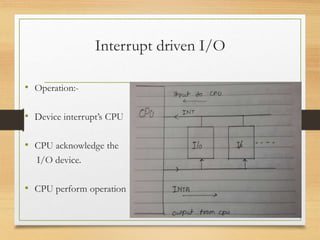
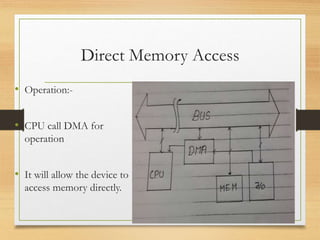
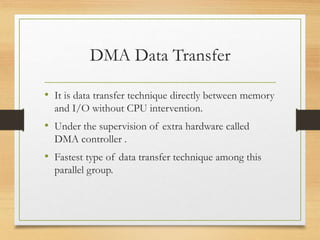
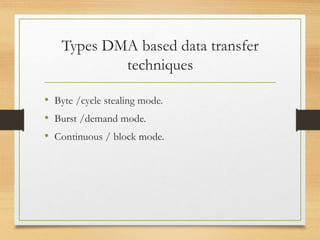
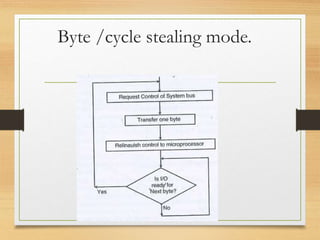
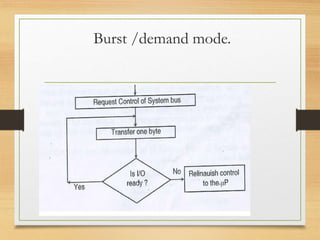
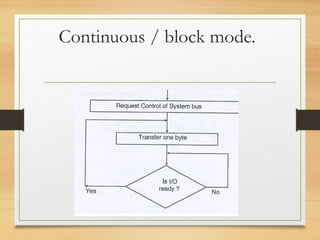
This document discusses different types of data transfer modes between I/O devices and memory, including programmed I/O, interrupt-driven I/O, and direct memory access (DMA). It explains that DMA allows I/O devices to access memory directly without CPU intervention by using a DMA controller. The basic operations of DMA include the DMA controller gaining control of the system bus, transferring data directly between memory and I/O devices by updating address and count registers, and then relinquishing control back to the CPU. Different DMA transfer techniques like byte stealing, burst, and continuous modes are also covered.
![Types of data transfer mode
• Programmed I/O
• Interrupt driven I/O
• DMA (Direct Memory Access)
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/directmemoryaccess-160909142945/85/Direct-memory-access-2-320.jpg)





![Questions
1) Q. Write short note on DMA/programmed i/o and
interrupt i/o?
M[15]
2) Q. Explain in brief DMA data transfer techniques
with diagram?
M[10 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/directmemoryaccess-160909142945/85/Direct-memory-access-15-320.jpg)
