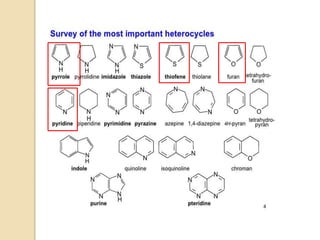
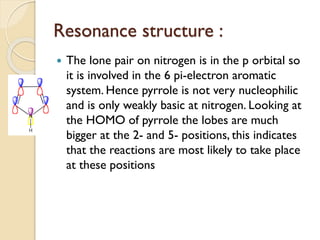
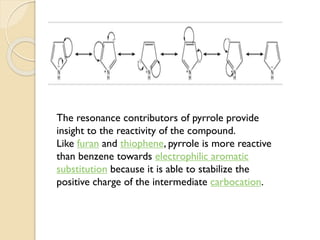
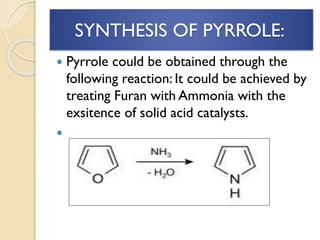
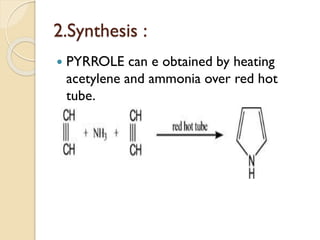
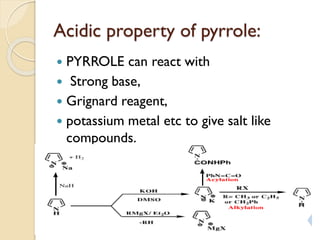
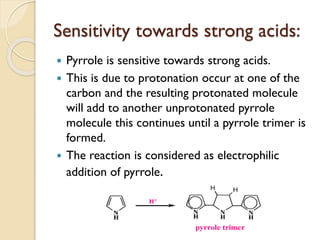
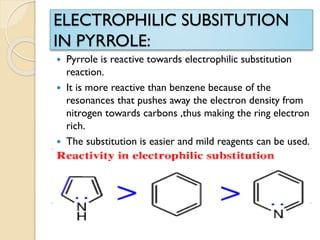
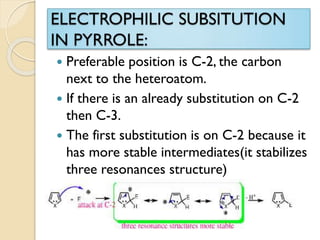
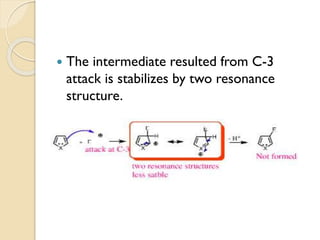
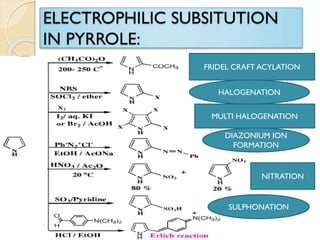
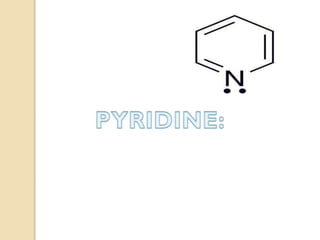
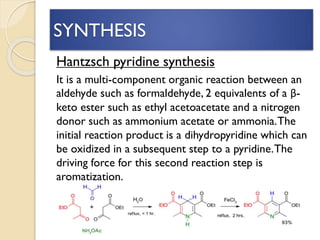
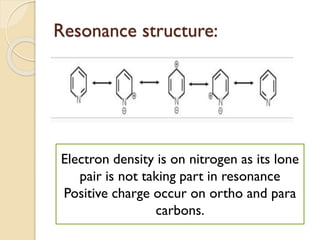
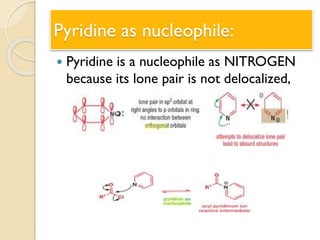
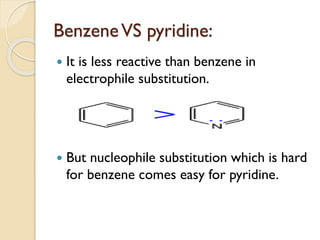
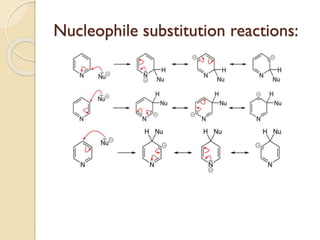
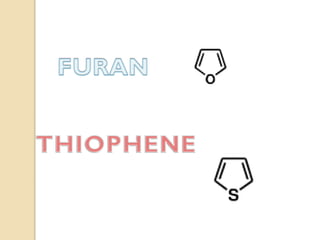
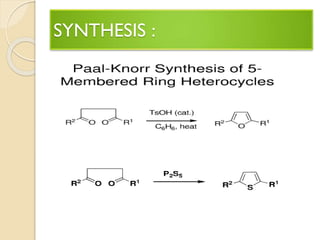
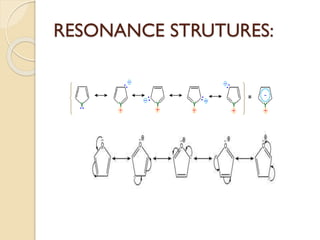
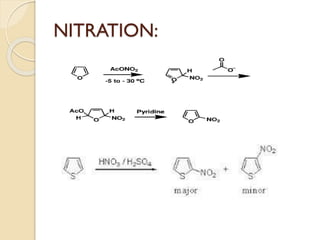
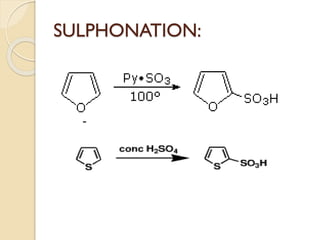
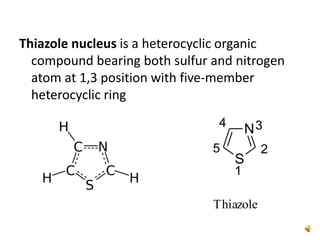
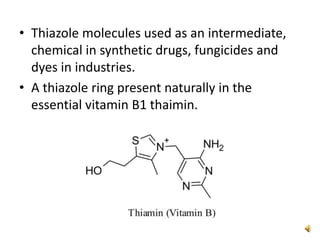
