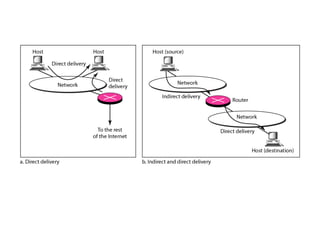
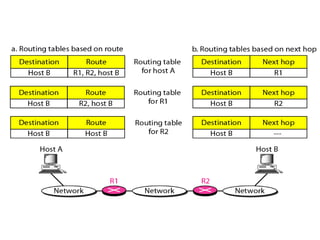
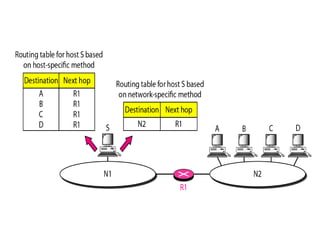
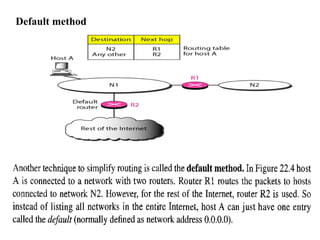
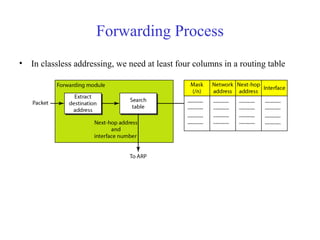
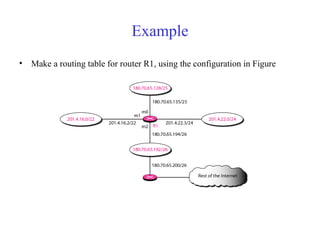
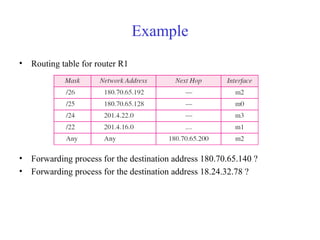
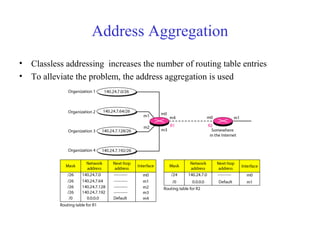
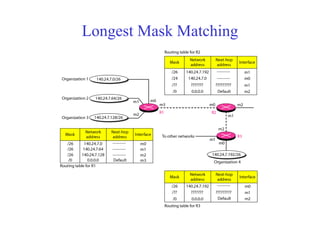
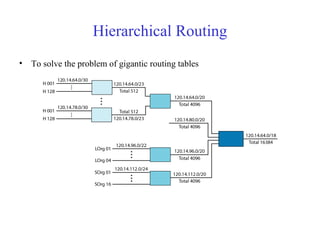
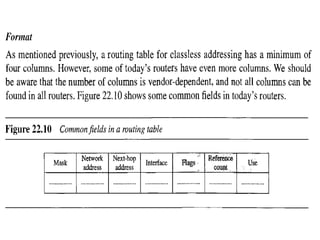
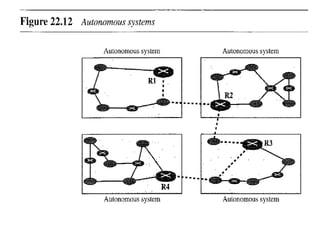
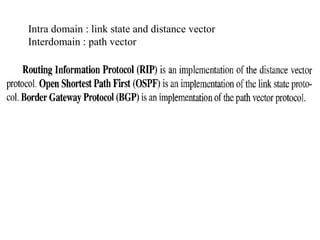
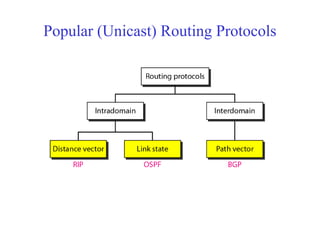
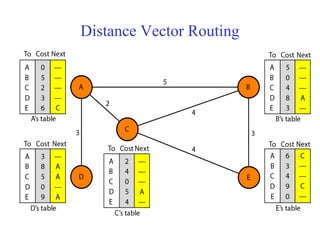
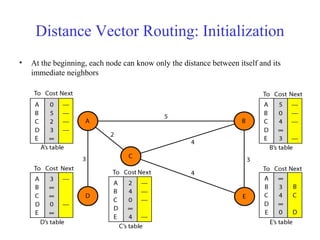
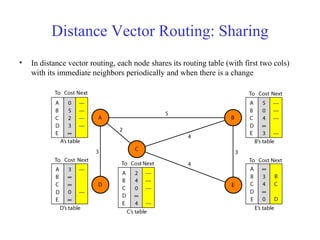
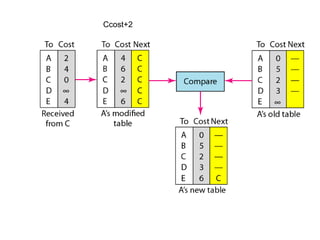
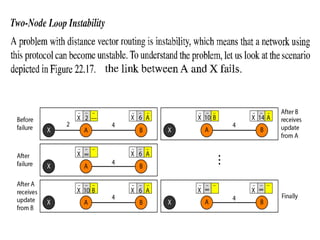
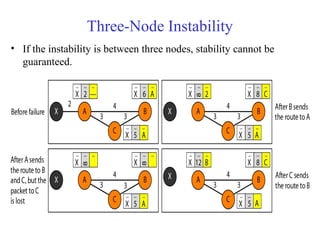
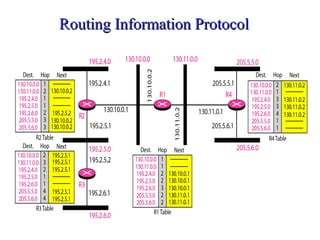
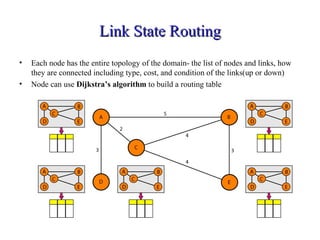
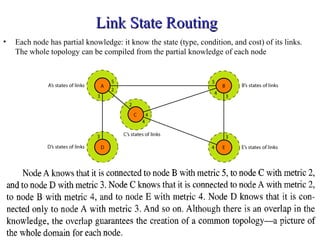
