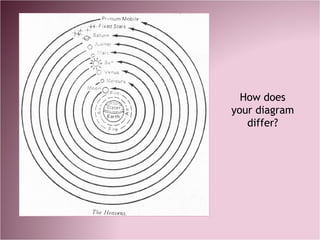
The Scientific Revolution began in the 17th century and marked a shift from the medieval worldview to a new scientific method. Key developments included Copernicus proposing a heliocentric solar system, Galileo providing evidence for it through telescope observations, and Kepler discovering the laws of planetary motion. Newton then published laws of motion and universal gravitation, explaining the motions of the heavens. This transition required challenging old assumptions through experimentation and reason, establishing science as the new path to understanding the natural world.