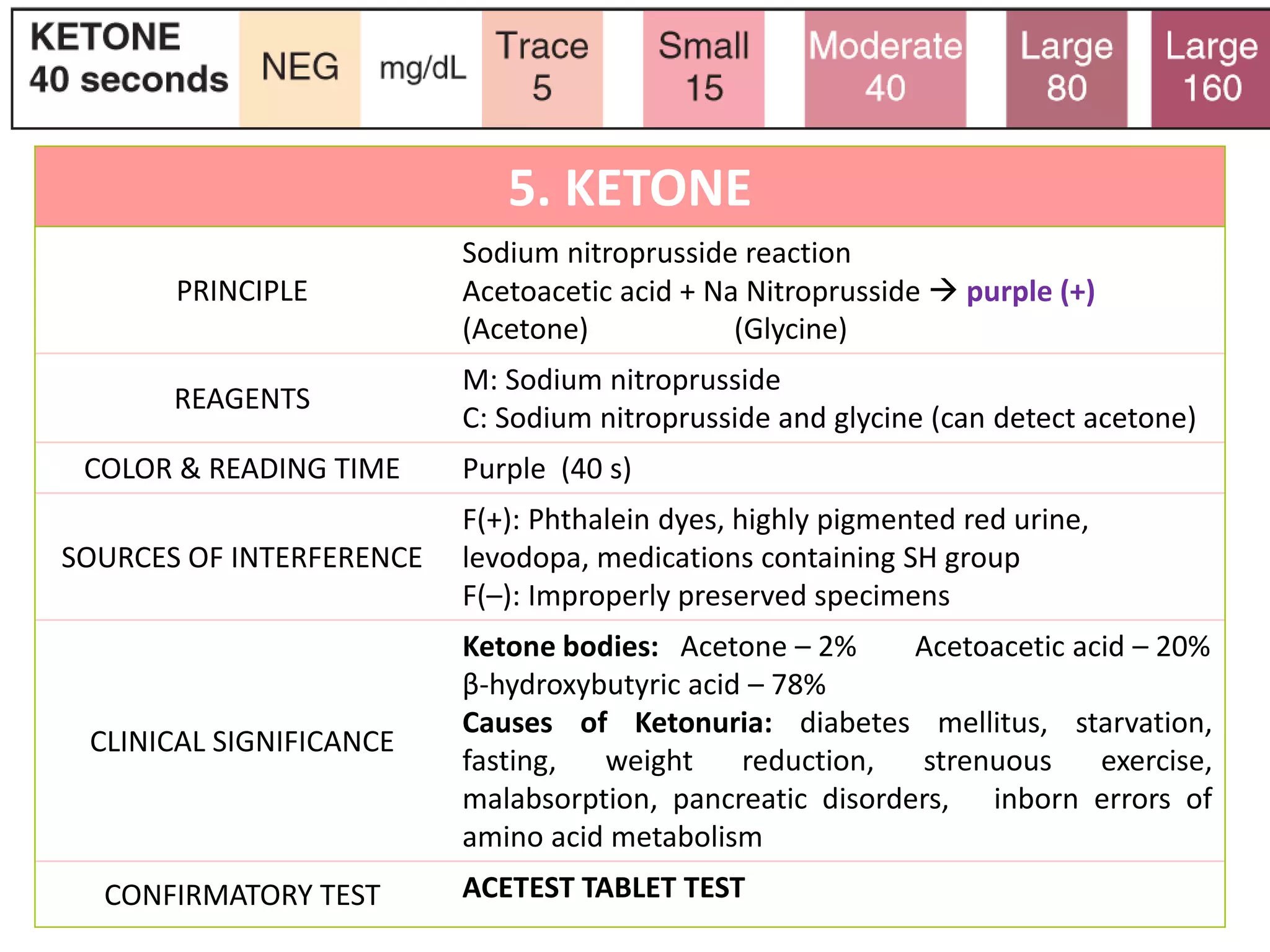
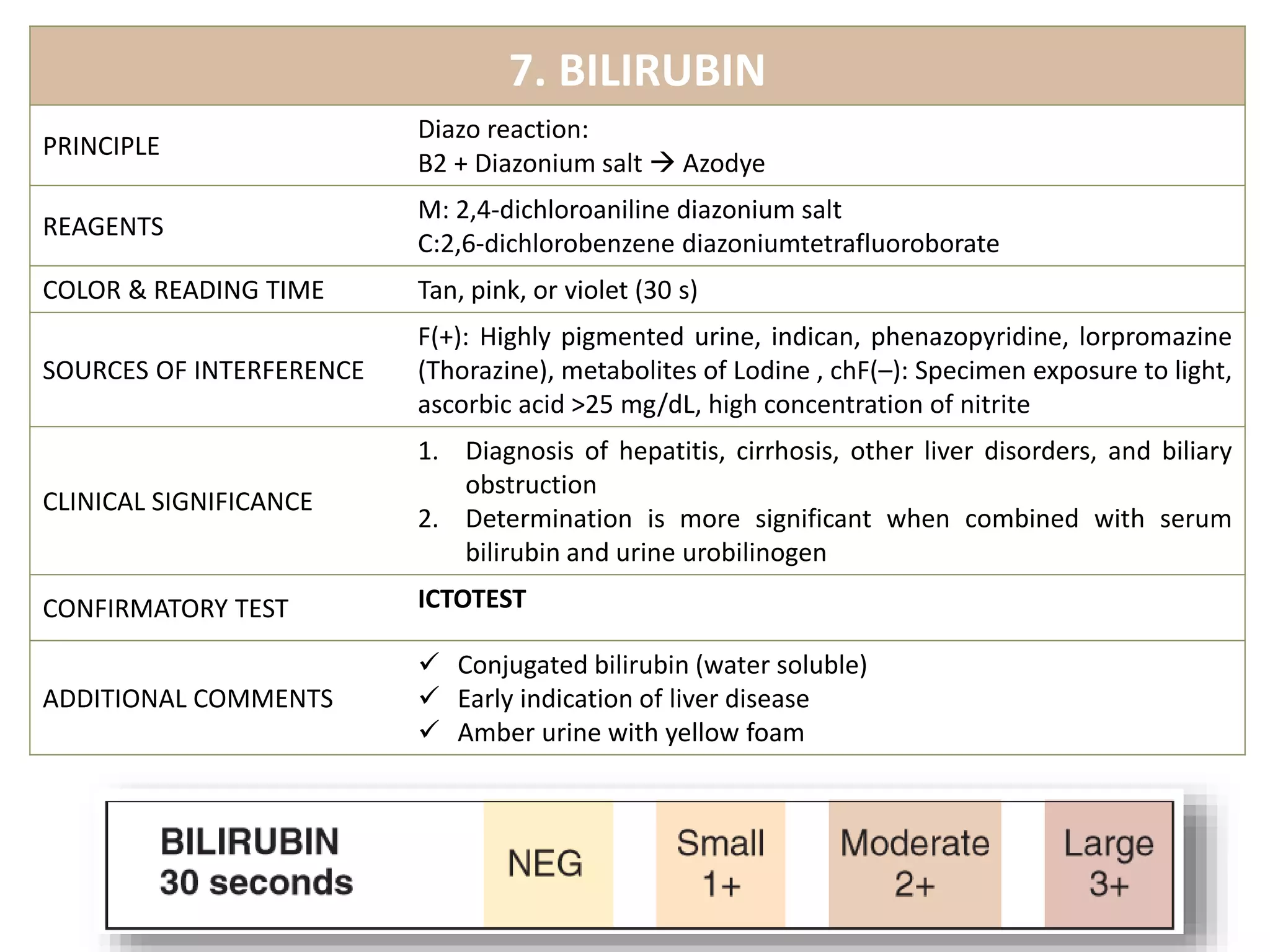
This document provides information on urine analysis tests, including specific gravity, pH, protein, glucose, ketone, blood, and bilirubin. It describes the principle, reagents, expected colors, sources of interference, and clinical significance of each test. The tests can be used to detect and monitor various conditions like diabetes, kidney disease, urinary tract infections, and more. Proper interpretation requires correlating the urine test results with the patient's symptoms and medical history.