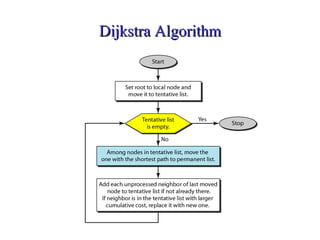
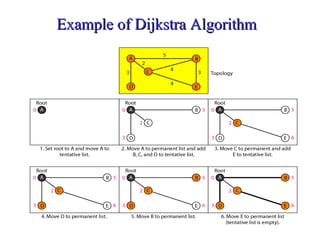
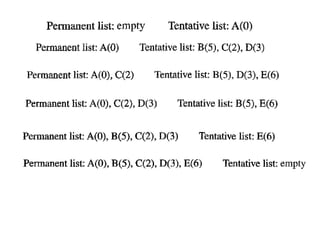
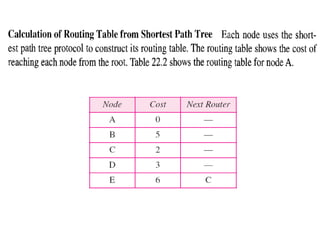
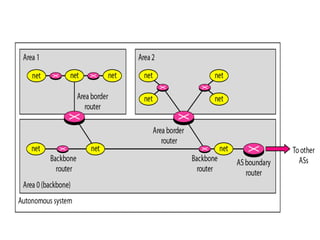
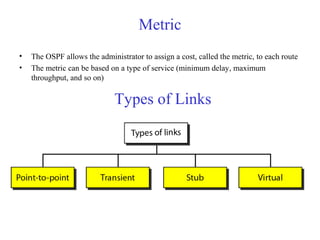
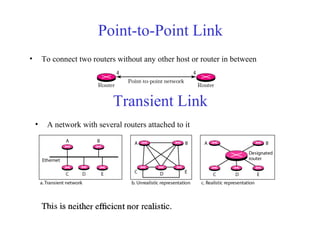
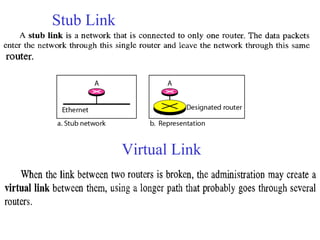
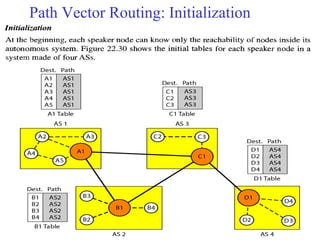
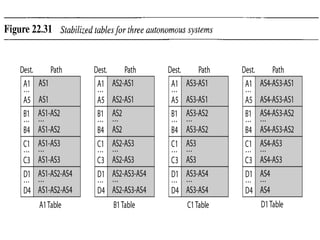
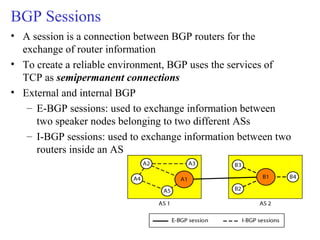
This document provides an overview of key concepts in network layer delivery, forwarding, and routing. It discusses delivery and forwarding of packets, including direct vs indirect delivery and next-hop vs route forwarding methods. It also summarizes several unicast routing protocols, including distance vector protocols like RIP and link state protocols like OSPF. Finally, it discusses path vector routing and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) for interdomain routing.