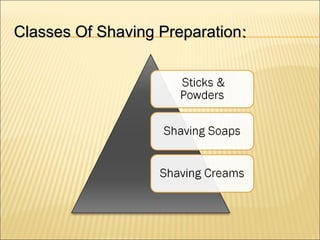
The document provides an overview of shaving cream, including its history, types, manufacturing process, quality control, criteria, applications, side effects, comparisons to other products, popular brands, and references. It discusses how shaving cream is made through heating and cooling various raw materials like oils and surfactants to form an emulsion. Quality control testing examines factors like pH levels. Shaving cream softens hair and skin to allow for a smoother shave while also cleaning and lubricating surfaces around the home.