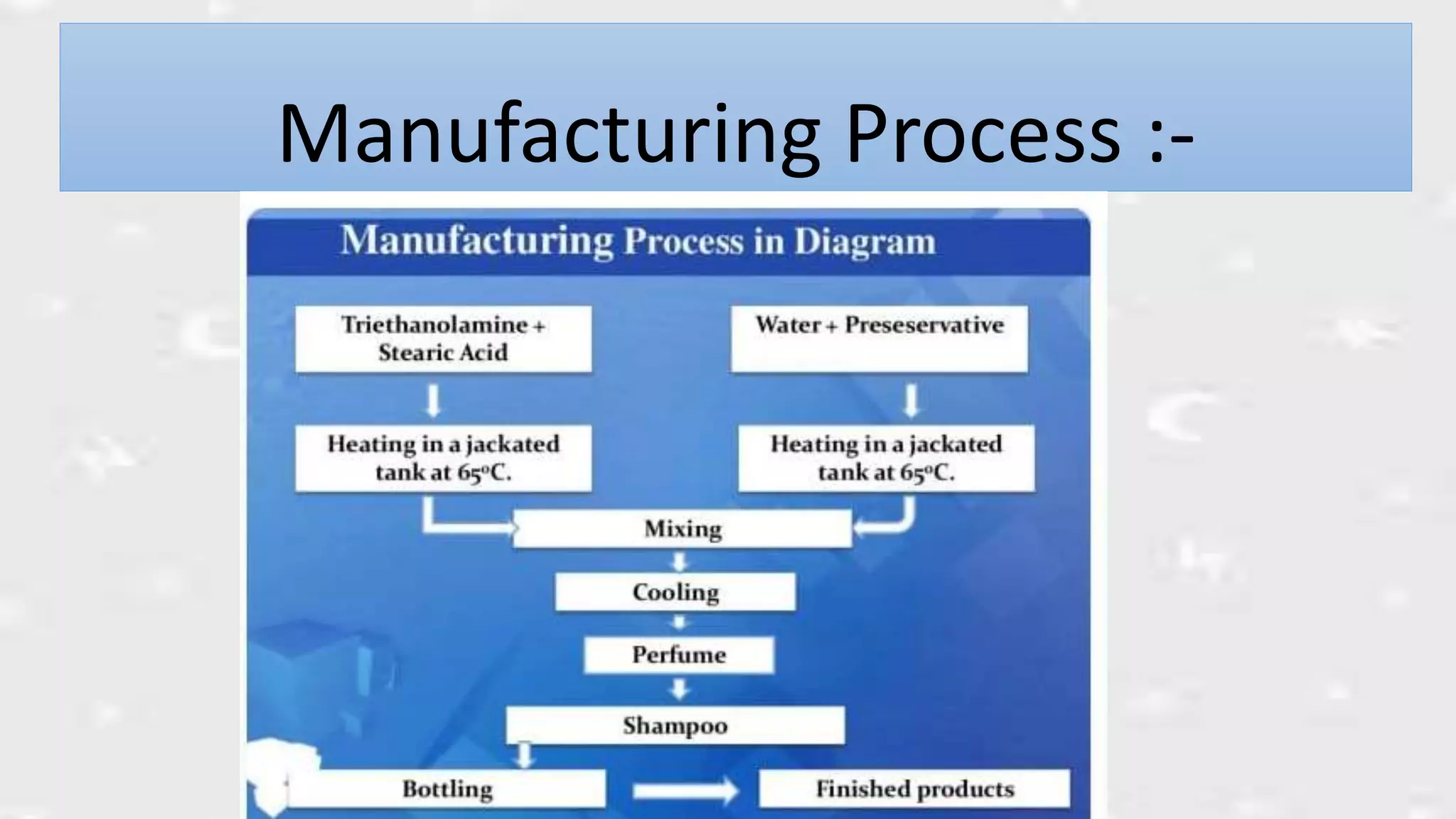
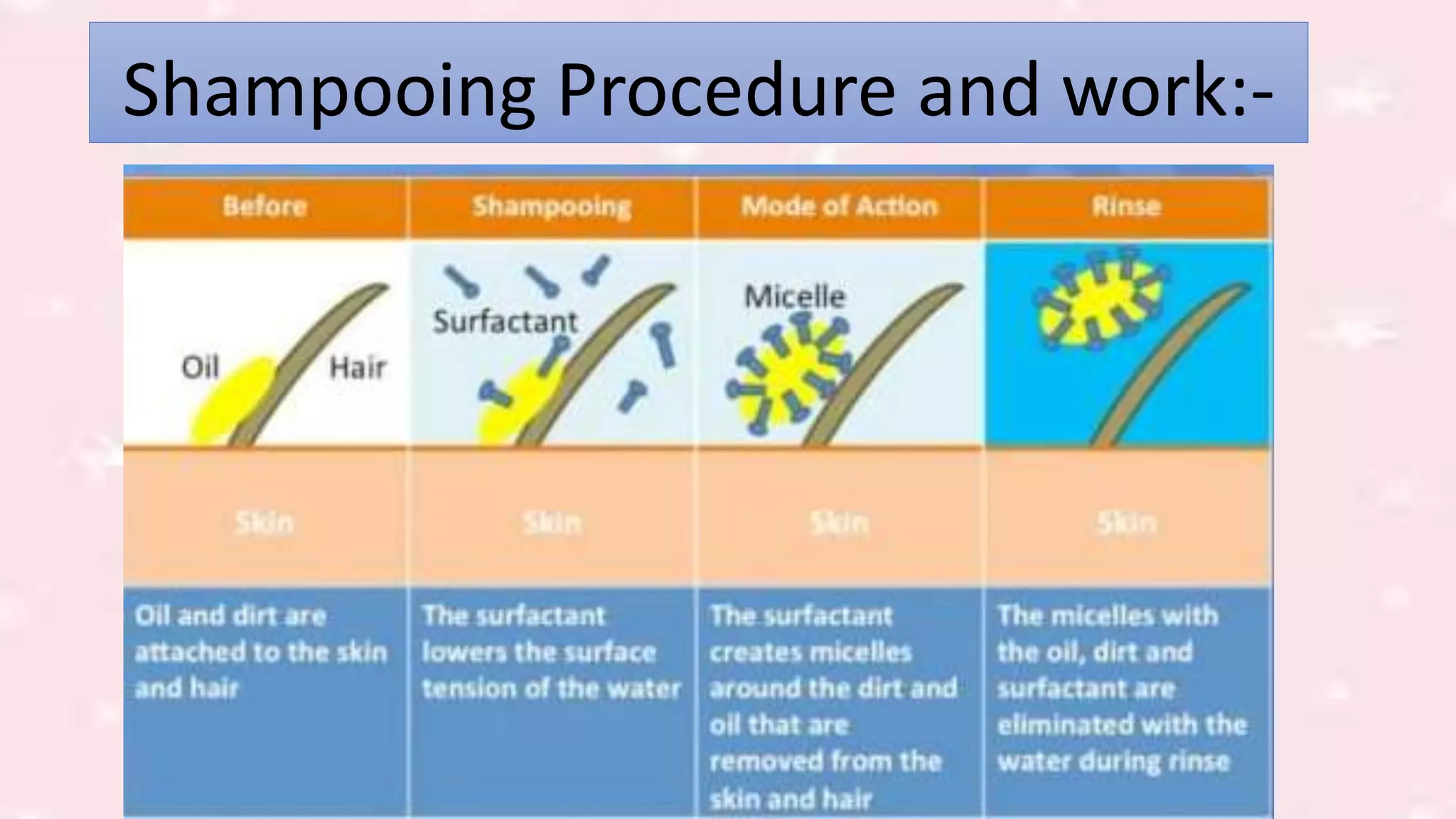
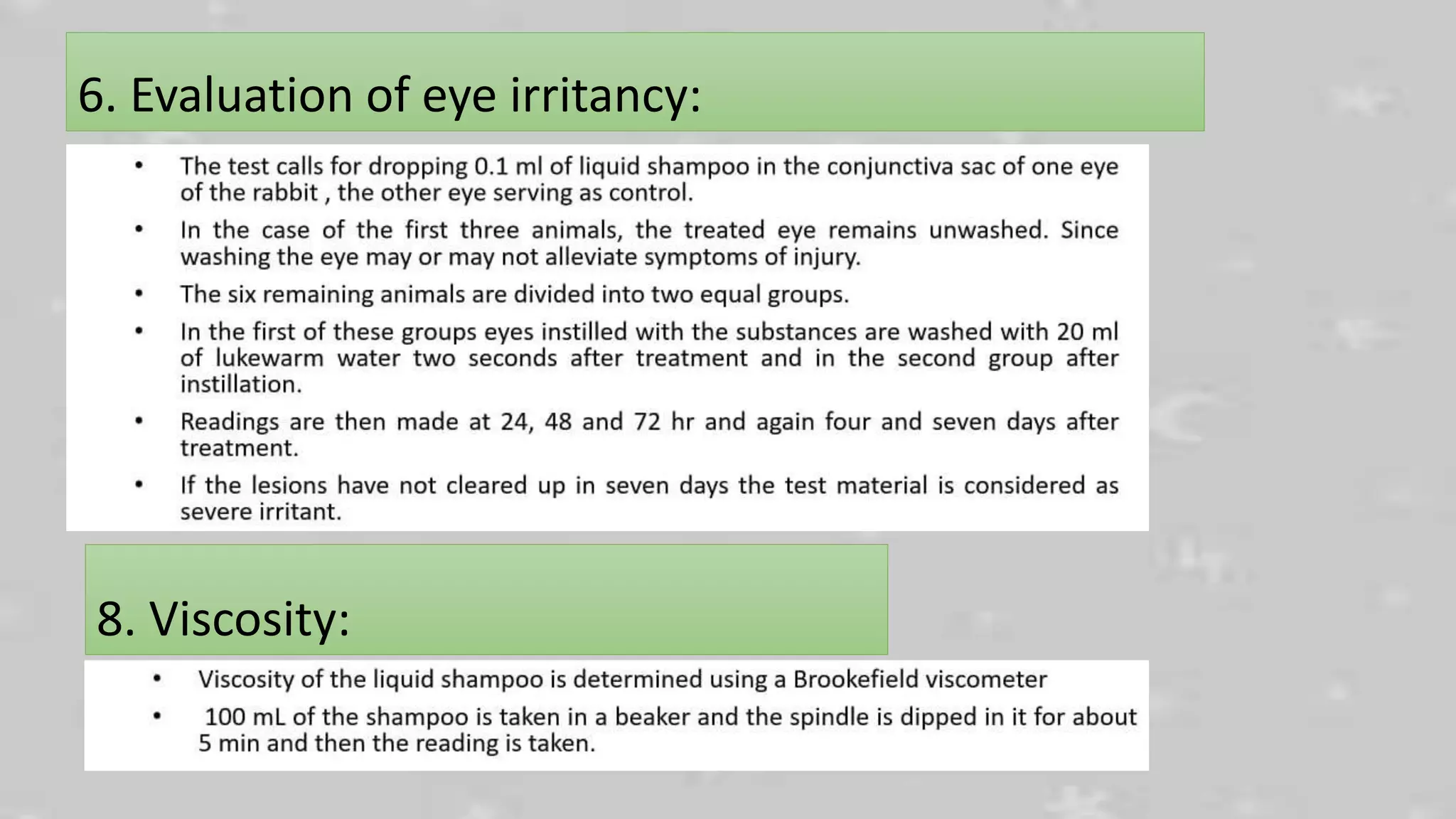
This document discusses the formulation and preparation of shampoo. It defines shampoo as a hair care product used to remove oils, dirt, and other contaminants from hair without damaging it. The key components of shampoo include water, surfactants such as sodium lauryl sulfate, thickeners, preservatives, conditioning agents, and fragrances. Anionic surfactants are primarily used for their good foaming properties. The document outlines the manufacturing process and ideal properties of shampoo, and methods for evaluating shampoo performance characteristics such as foam production, cleaning ability, and conditioning effects.