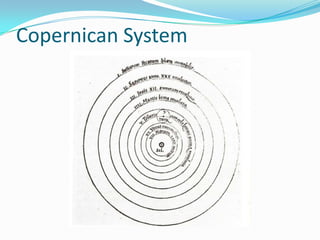
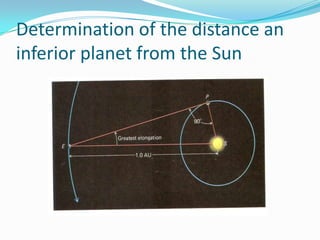
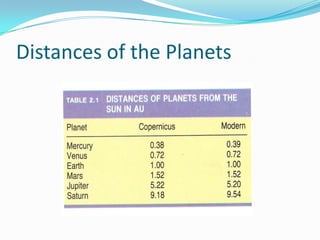
Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543) was a Polish astronomer who proposed a model of the solar system in which the Sun is at the center and the Earth and planets orbit around it. This contradicted the prevailing Ptolemaic system where Earth was the center. Copernicus published his theory, called the Copernican or heliocentric system, in 1543 in his book On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres. Although not widely accepted in his lifetime, Copernicus' model eventually replaced the Ptolemaic system as the accepted astronomical model.