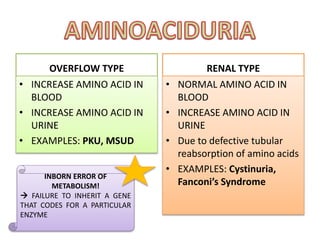
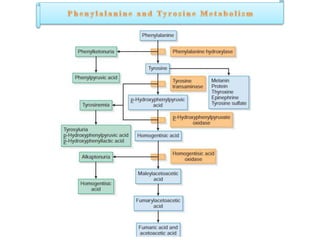
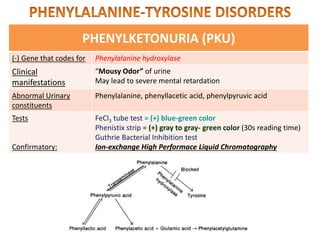
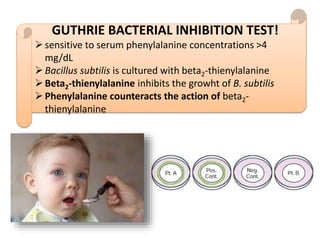
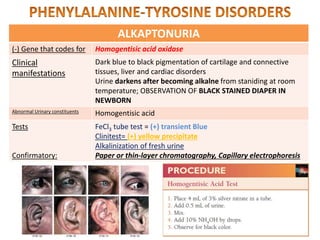
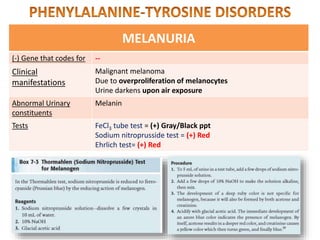
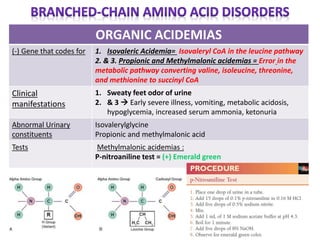
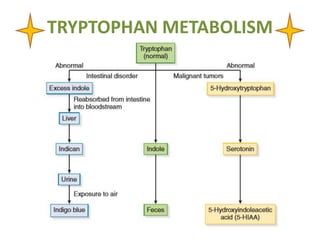
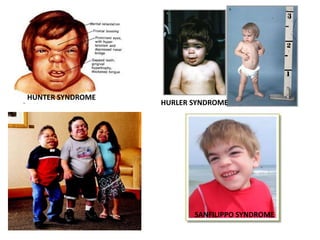
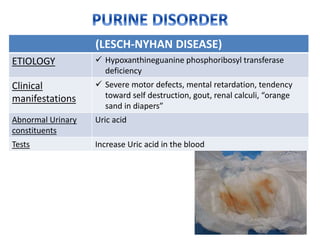
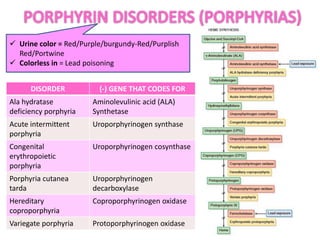
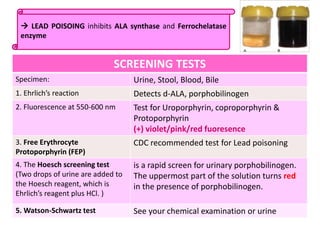
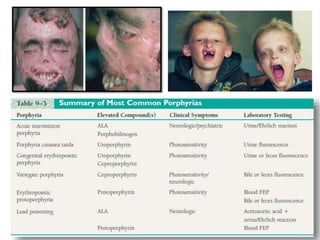
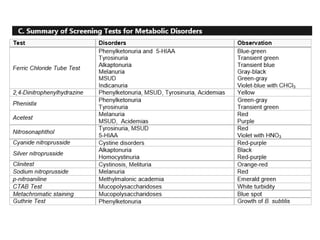
This document discusses various inborn errors of metabolism that can be detected by analyzing amino acids and other compounds in the urine. It covers different types of aminoaciduria including overflow aminoaciduria, renal aminoaciduria, and those caused by inborn errors of metabolism. Specific disorders covered include phenylketonuria (PKU), tyrosinuria, alkaptonuria, melanuria, maple syrup urine disease, organic acidemias, cystinuria, cystinosis, homocystinuria, and Lesch-Nyhan disease. It also discusses porphyrias, screening tests for various compounds, and references for further information.