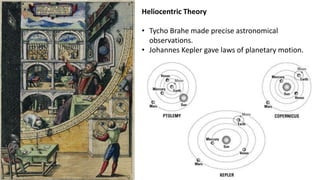
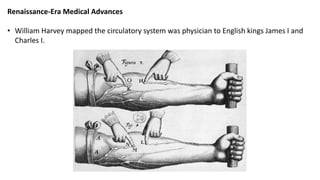
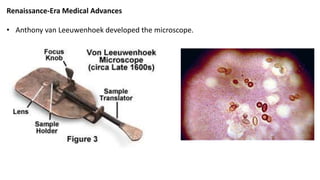
The Scientific Revolution began in the late 1300s-1500s with the Renaissance and Reformation which led to the rediscovery of ancient learning and challenges to traditional thinking. In the late 1400s-1600s, the Age of Exploration resulted in the discovery of new lands, people, flora, and fauna. During the mid-1500s-1700s, the Scientific Revolution brought new explanations of nature. Key figures like Copernicus, Kepler, Galileo, Descartes, Newton, and Boyle helped establish the heliocentric model of the solar system and develop the scientific method through observations, experimentation, and mathematics.