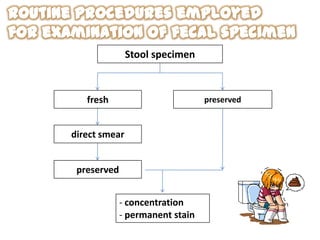
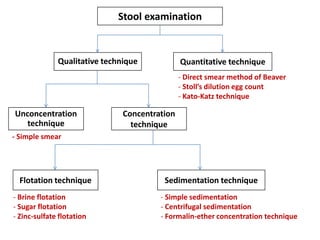
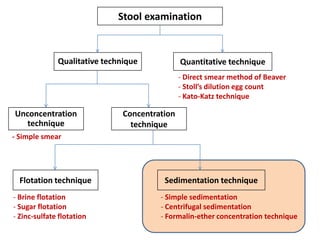
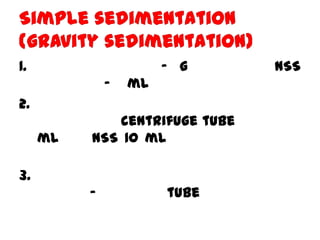
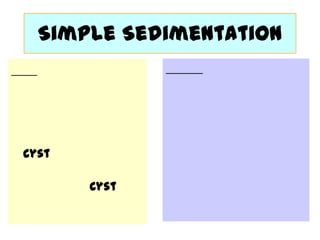
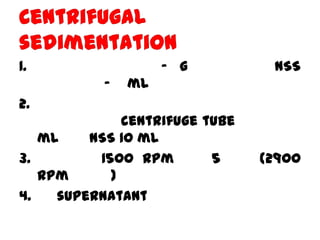
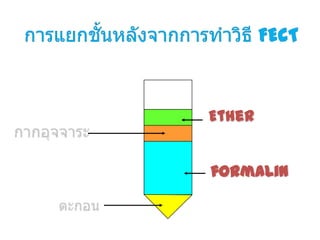
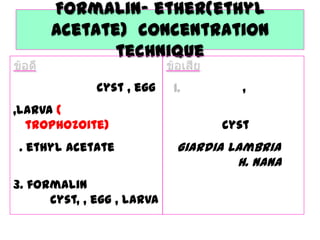
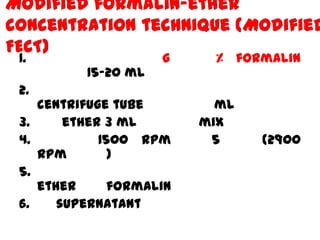
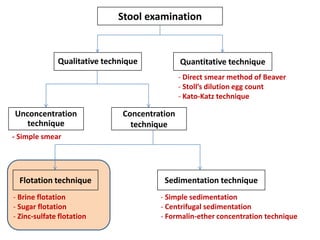
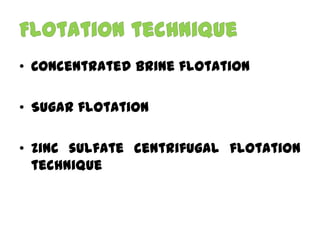
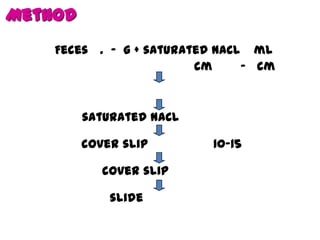
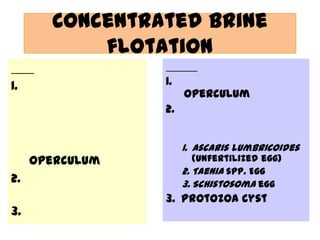
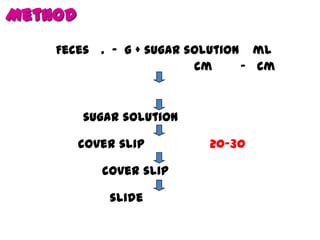
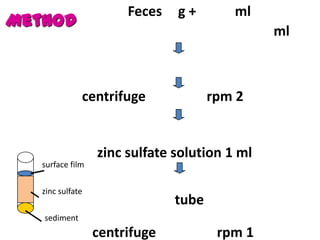
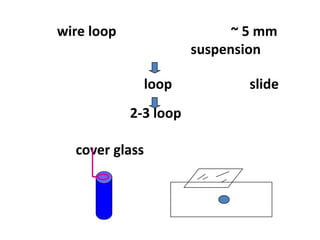
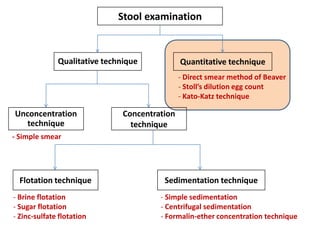
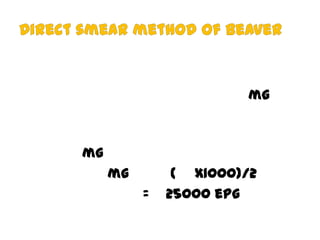
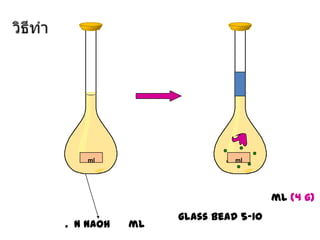
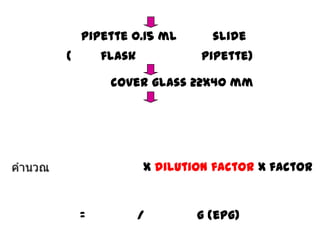
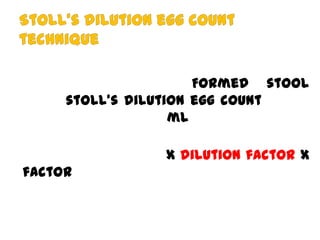
