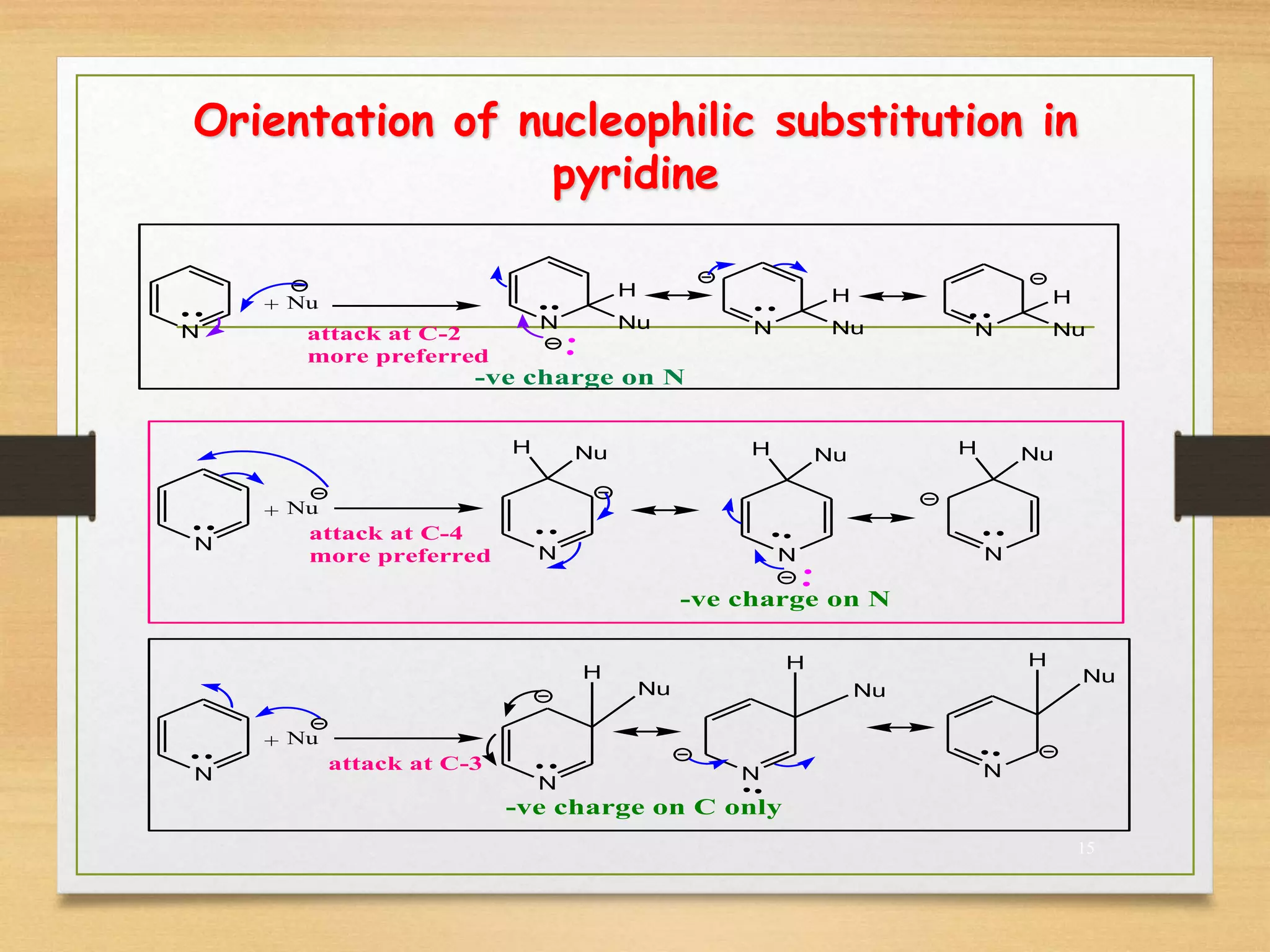
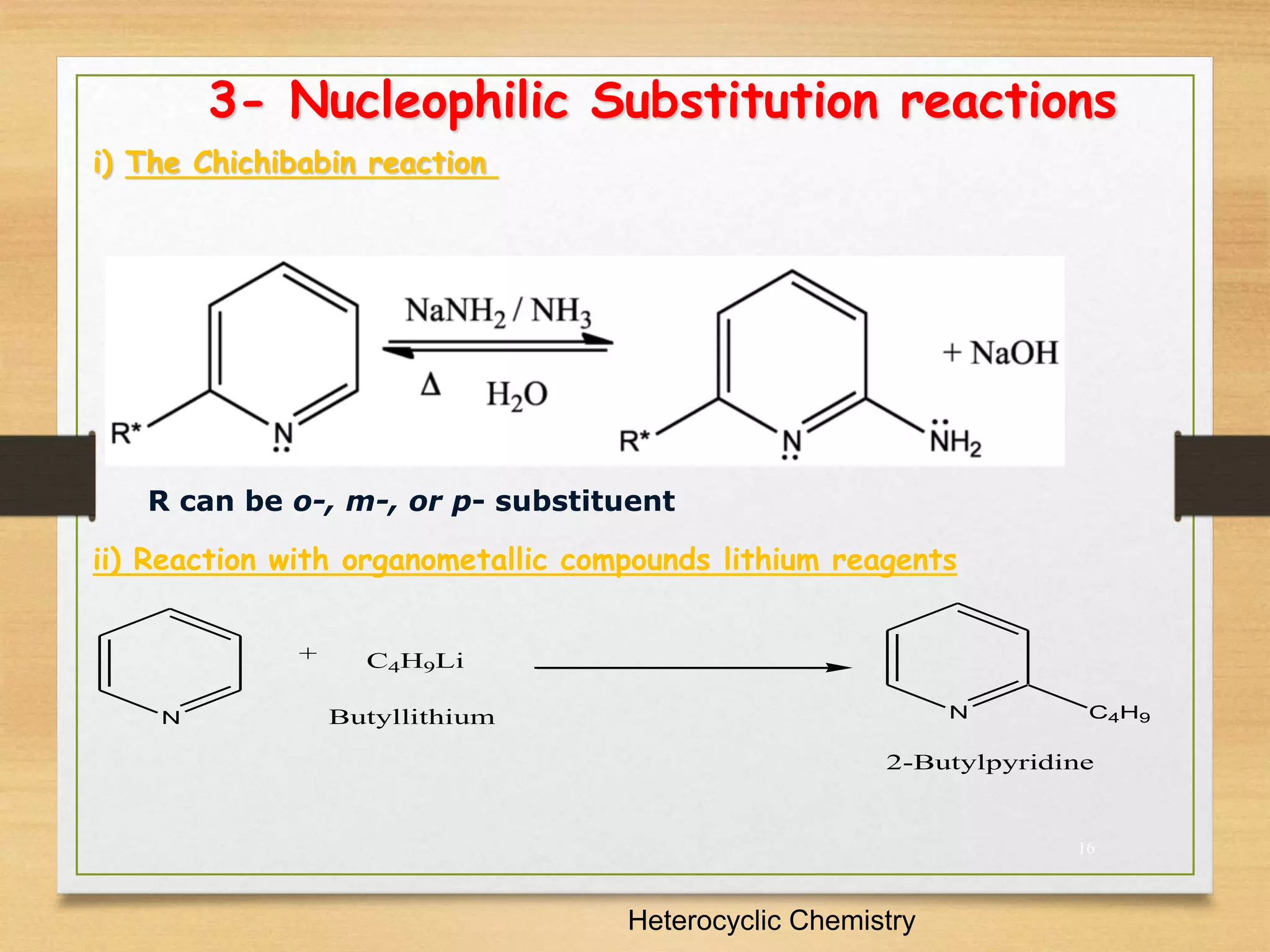
