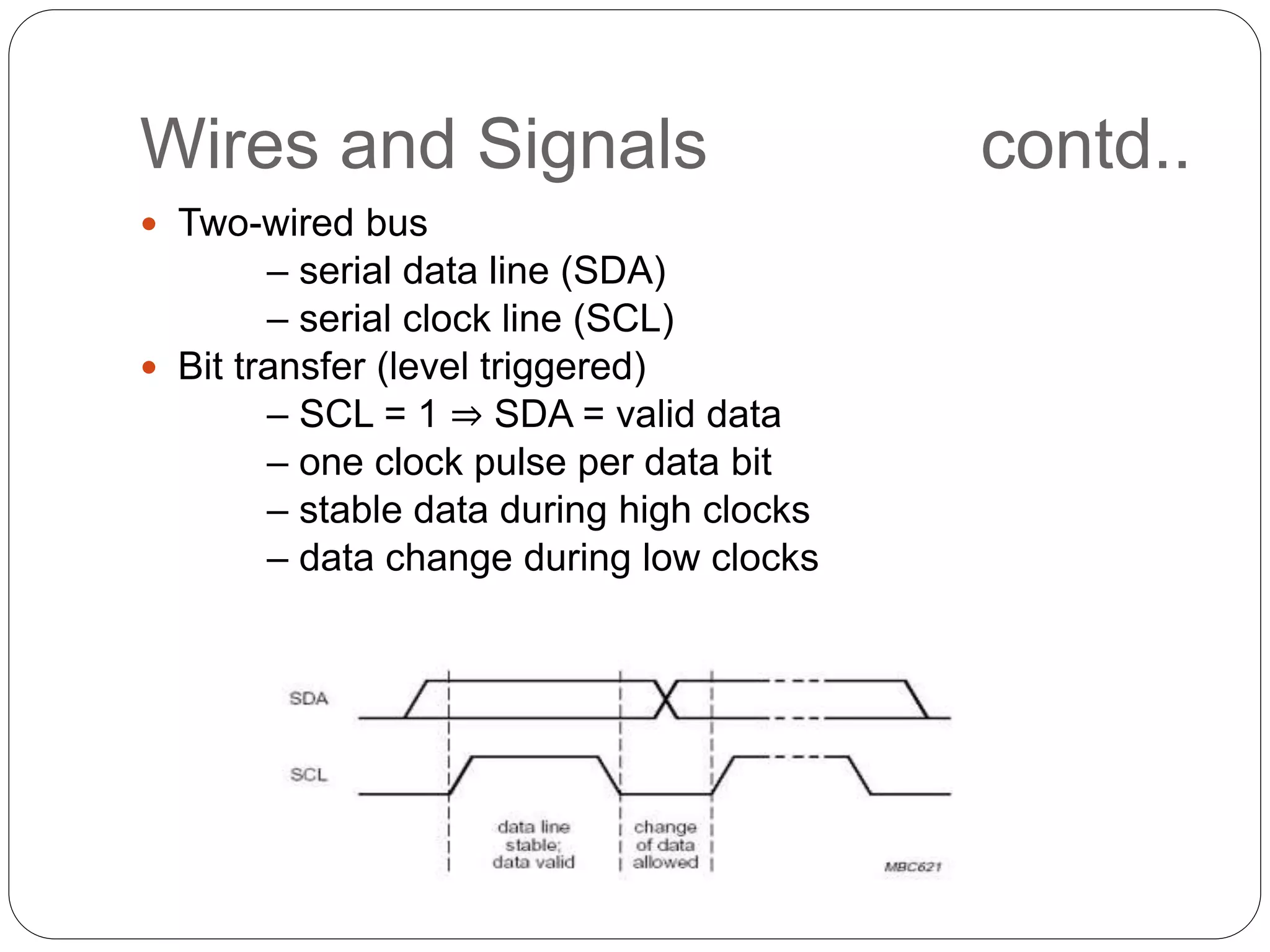
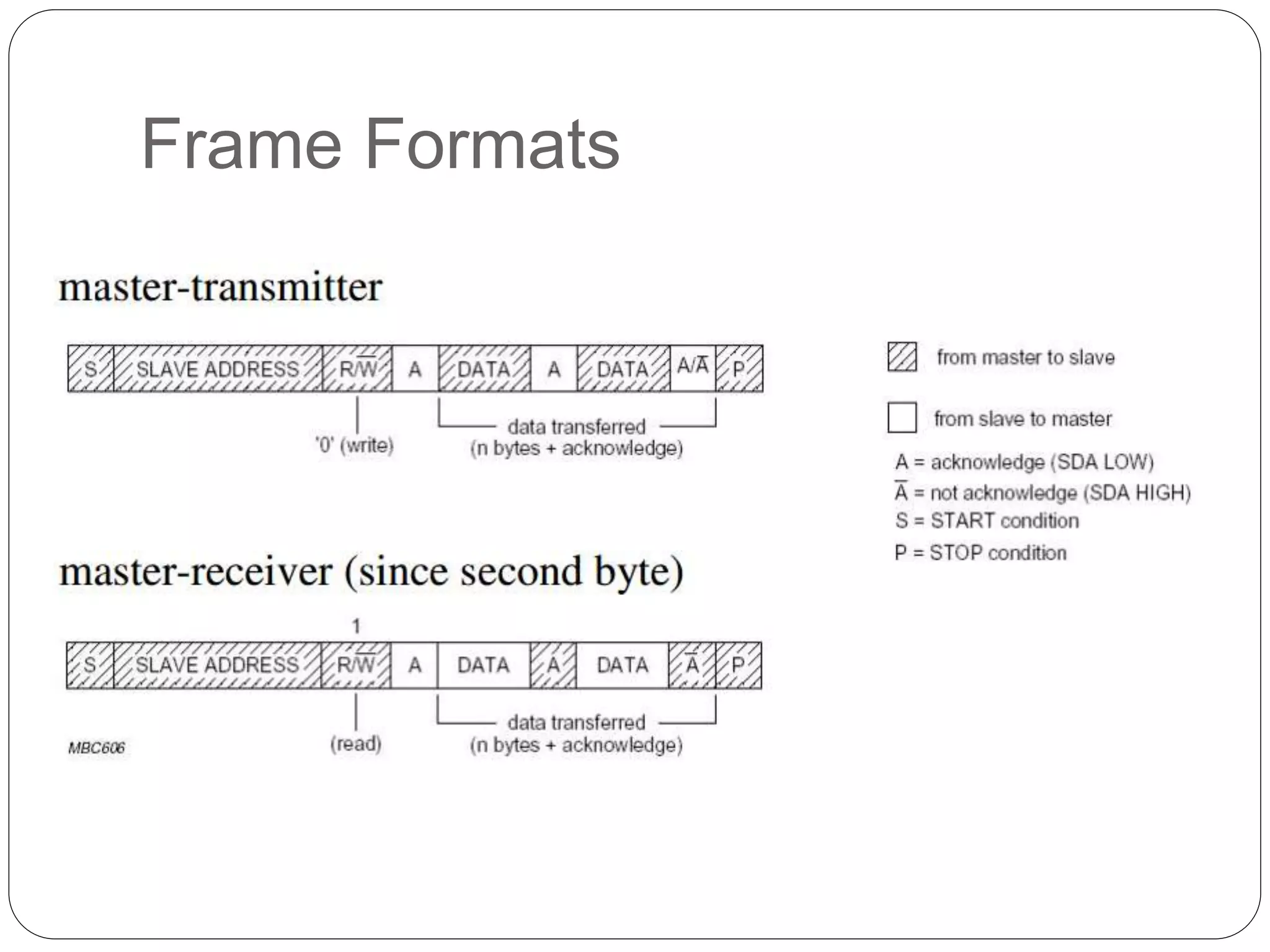
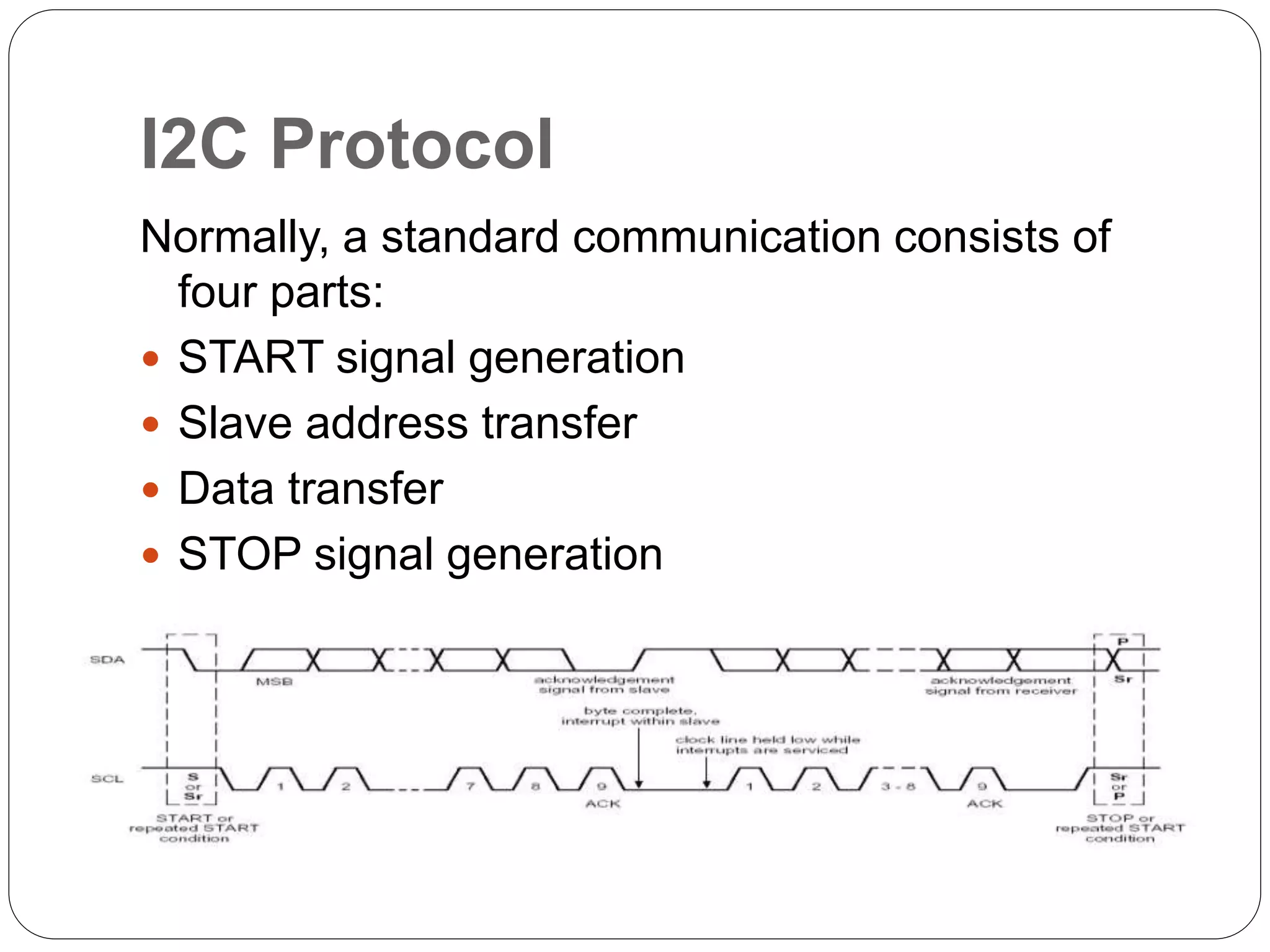
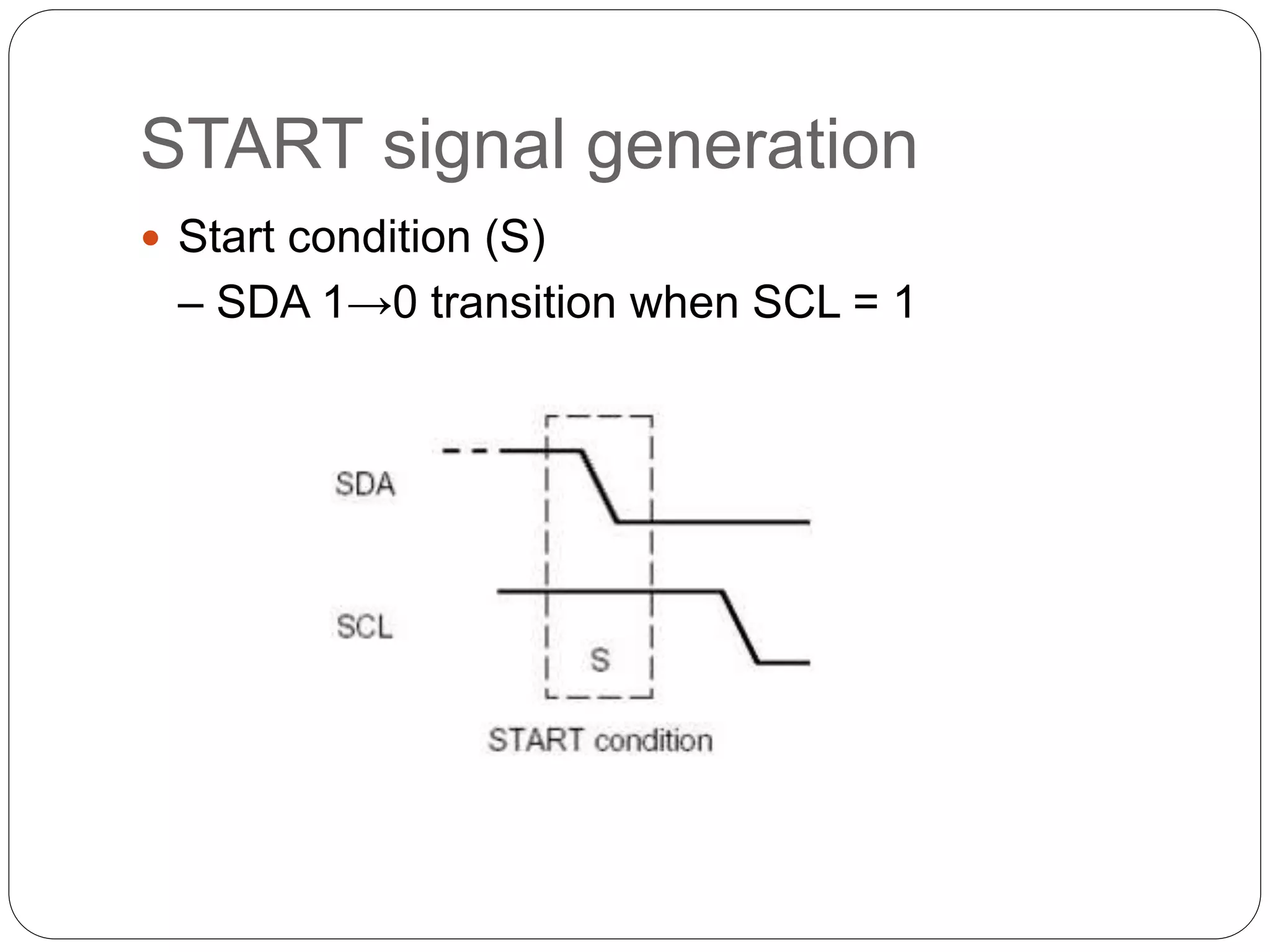
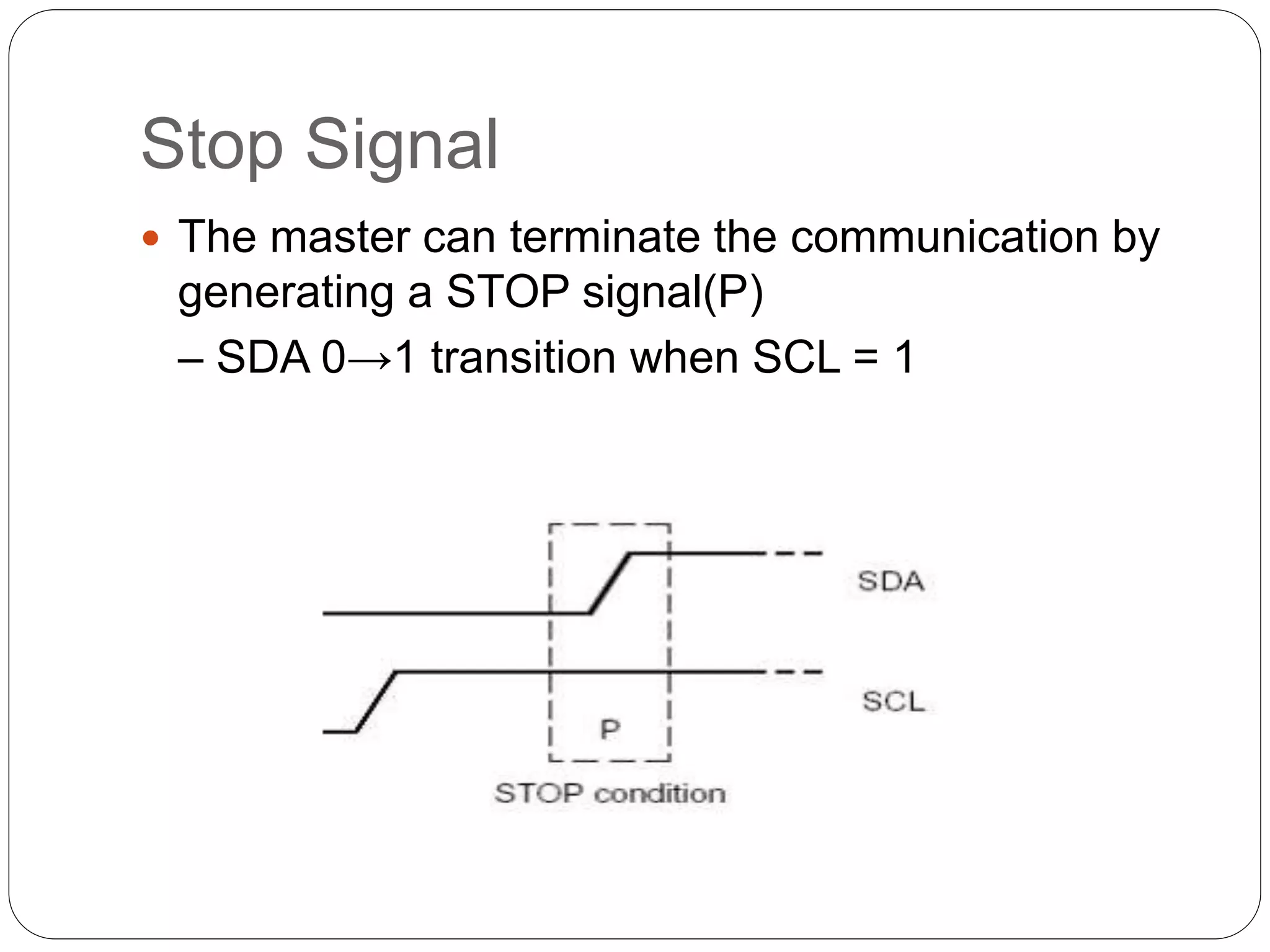
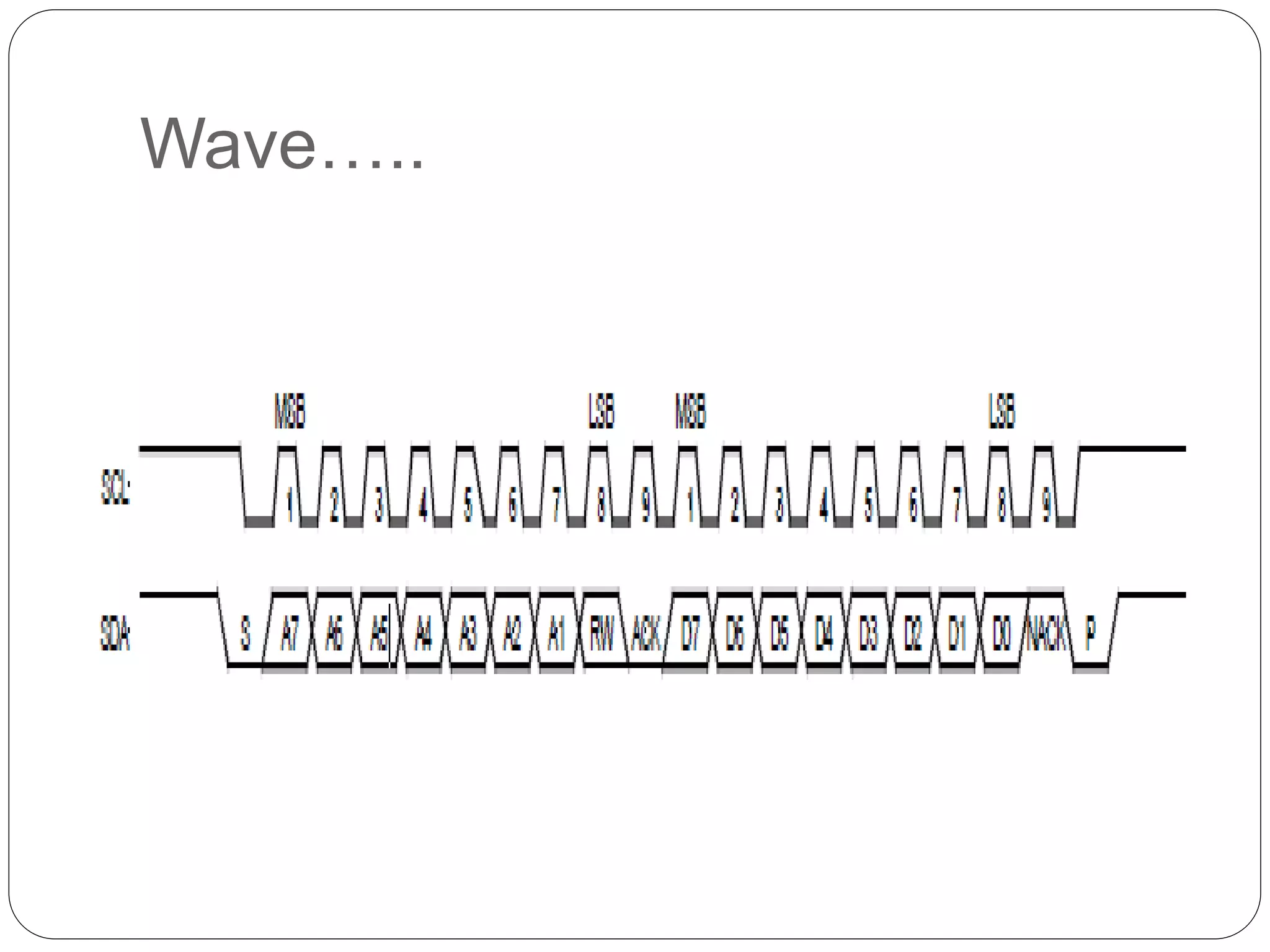
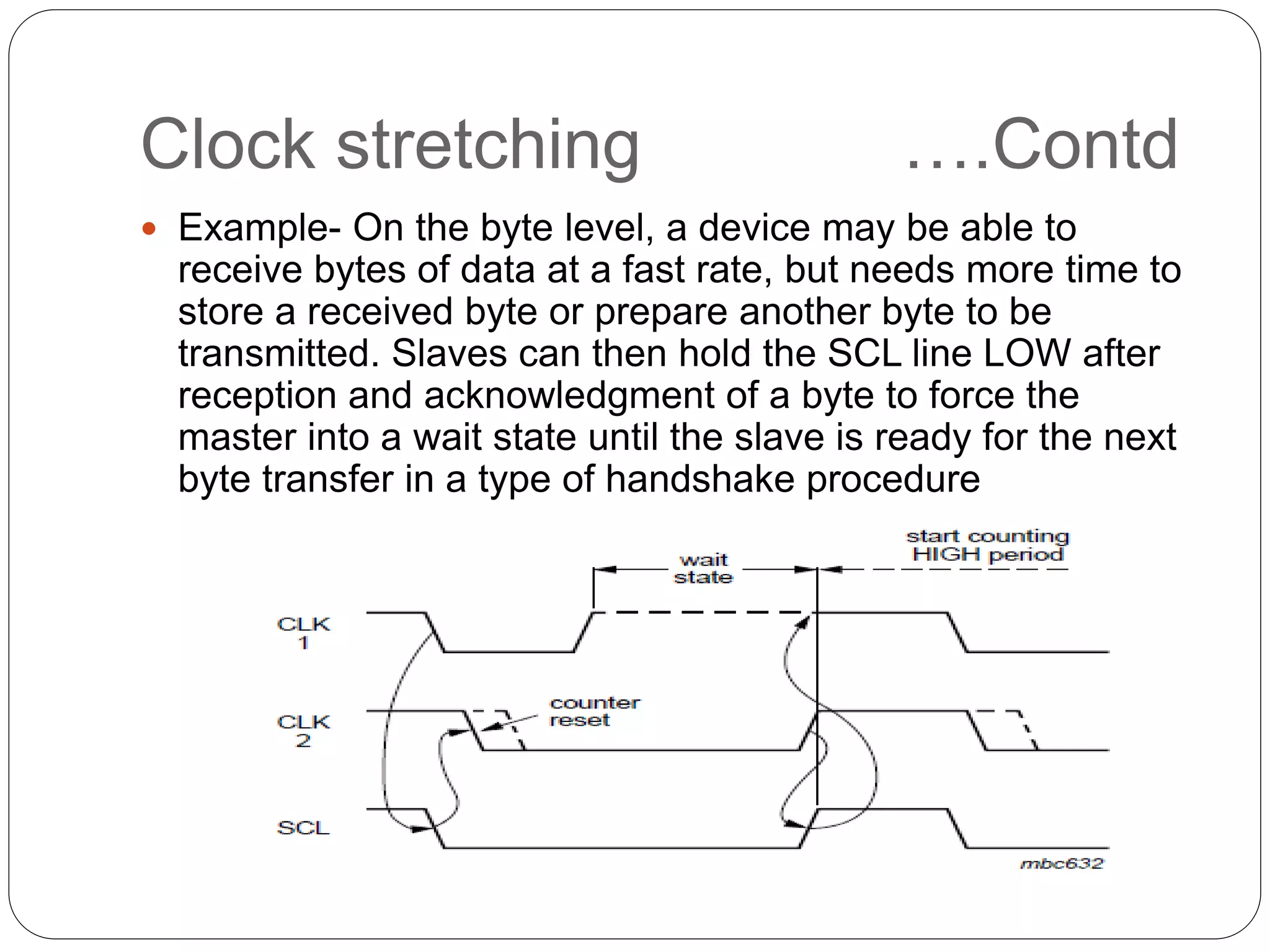
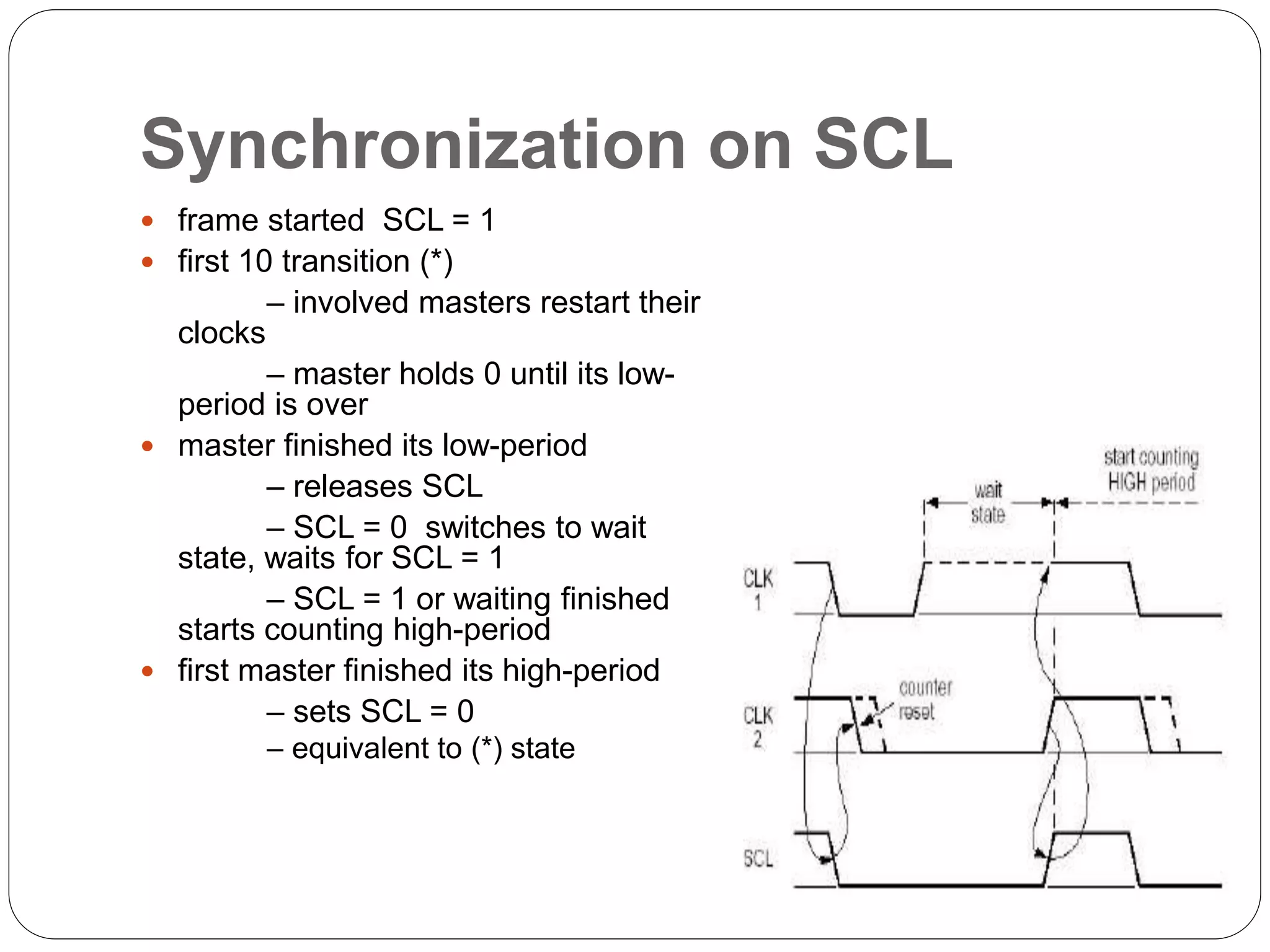
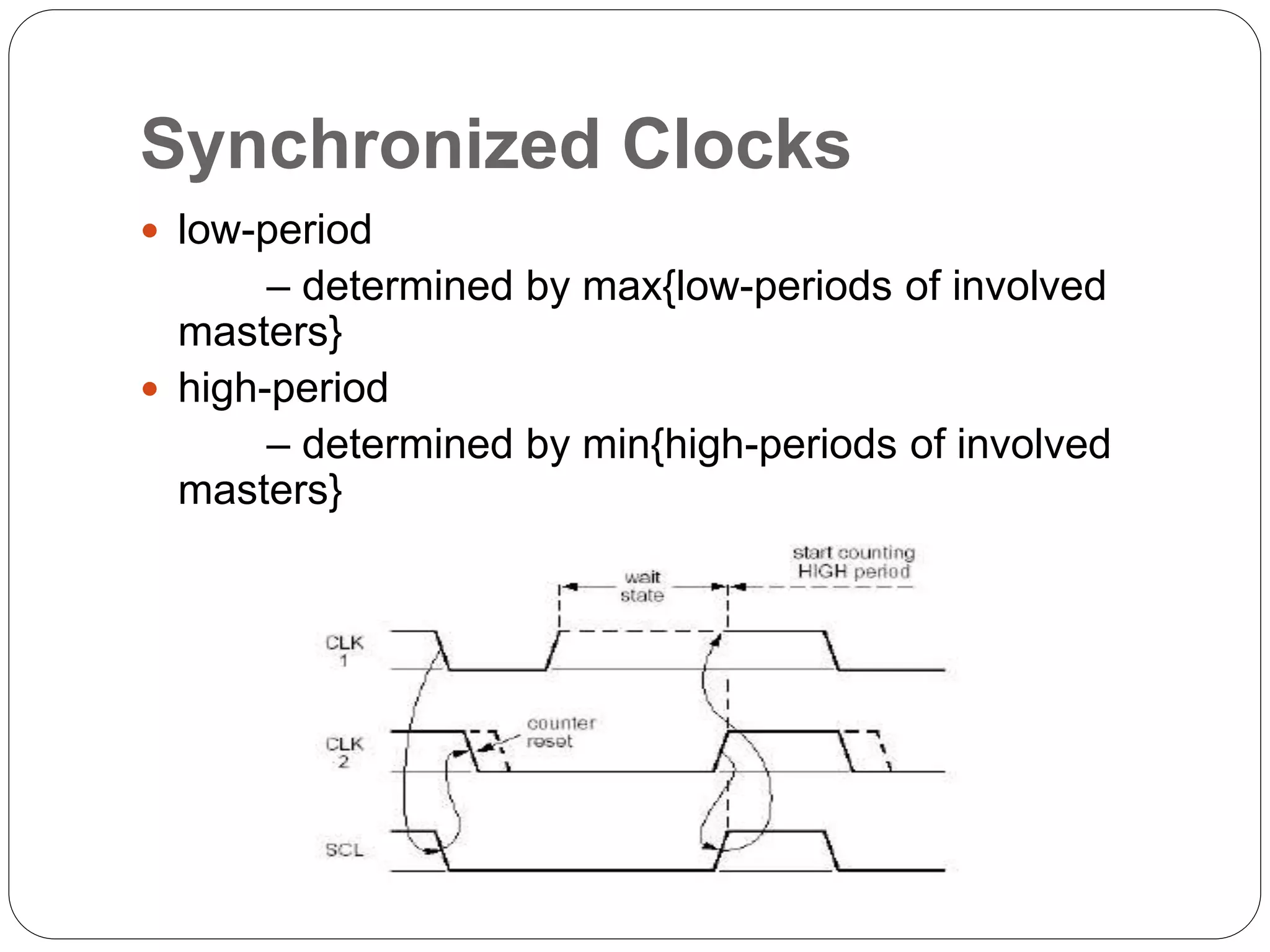
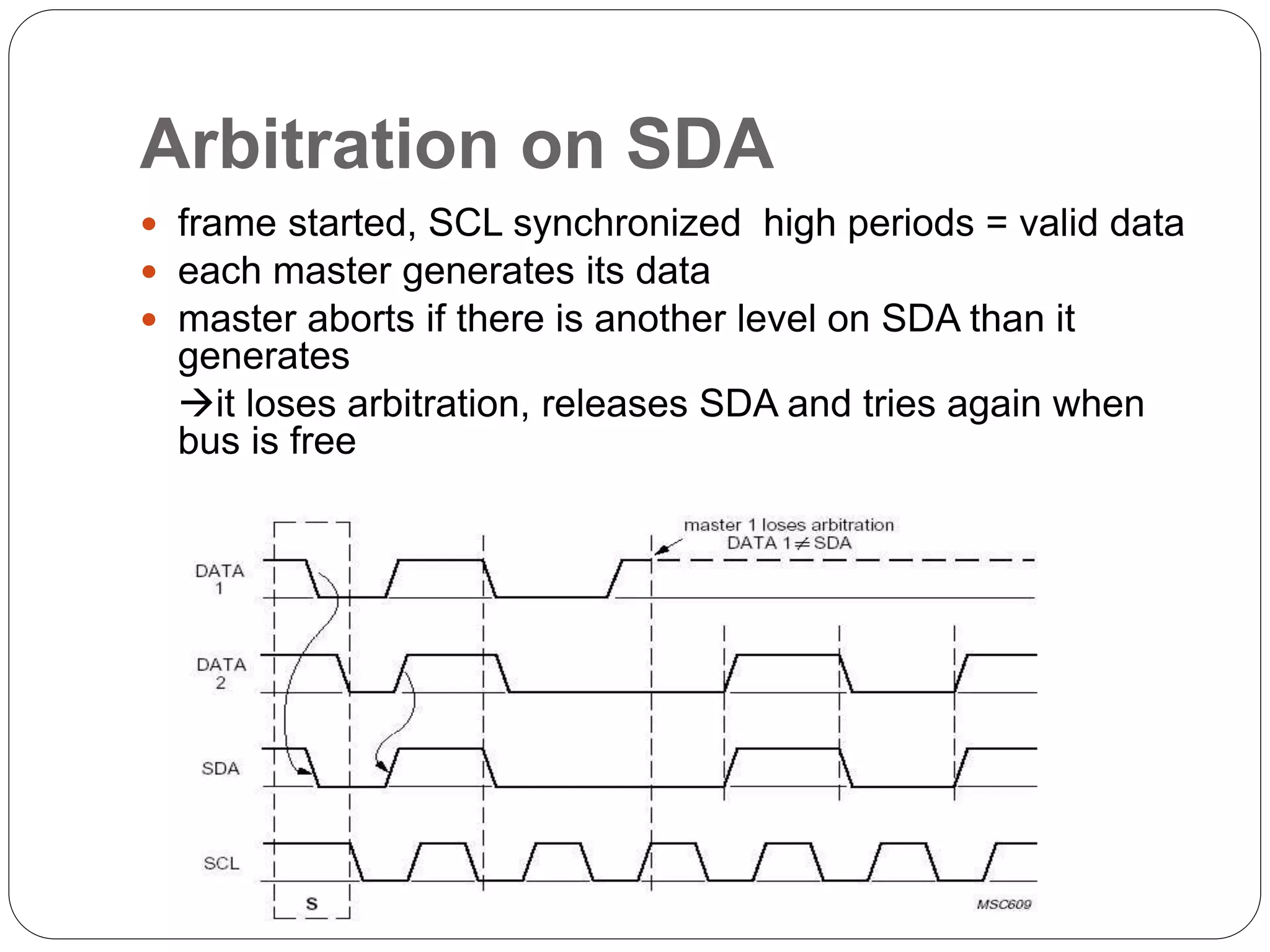
This document summarizes the key characteristics and protocol of the I2C bus, which is a serial communication protocol used in embedded systems. It operates at speeds up to 5Mbps and uses just two bidirectional open-drain lines: a serial data line and a serial clock line. The I2C protocol uses a master-slave architecture, where the master device initiates data transfers by sending a start signal and addressing a slave device to read or write data. Transfers use 7 or 10-bit addressing and are acknowledged by the slave after each byte. The protocol supports multiple masters that must synchronize clocks and arbitrate access to the data line.