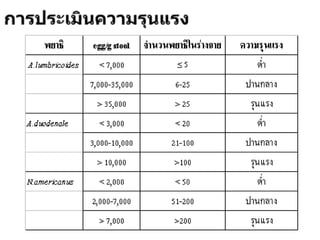
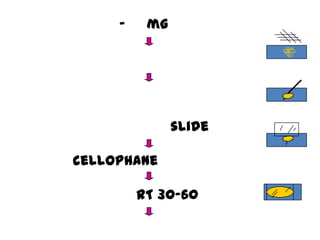
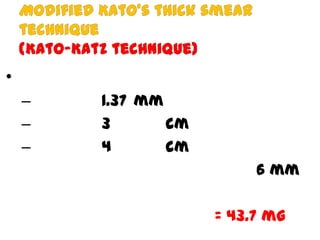
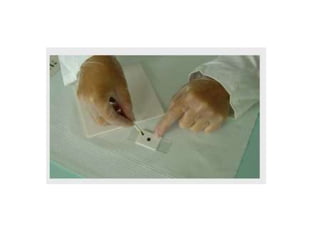
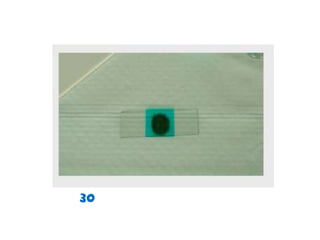
The document discusses techniques for stool examination including qualitative and quantitative methods. For qualitative examination, simple smear and Kato-Katz techniques are described. Quantitative methods include Stoll's dilution egg count and Kato-Katz technique. The Kato-Katz technique involves pressing a fixed amount of stool (typically 41.7 mg) through a cellophane filter, then examining the filter under a microscope to identify and count parasites. Concentration techniques like sedimentation, flotation in brine, sugar solution, or zinc sulfate are used to detect parasites that may otherwise be missed on direct smear.