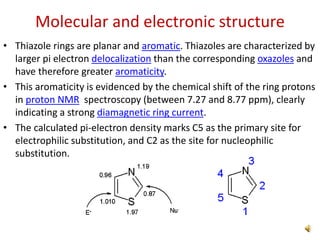
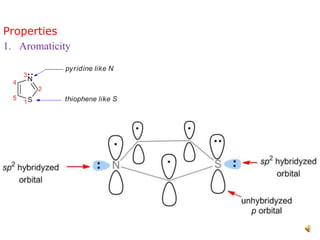
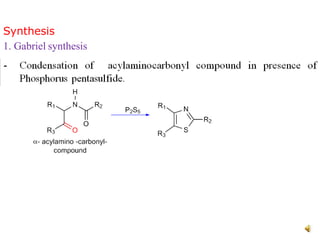
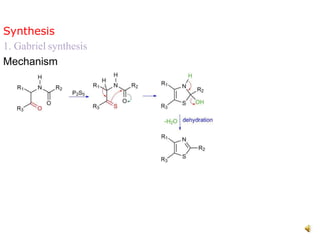
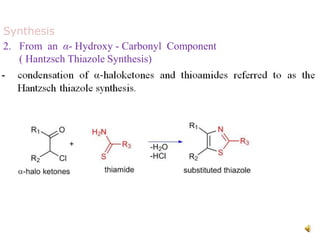
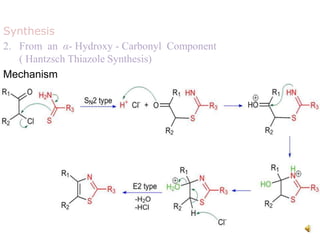
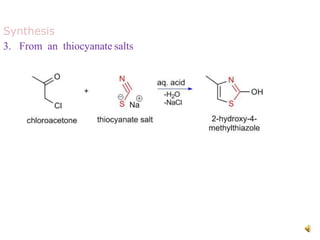
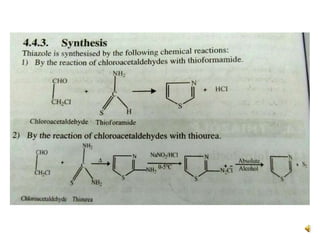
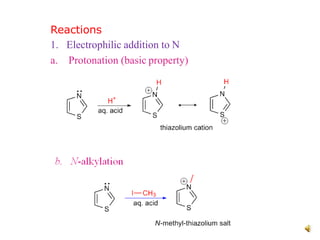
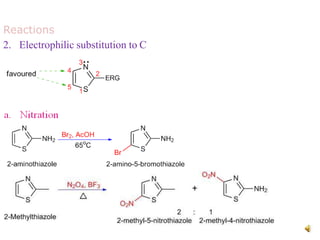
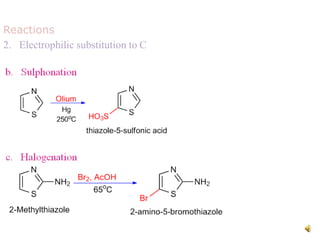
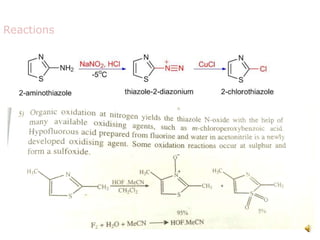
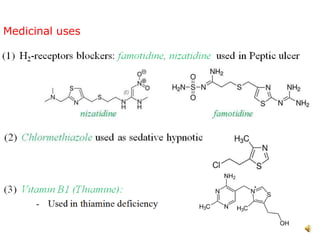
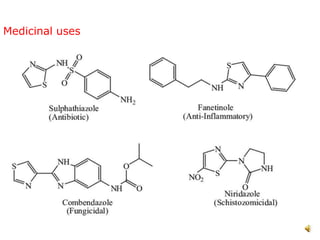
Pyrrole is a colorless, volatile, aromatic 5-membered heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4NH. It is more reactive than benzene towards electrophilic aromatic substitution due to resonance structures that stabilize positive intermediates. Pyrrole can be synthesized by treating furan with ammonia in the presence of an acid catalyst or by heating acetylene and ammonia. Substitutions occur preferentially at the 2-position carbon.