Embed presentation
Downloaded 171 times

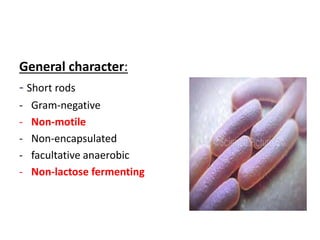








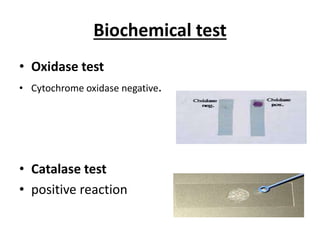

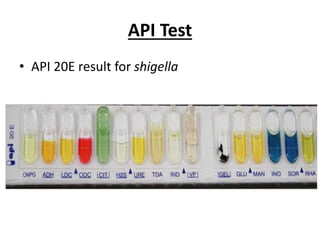


This document provides information about Shigella spp., including its general characteristics as a gram-negative, non-motile, non-encapsulated, facultative anaerobic rod. It describes specimens used for laboratory diagnosis and various tests run, including microscopy showing gram-negative bacilli, growth on culture media like MacConkey agar and EMB agar, biochemical tests for oxidase, catalase, urease and citrate, and API 20E testing. It also covers serologic diagnosis and serotyping of Shigella into four serogroups.














