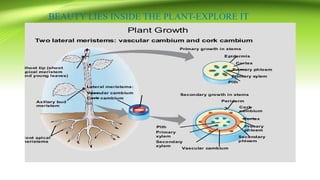
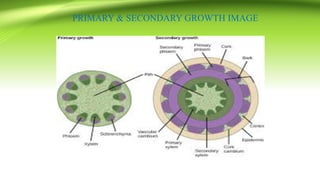
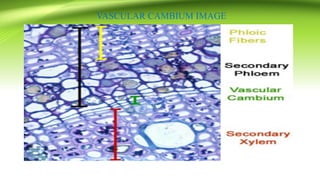
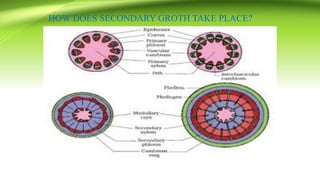
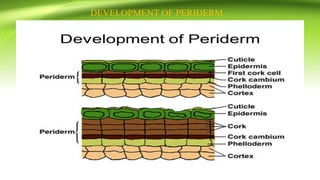
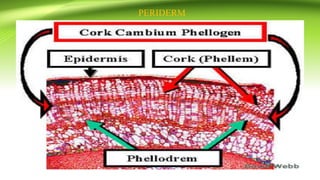
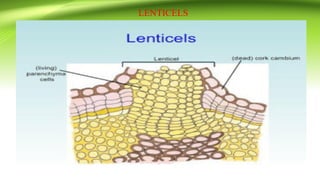
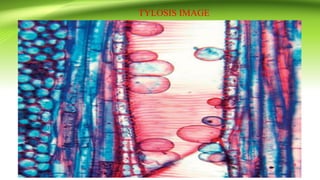
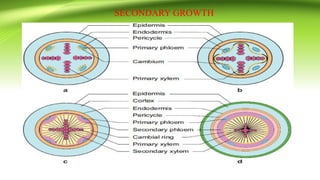
The document discusses plant anatomy with a focus on secondary growth in dicot stems and roots, detailing the processes of cambial activity and the formation of various tissues. It explains the differences between intrastealer and extrastealer growth, the development of periderm as protective tissue, and the types of wood including spring and autumn wood. Additionally, it touches upon various characteristics of hardwood and softwood, along with the significance of annual growth rings and their use in determining plant age.