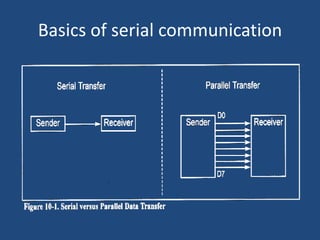
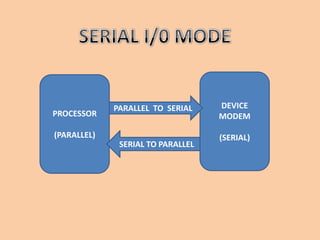
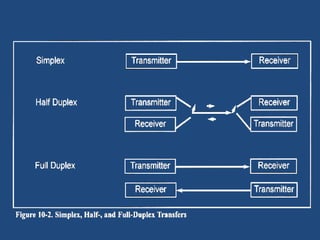
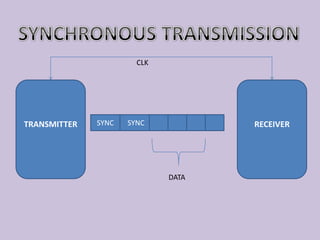
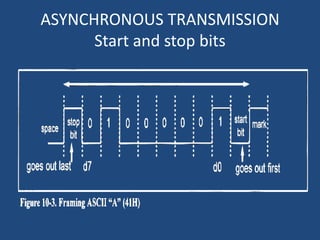
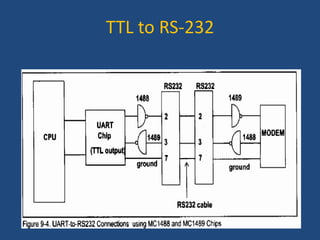
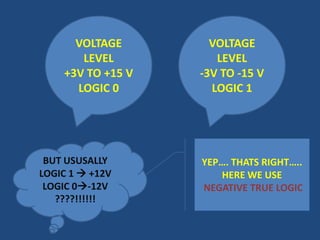
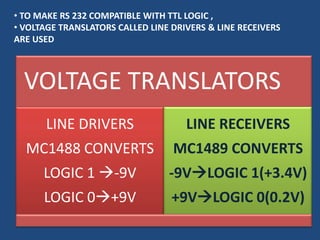
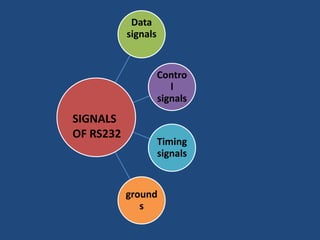
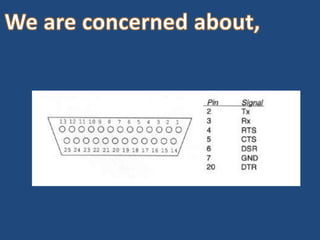
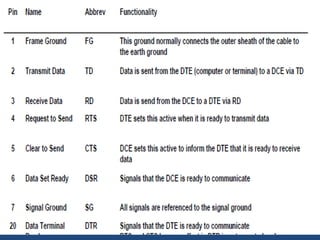
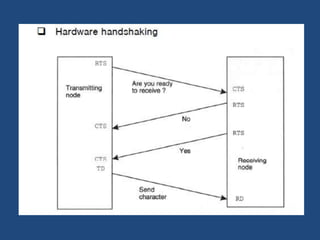
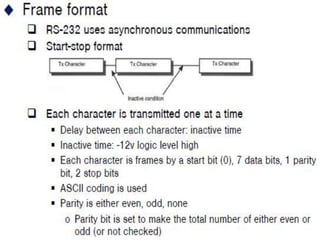
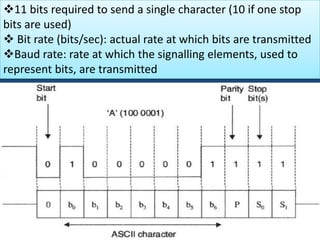
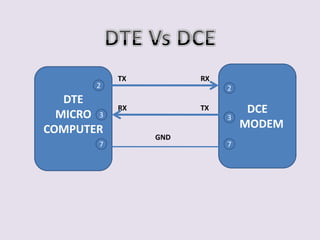
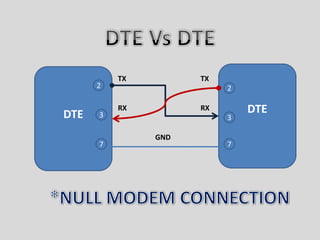
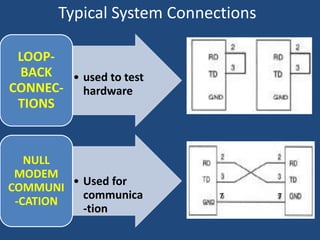
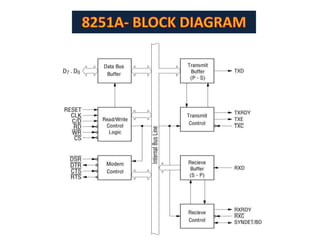
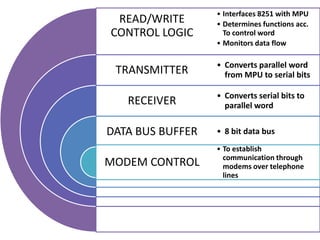
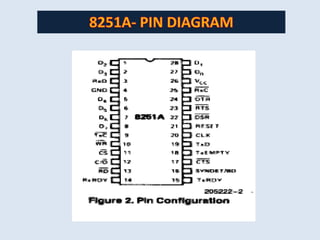
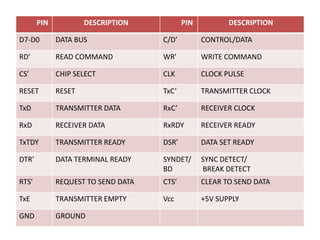
