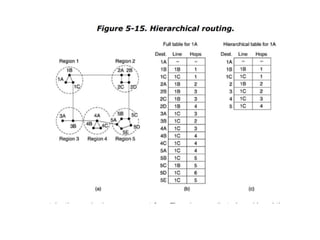
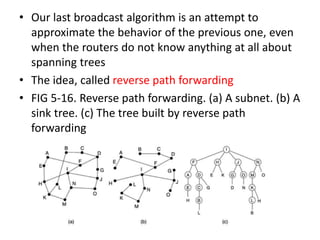
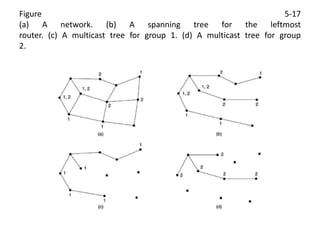
The network layer is responsible for end-to-end packet transmission across multiple hops between source and destination machines. It uses routing algorithms to decide the optimal path for packet forwarding. Common routing algorithms include distance vector routing where each router shares its routing table with neighbors, and link state routing where each router floods information about connected links to other routers which then compute the shortest paths. Hierarchical routing reduces routing table sizes by grouping routers into regions. Broadcast and multicast routing are used to transmit packets from one source to multiple destinations.











![• In distance vector routing [4,7, 9, 10] each
router collects and forwards the information
from and to the neighbors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networklayer-230915063100-55a4e623/85/NETWORK-LAYER-ppt-20-320.jpg)