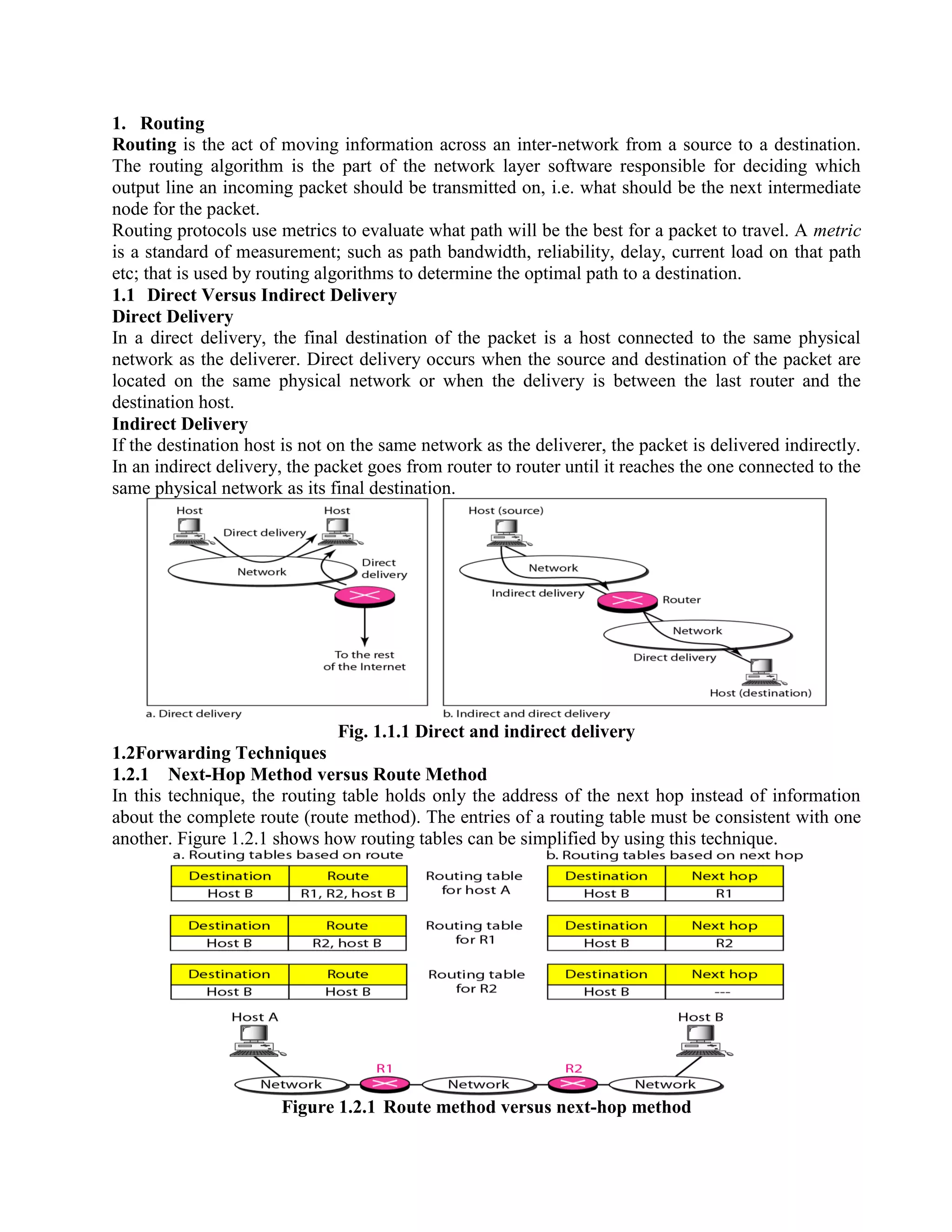
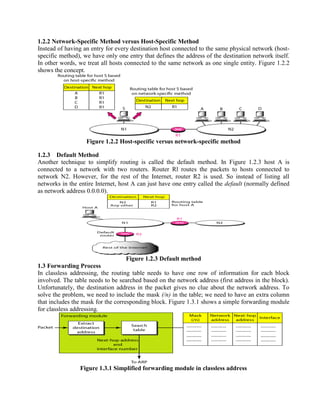
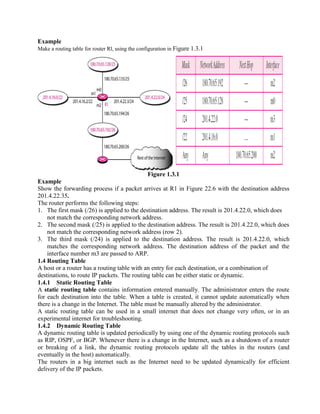
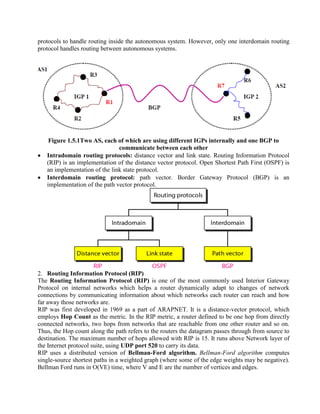
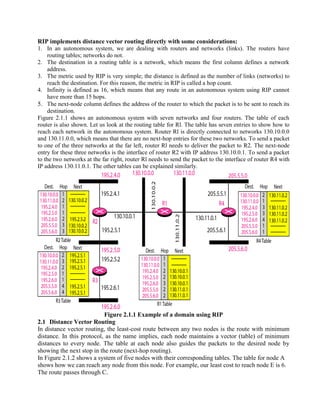
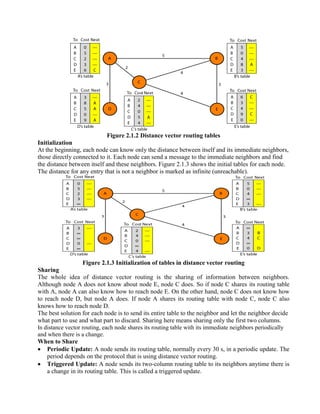
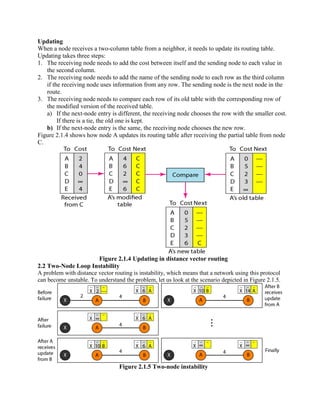
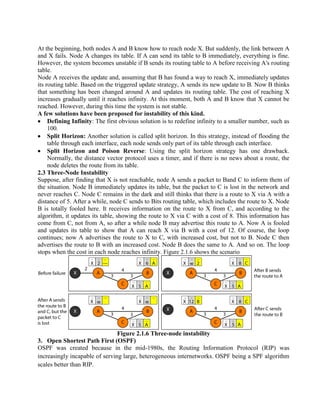
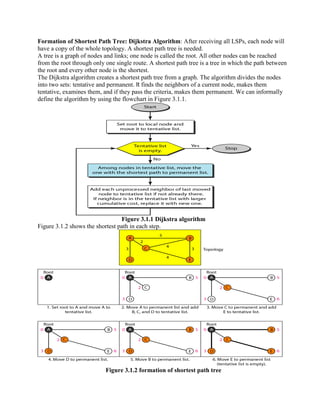
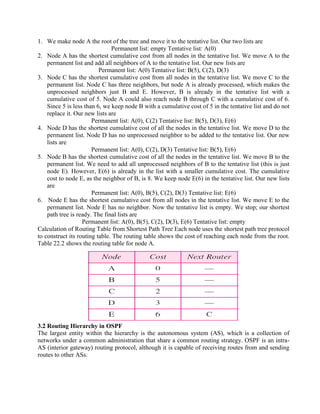
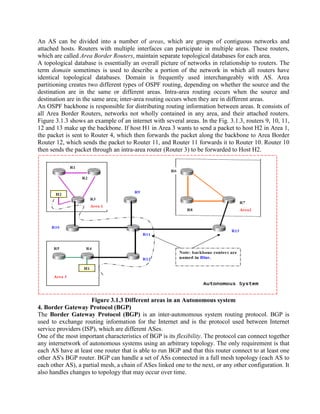
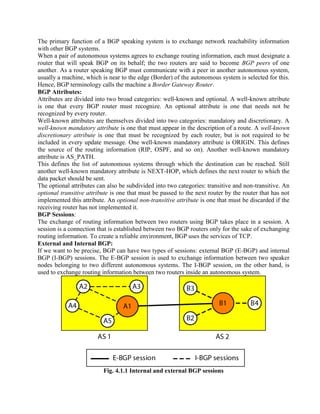
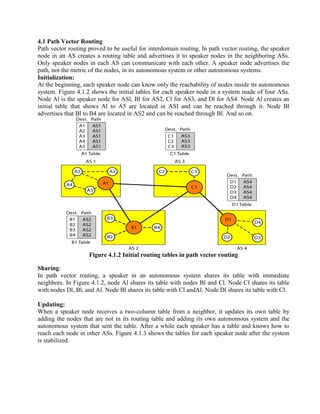
Routing is the process of moving information across an internetwork from a source to a destination. There are two types of routing: direct delivery where the source and destination are on the same network, and indirect delivery where packets travel through multiple routers to reach the destination on a different network. Distance vector routing protocols like RIP use hop count as the metric and periodically share routing tables with neighboring routers to allow all routers to learn the optimal paths. However, this can cause instability issues like two-node and three-node loops where routers incorrectly update their routing tables.