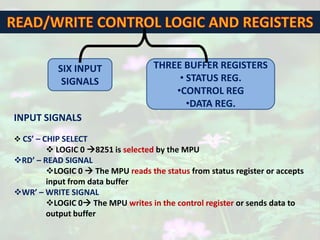
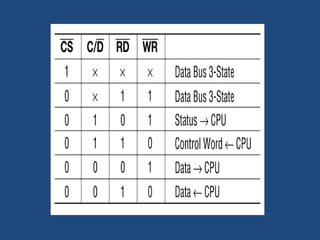
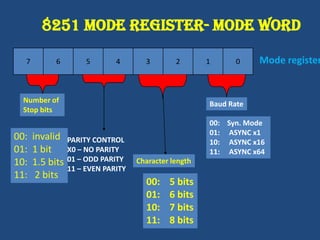
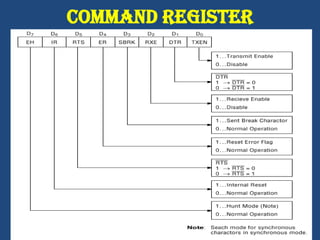
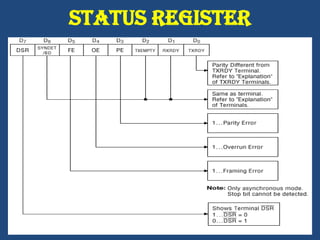
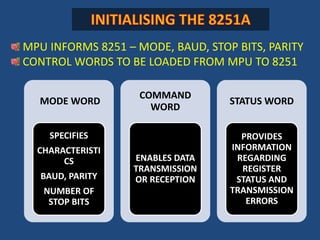
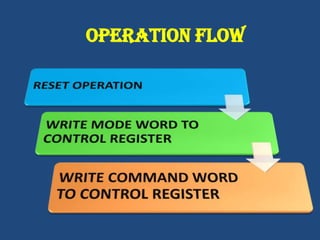
This document discusses serial communication using the 8085 microprocessor and 8251A USART chip. It describes the basics of synchronous and asynchronous serial transmission including start/stop bits and framing. It provides details on the RS-232 serial interface standard including voltage levels, connectors, and DTE/DCE roles. The 8251A USART chip is explained in detail, including its block diagram, pinout, registers for control, status, and data, and how it converts parallel to serial and vice versa. Modes of operation and initialization of the 8251A are also covered.