Embed presentation
Downloaded 32 times
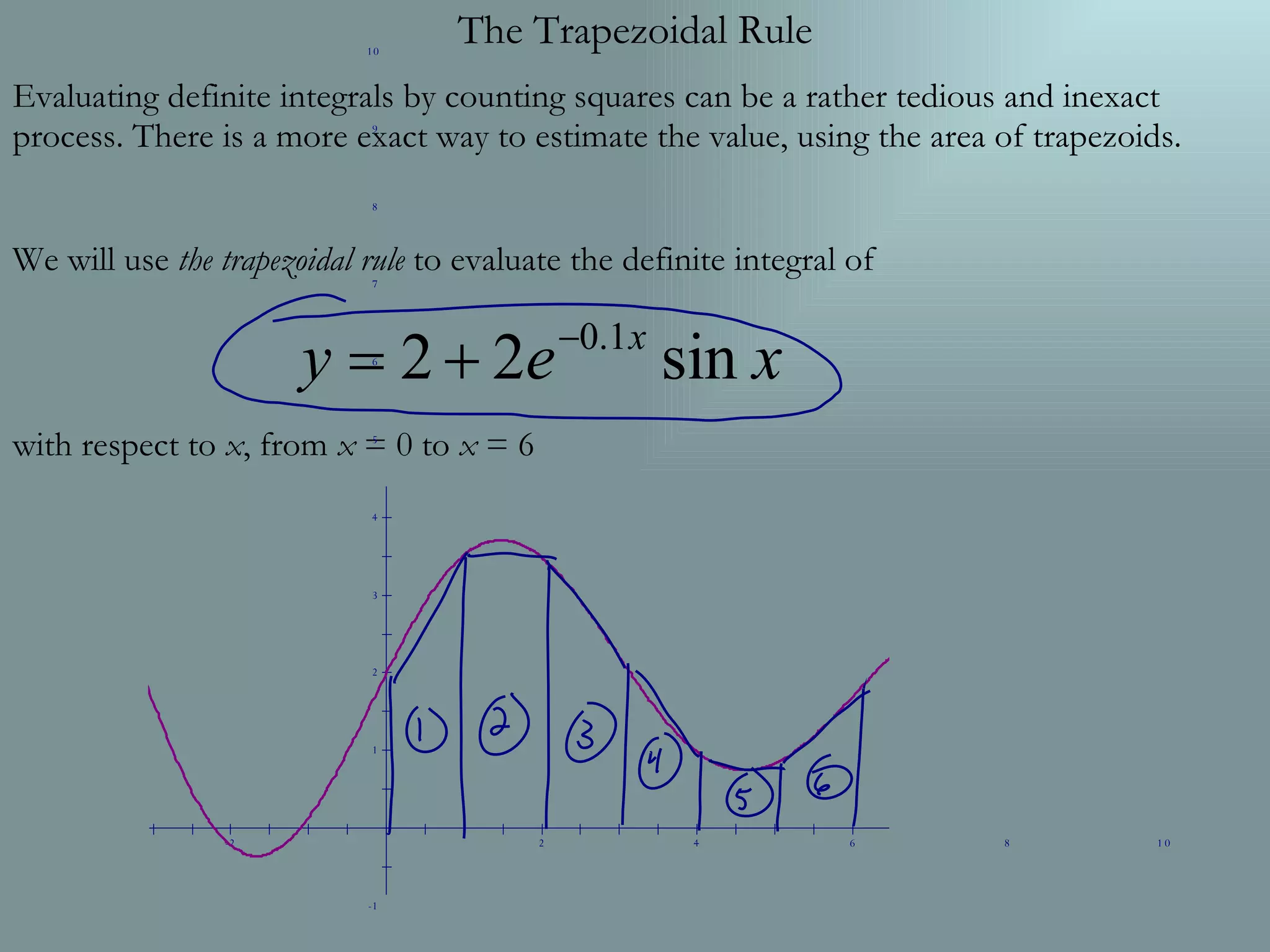
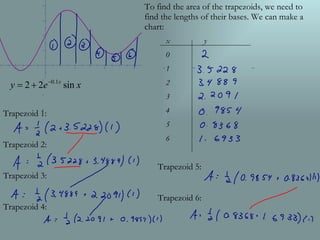


The document discusses using the trapezoidal rule to evaluate definite integrals by approximating the area under a curve between bounds with trapezoids. It explains that the trapezoidal rule is a more exact method than counting squares. To use the rule, the integral bounds are divided into trapezoids, the function is evaluated at the endpoints, and the areas are calculated by multiplying the average base by the height and summing the results, with endpoints weighted by one half.



