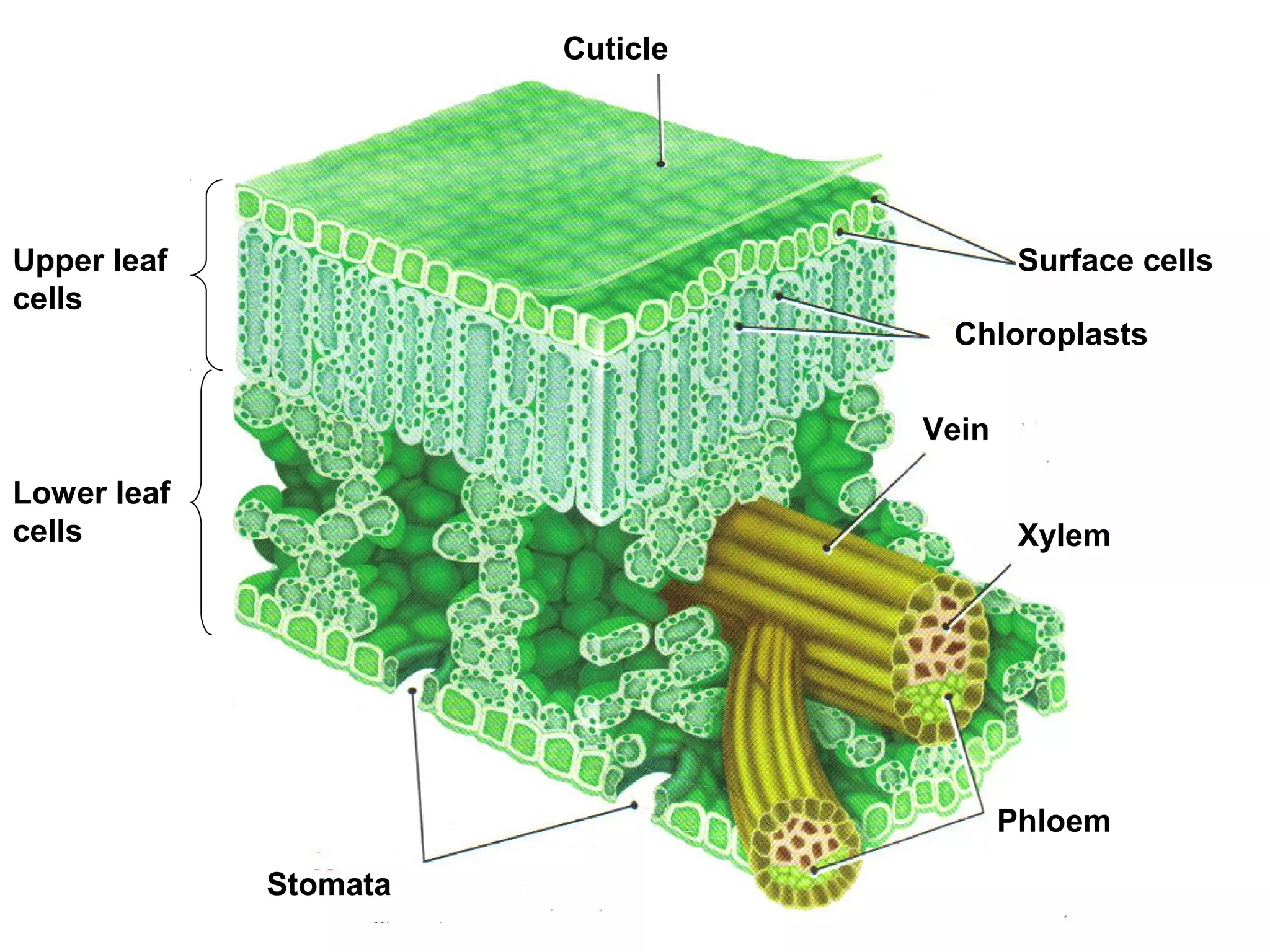
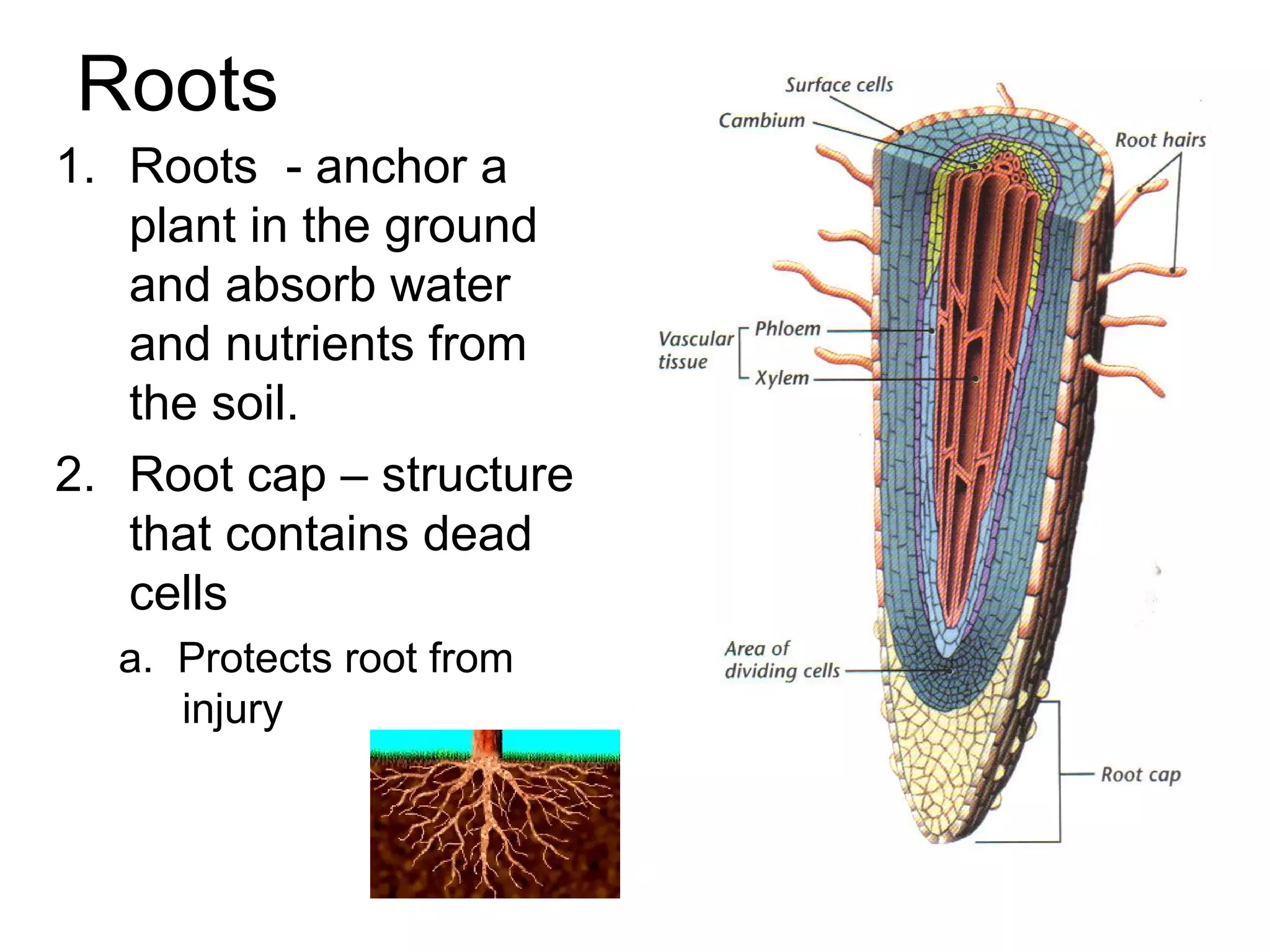
Seed plants have three main characteristics: 1) they have vascular tissue that transports nutrients and water throughout the plant, 2) they reproduce using seeds, and 3) they have a complex life cycle involving sporophytes and gametophytes. Seeds contain an embryo, stored food, and a protective seed coat. The embryo develops into a new plant, the stored food nourishes the embryo's growth, and the seed coat protects these parts. Leaves capture sunlight for photosynthesis, stems transport nutrients and provide structure/support, and roots anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients.