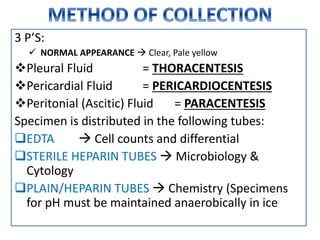
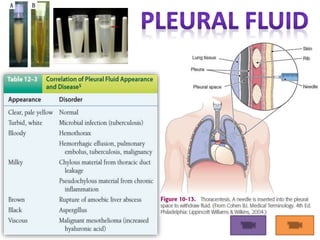
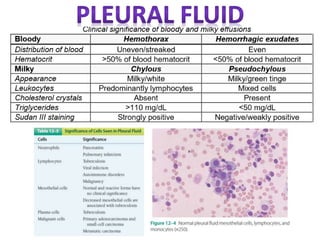
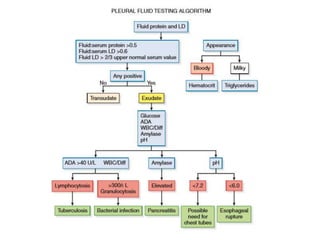
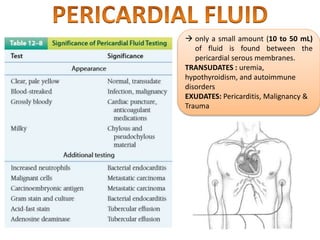
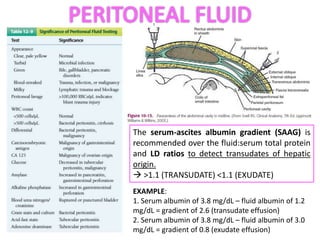
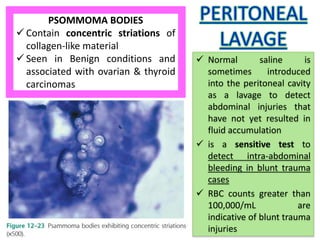
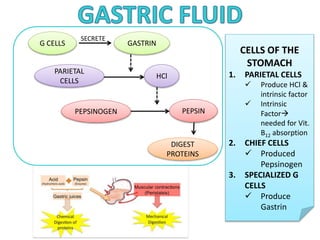
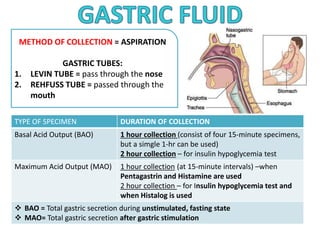
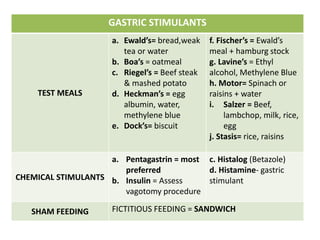
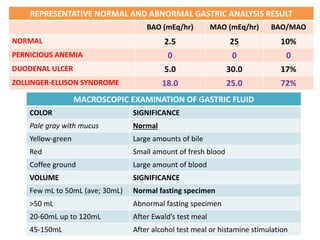
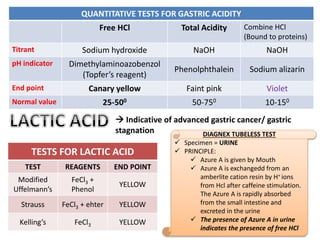
This document provides information on serous fluid, effusions, and tests used to analyze body fluids. It discusses:
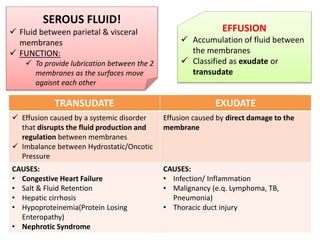
- Serous fluid's function of lubricating membranes and effusions occurring when fluid accumulates between membranes. Effusions are classified as transudates or exudates.
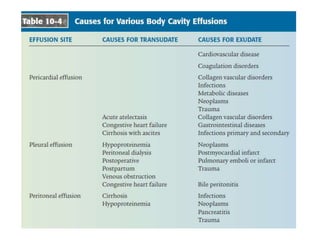
- Causes of transudates include systemic disorders, while exudates are caused by direct membrane damage from infection, inflammation, or malignancy.
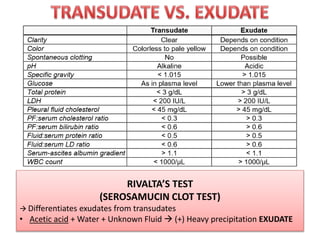
- The Rivalta's test differentiates exudates from transudates based on precipitation with acetic acid and water.