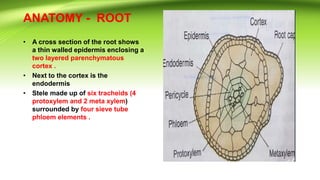
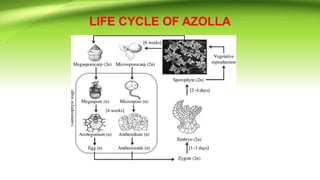
Azolla is a small floating fern that lives in freshwater. It has a symbiotic relationship with the cyanobacterium Anabaena azollae. Azolla reproduces both asexually through fragmentation and sexually through heterosporous sporocarps containing microspores or megaspores. It has several economic uses including being used as a green manure in rice paddies due to its ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen.