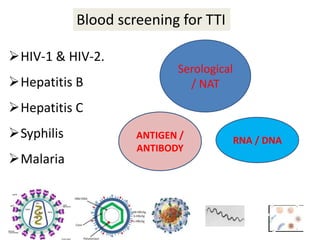
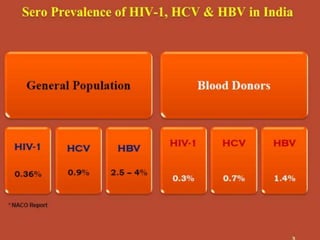
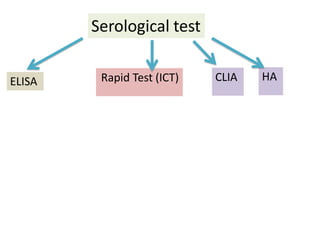
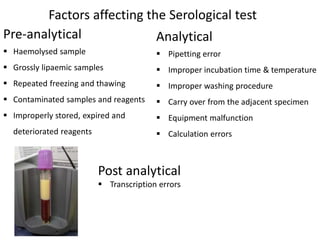
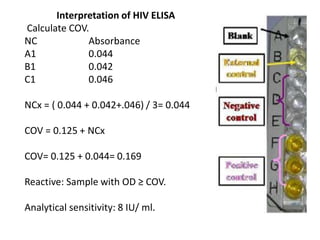
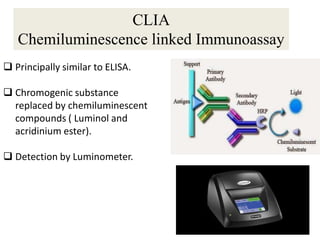
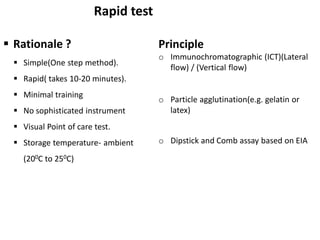
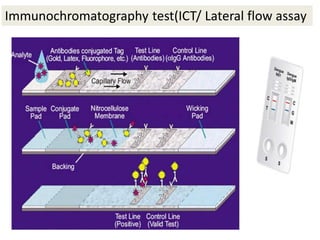
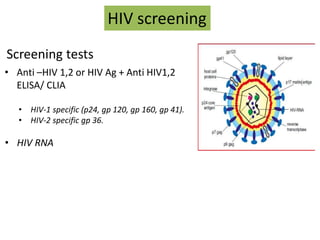
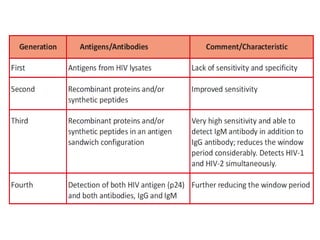
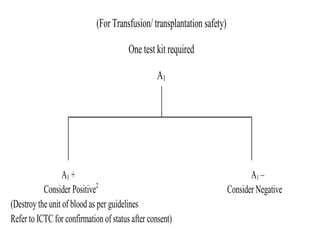
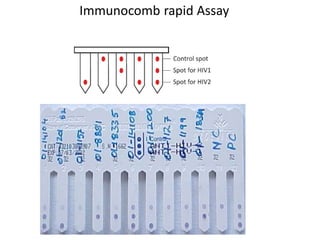
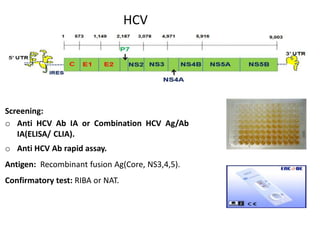
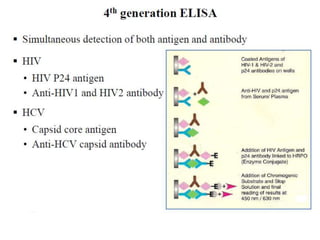
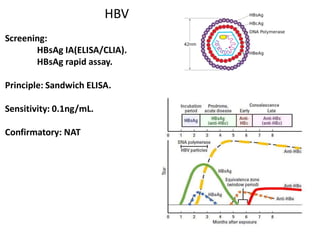
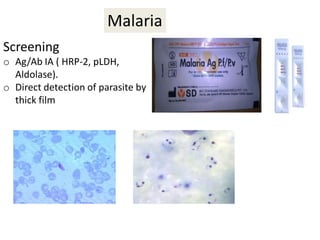
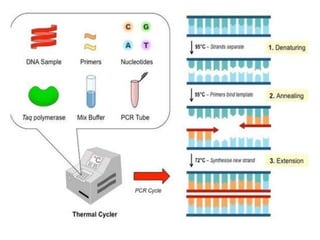
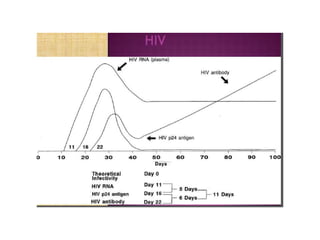
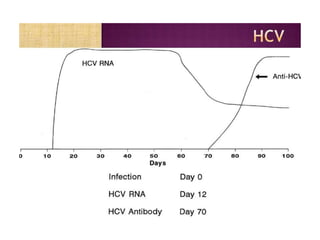
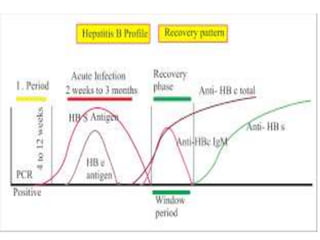
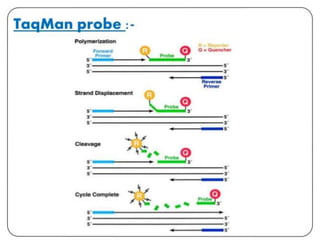
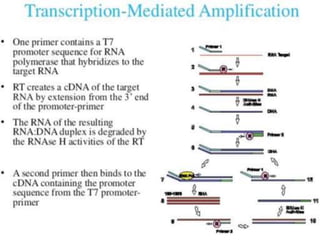
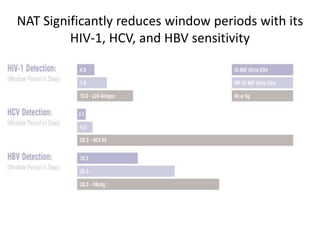
This document discusses transfusion-transmitted infections (TTIs) and methods for screening donated blood. It notes that TTIs include viruses like HIV, HBV, HCV that can remain undetected in the blood donor but be transmissible. Screening methods include serological tests like ELISA, CLIA, rapid tests, as well as nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) that can detect infections earlier. Implementing individual donor NAT in addition to serological screening provides an additional safety layer and reduces the risk window period for TTIs in blood donations.