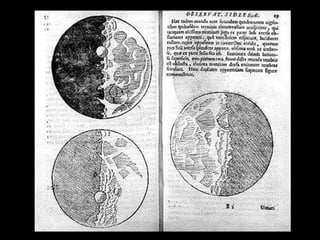
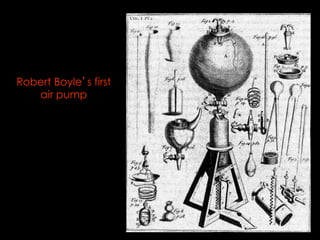
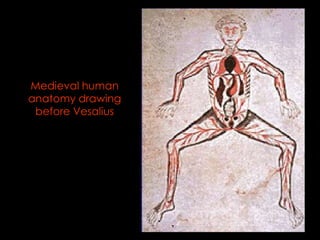
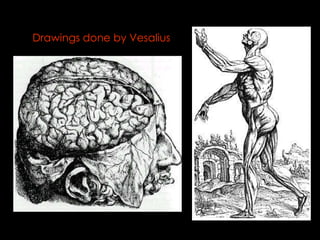
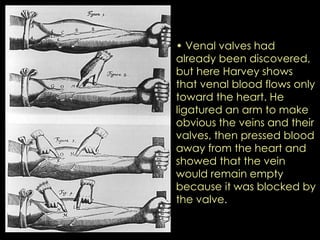
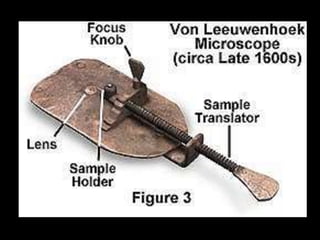
The Scientific Revolution of the 1500s and 1600s changed how Europeans viewed the world by encouraging conclusions based on experimentation rather than tradition. Copernicus published a theory that the Earth revolved around the sun, contradicting Ptolemy's geocentric model, while Galileo and Kepler provided evidence supporting Copernicus through observations with early telescopes and mathematical calculations. Newton later built on this work by formulating laws of motion and gravity and proving the existence and properties of light through experimentation and the new scientific method. These advances established modern science.