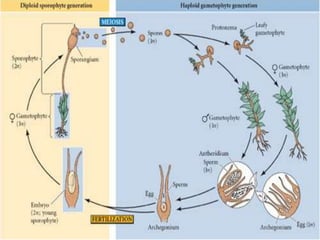
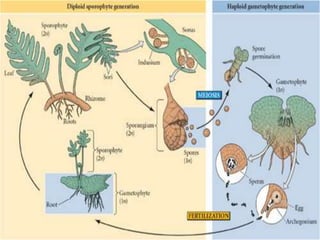
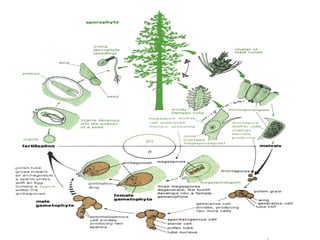
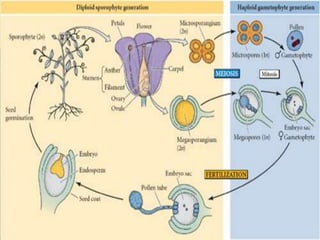
Vascular plants evolved adaptations for survival on land such as obtaining and preserving water. Seed-bearing plants were most successful with adaptations like producing seeds that could be dispersed independently of water. Gymnosperms were the first seed-bearing plants but had exposed seeds, while flowering plants (angiosperms) produced specialized reproductive structures called flowers and fruits to enclose and nurture seeds. Angiosperms diversified greatly and many provided benefits to humans like domesticated grains.