Embed presentation
Downloaded 44 times

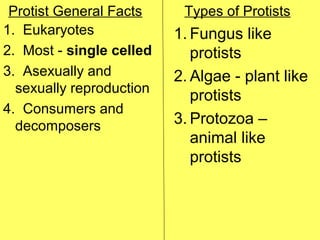


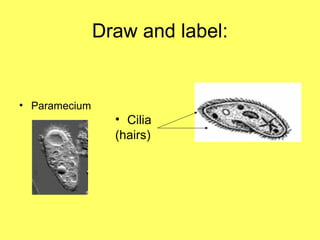
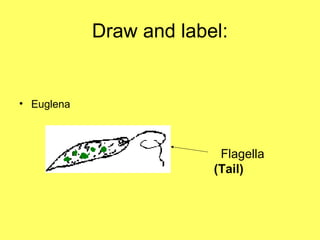
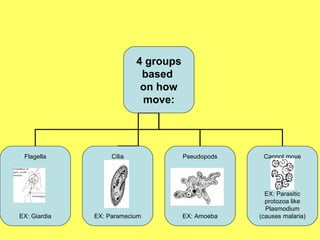



Protists are eukaryotic organisms that are mostly single-celled and can reproduce both sexually and asexually. They are decomposers and consumers. There are three main groups of protists: fungus-like protists, plant-like protists called algae, and animal-like protists called protozoa. Protozoa move using flagella, cilia, pseudopods, or they cannot move if they are parasitic. Some disease-causing protists are Giardia, which causes diarrhea, and Plasmodium, which is carried by mosquitoes and causes malaria.









