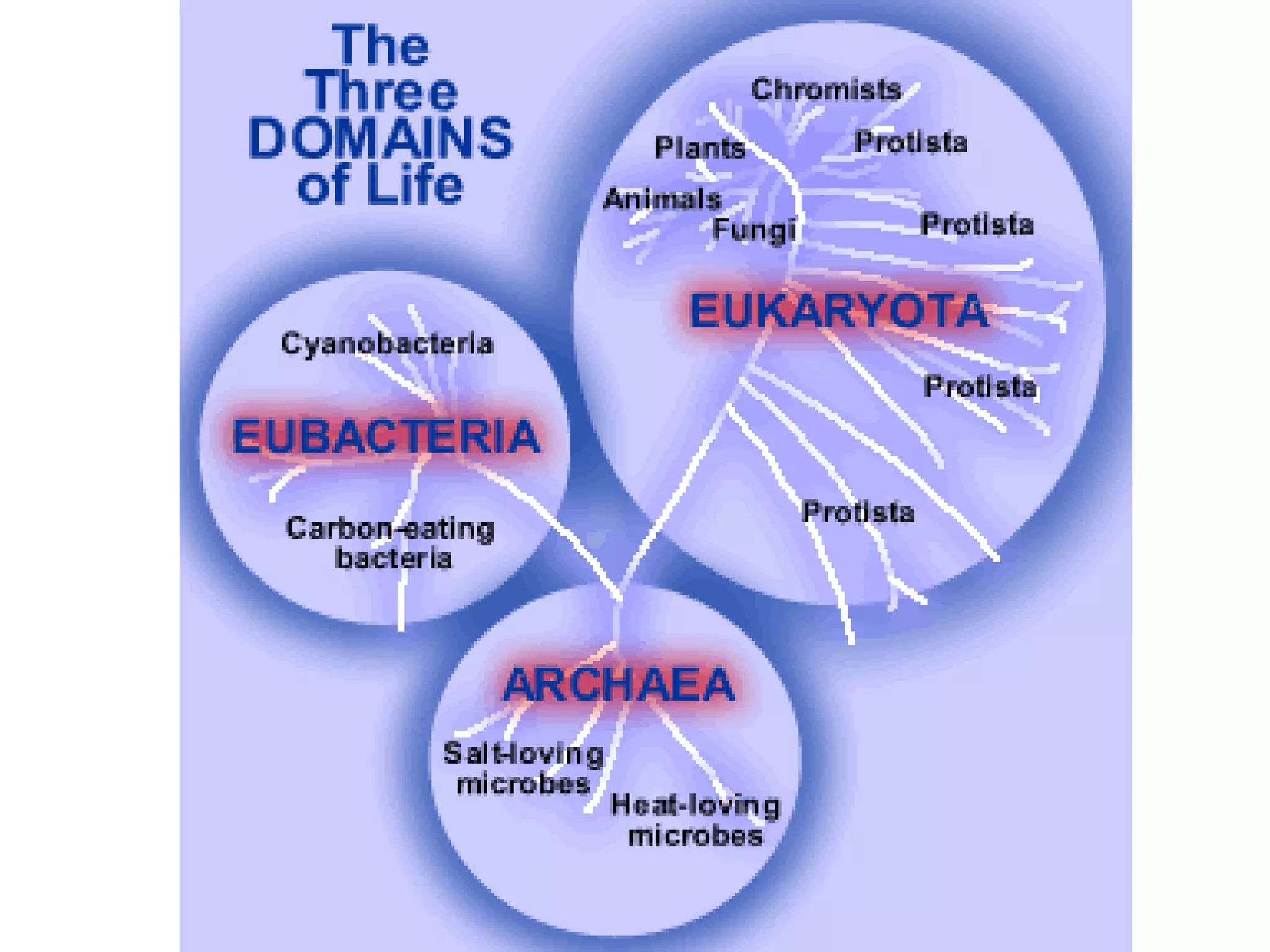
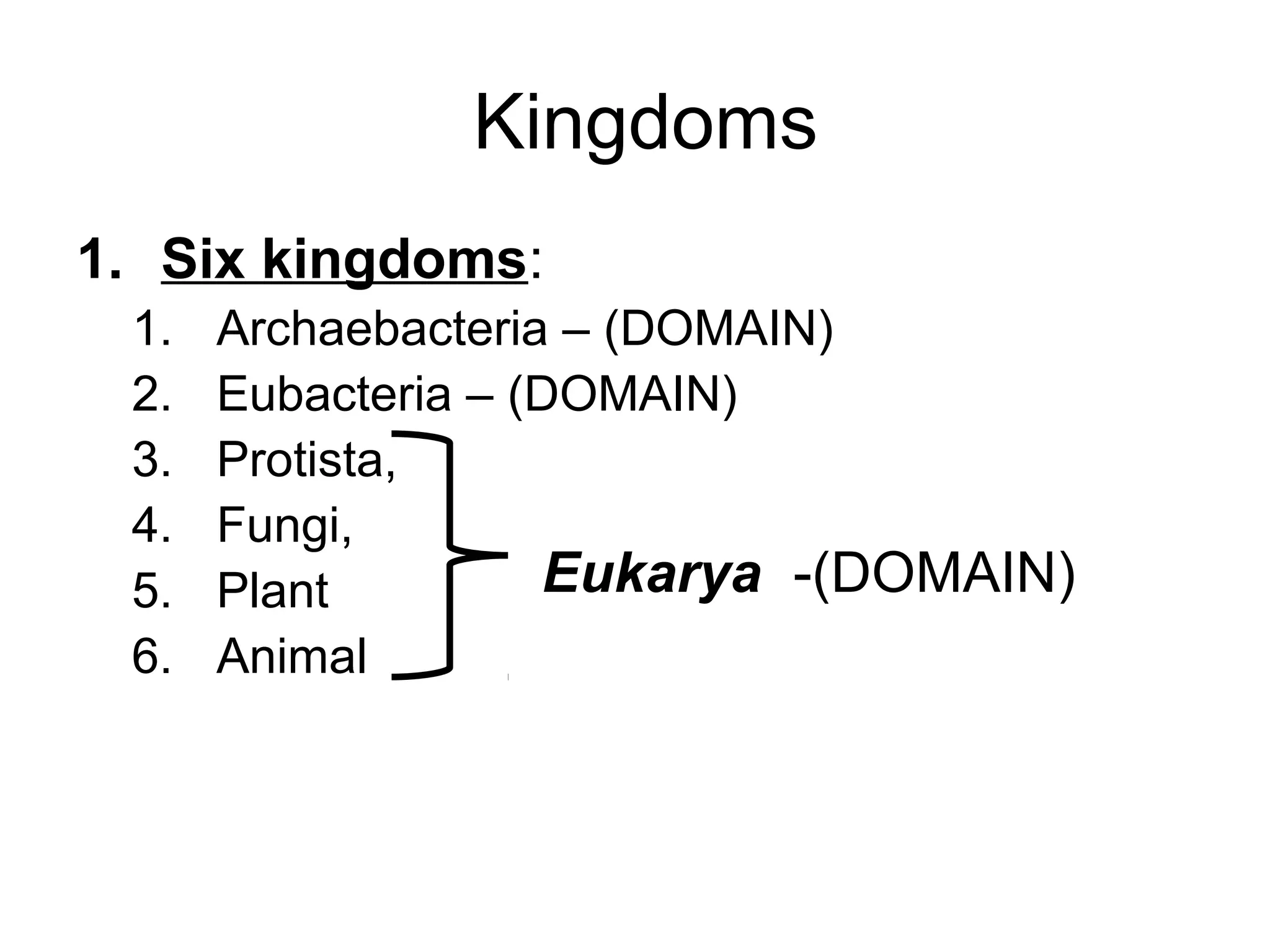
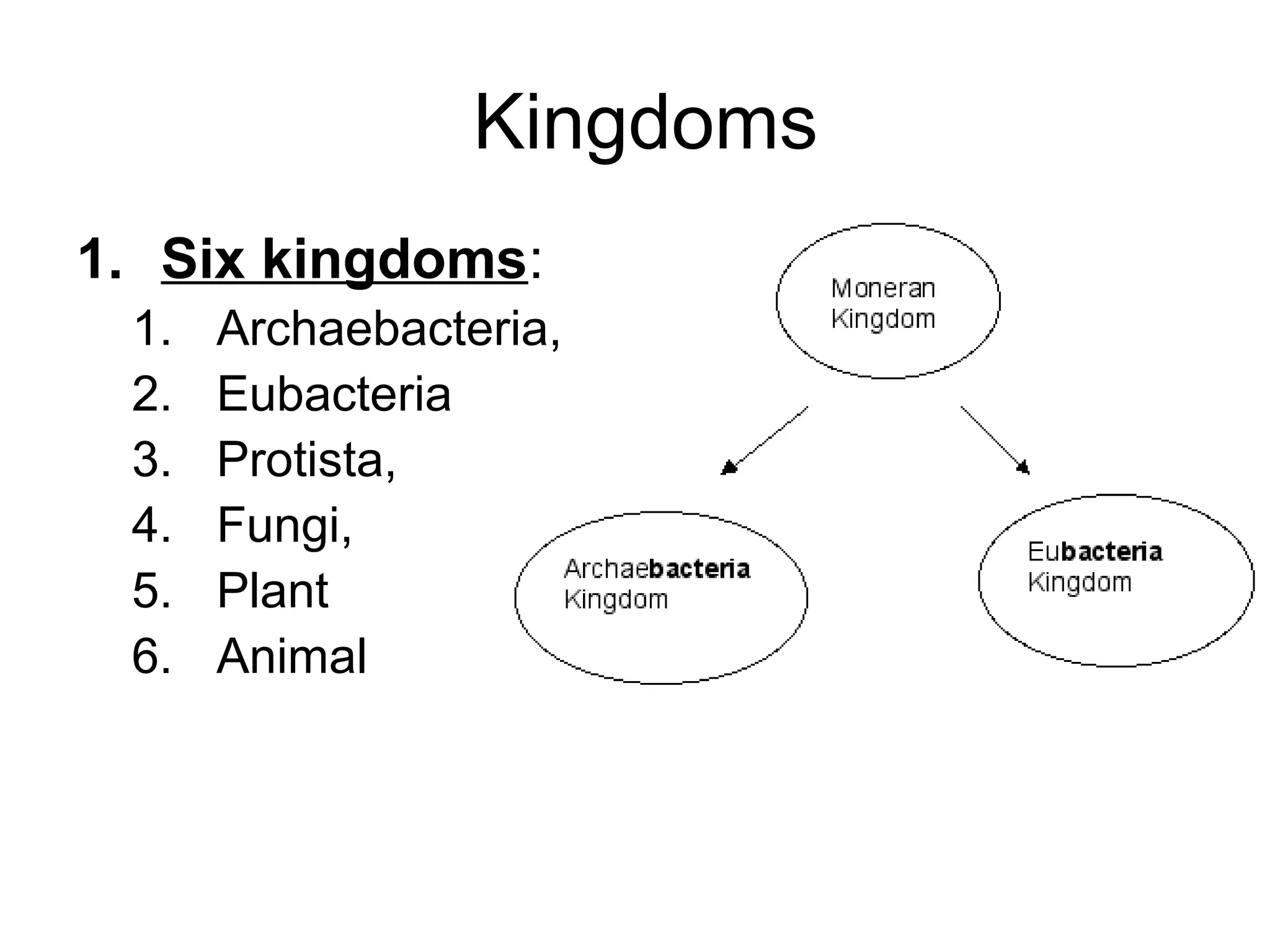
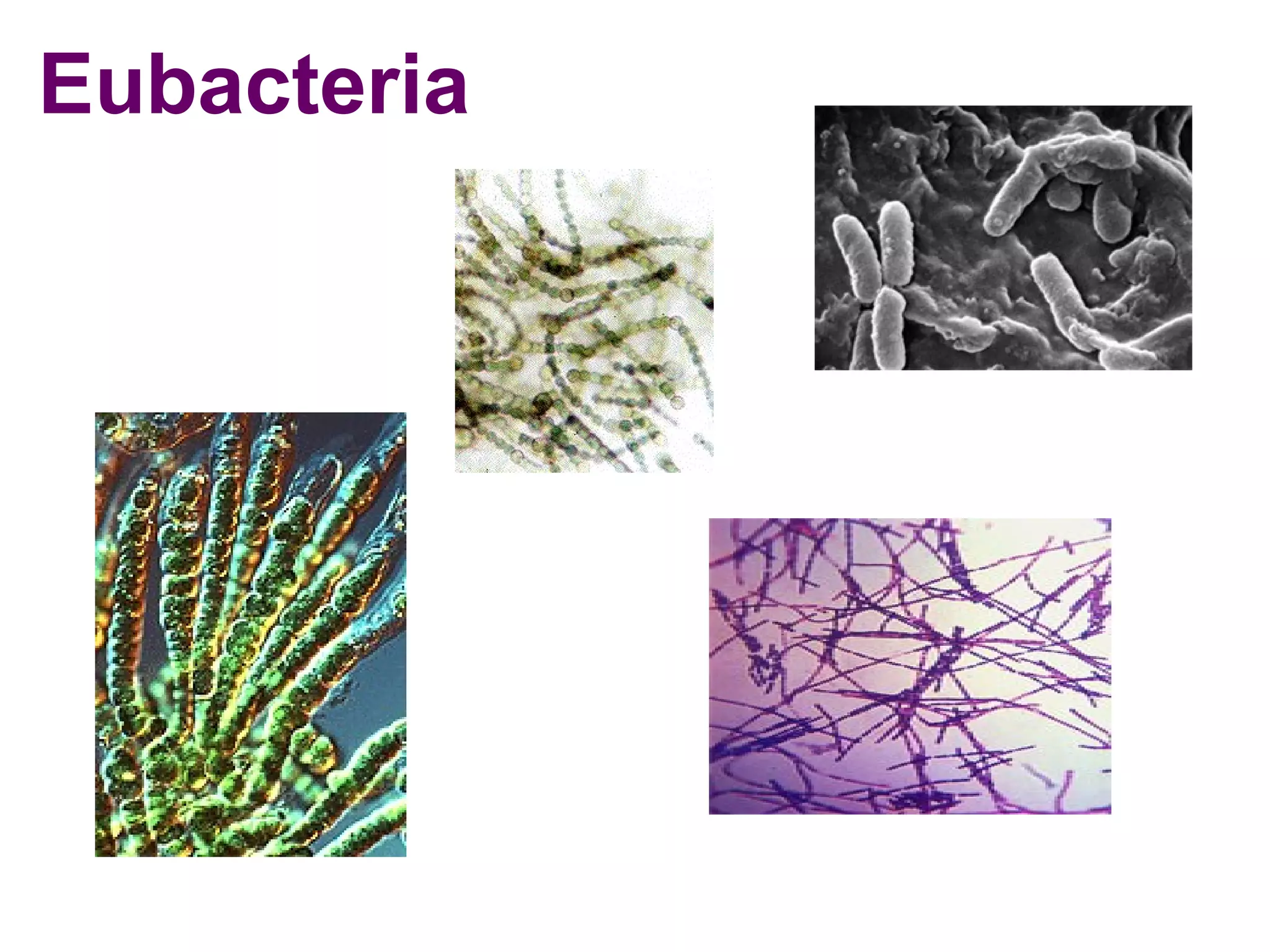
This document outlines the six kingdoms of classification: Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plant, and Animal. It provides details on the key characteristics of each kingdom, including whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, unicellular or multicellular, producers or consumers, and how they reproduce. Examples are given for each kingdom, such as archaebacteria living in extreme environments, eubacteria including decomposer bacteria, protista including algae and amoebas, fungi being decomposers like mushrooms and mold, plants being producers that undergo photosynthesis, and animals being able to move and being consumers.