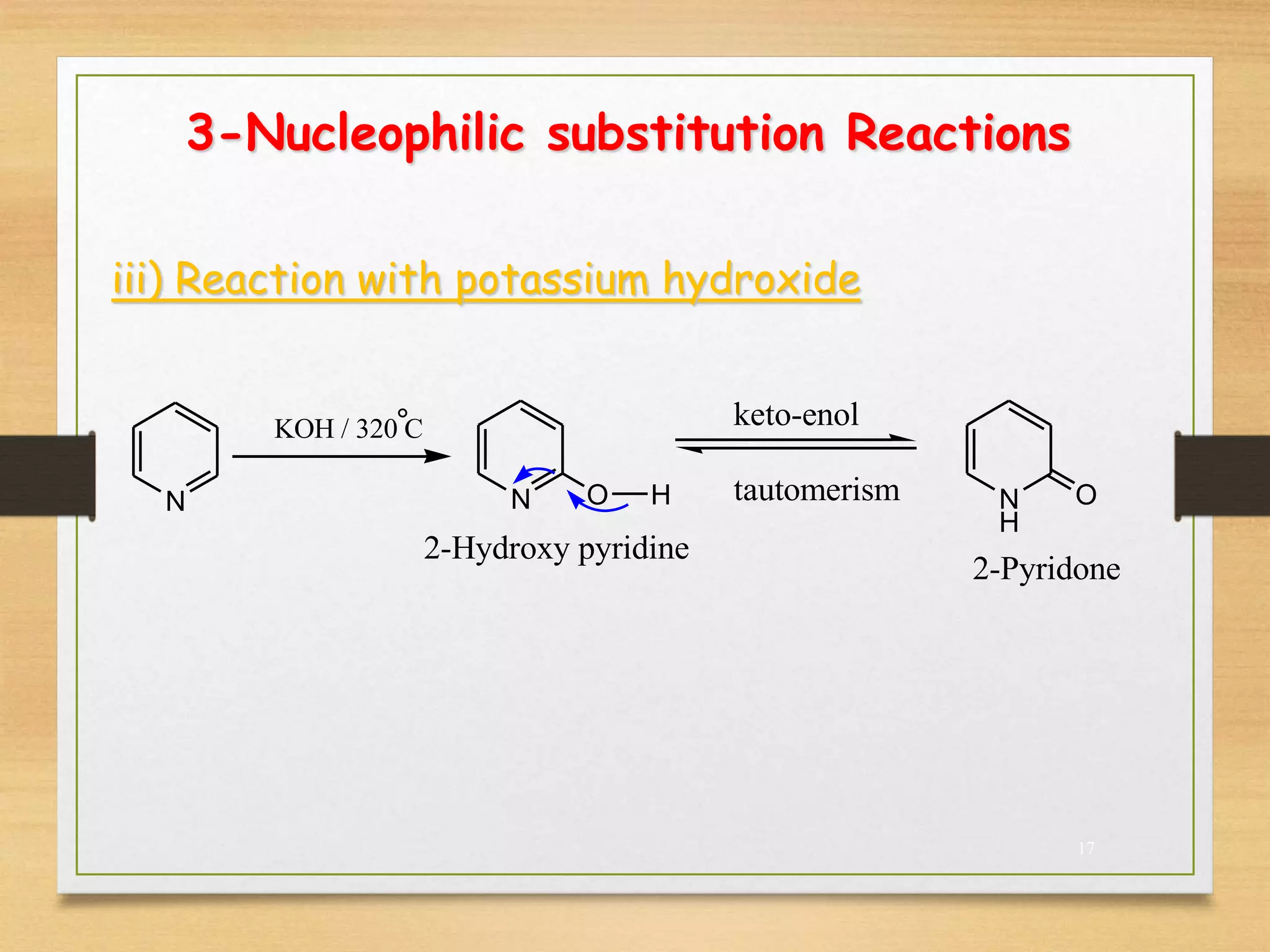
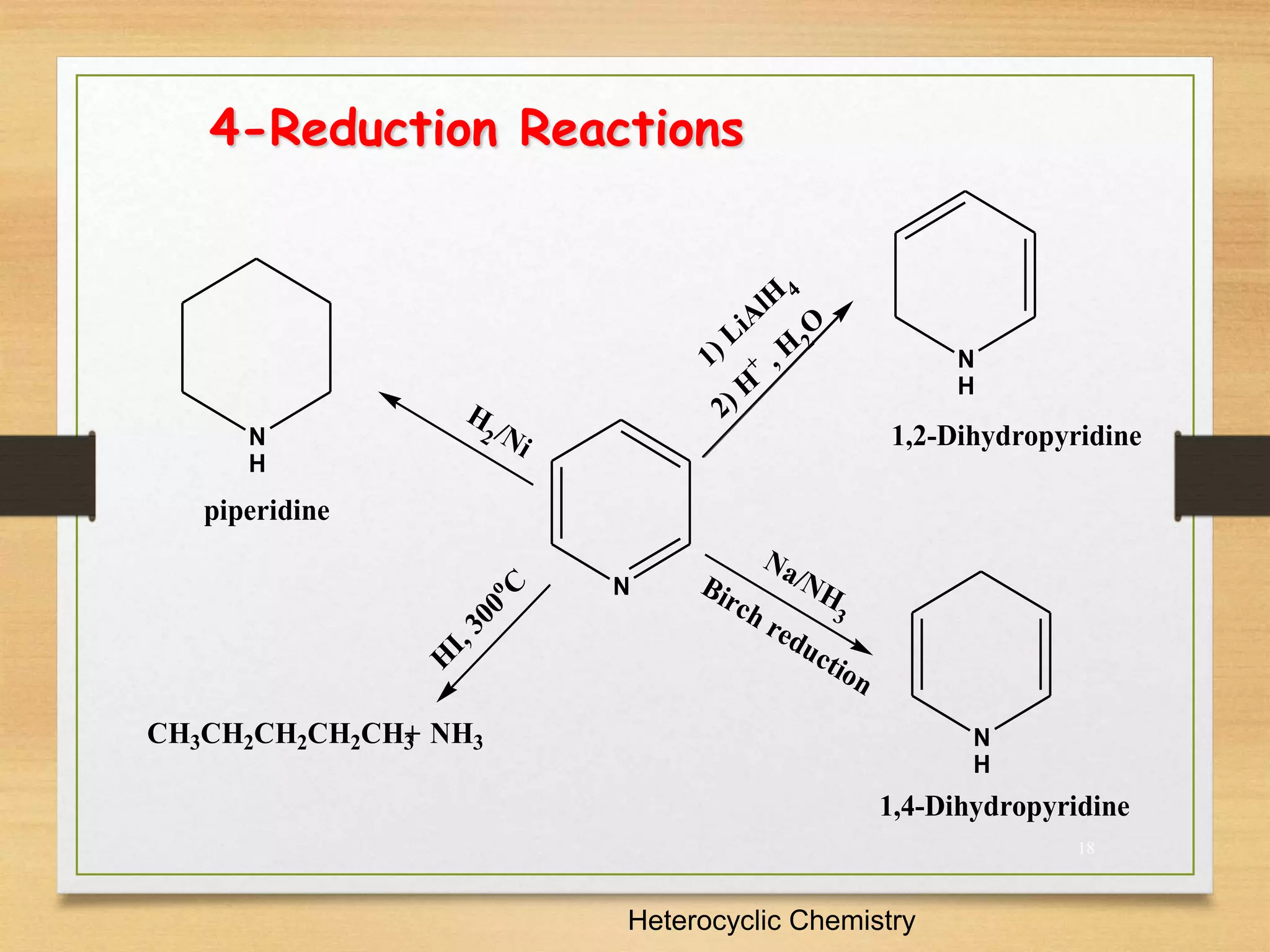
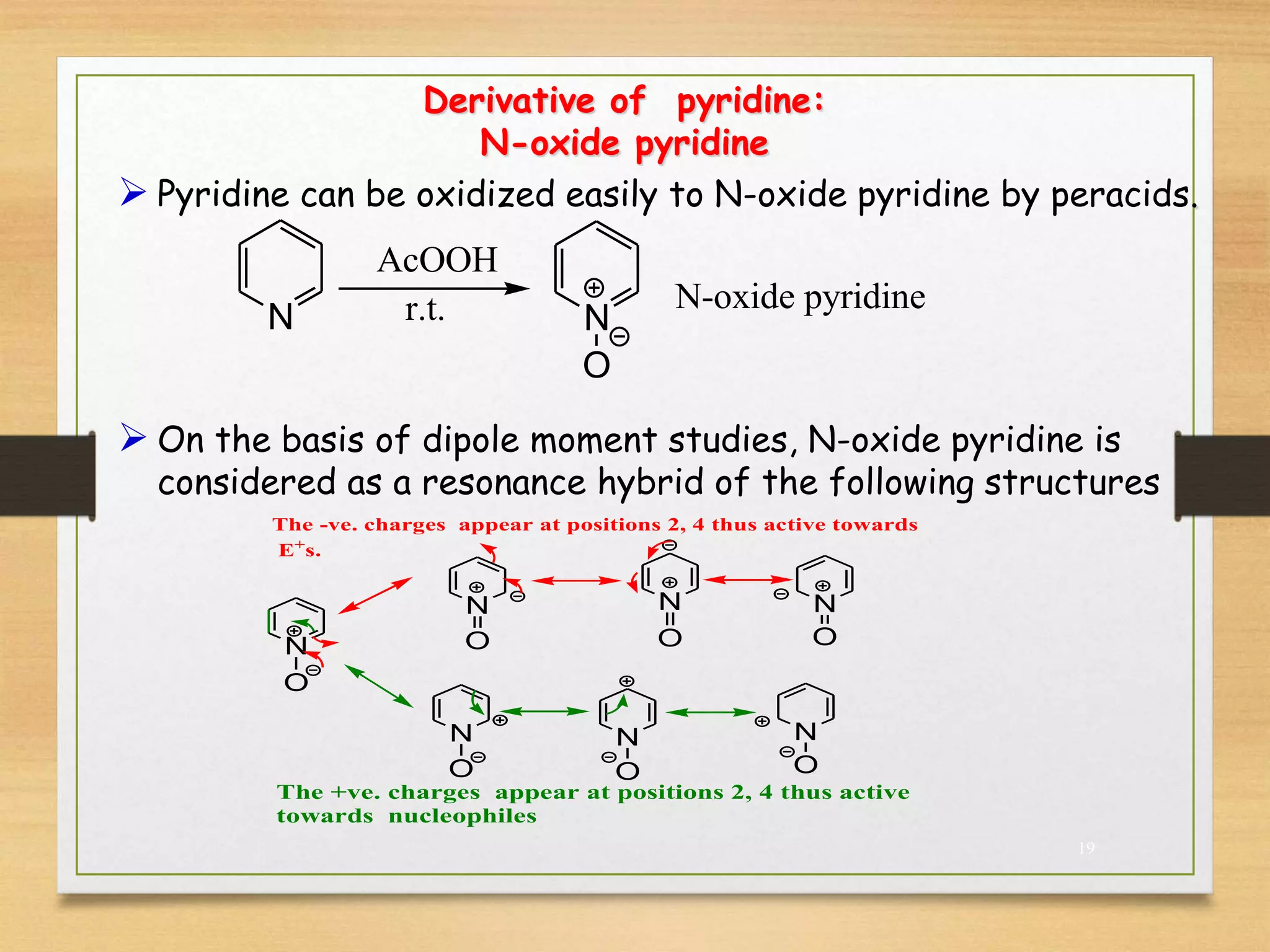
3. Pyridine undergoes electrophilic substitution and nucleophilic substitution reactions. N-oxide pyridine is more activated for these reactions and is an important intermediate for preparing substituted pyridines.



![6
Heterocyclic Chemistry
2- Bönnemann cyclization:
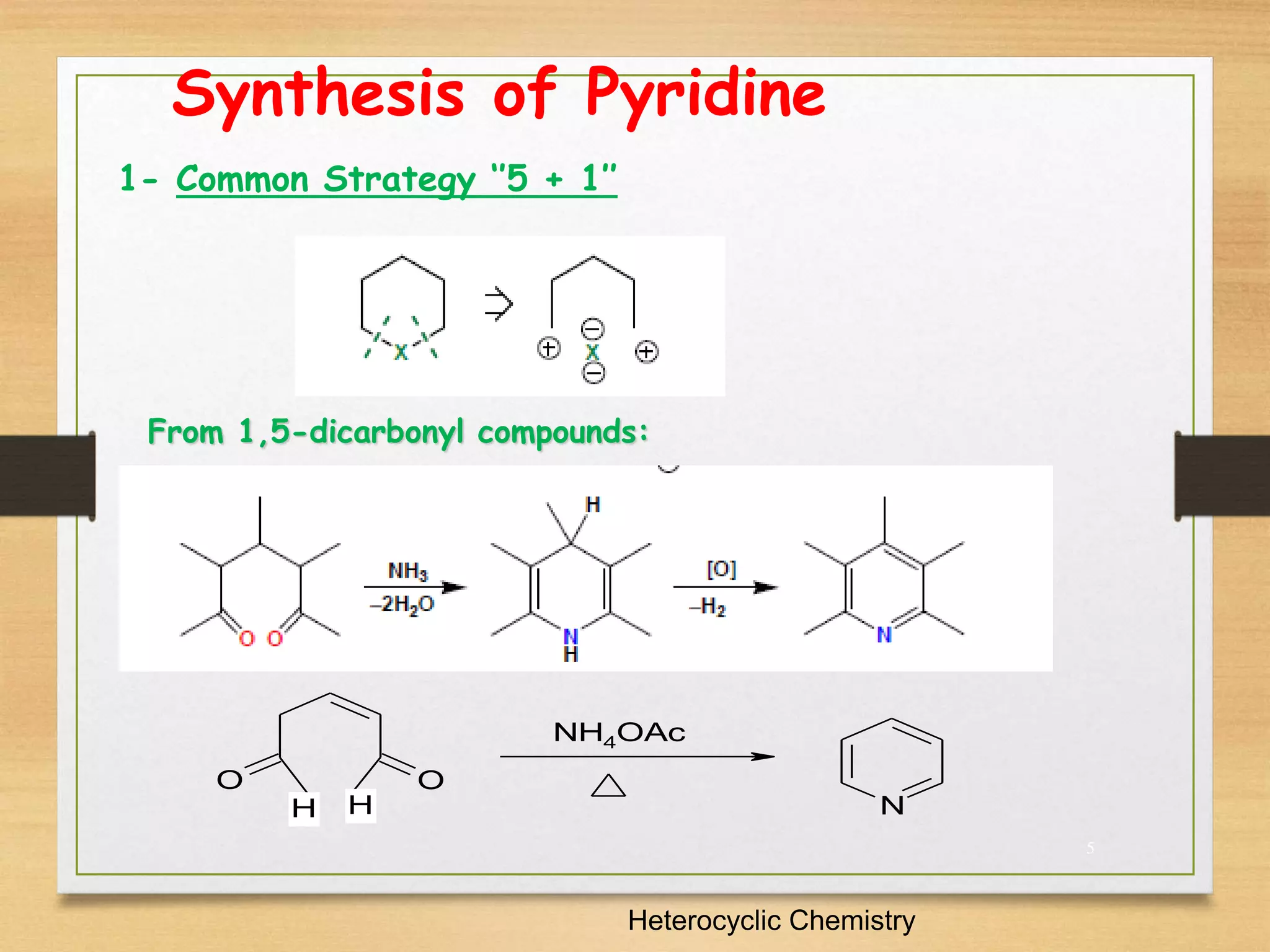
Synthesis of Pyridine
3- Hantzsch Synthesis:
O
OEt
O O
H H
OEt
O
O
+
+
N
H
EtO
O
OEt
O
HNO3
[O]
NH3
Ethylacetoacetate
-dicarbonyl cpd
dihydropyridine drivative 1) KOH
2) CaO,
N
O O
N
EtO
O
OEt
O
N
CH
CH
+ N
HC +
CH
CH
red hot tube](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heterocycliccompounds-221221062750-f4650893/75/heterocyclic-compounds-ppt-6-2048.jpg)