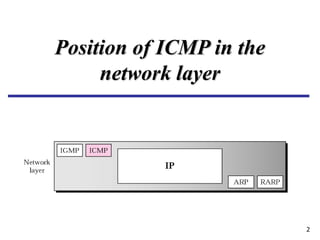
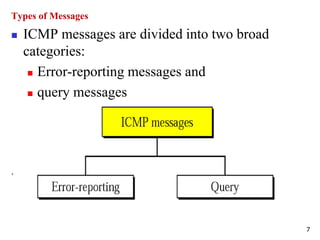
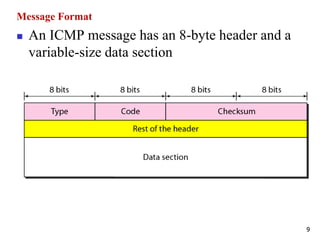
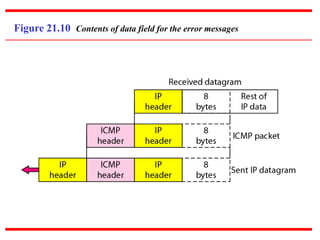
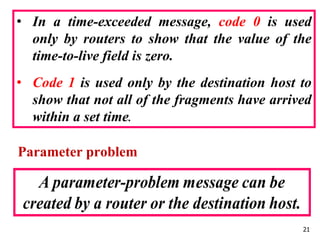
The document discusses the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) and its role in compensating for deficiencies in the Internet Protocol (IP). ICMP provides error reporting and query messages to detect and diagnose network problems. Some key points covered include:
- ICMP reports errors encountered in IP packet delivery such as packets being discarded due to congestion or expired time-to-live values.
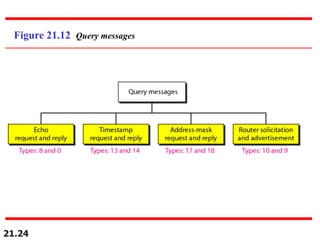
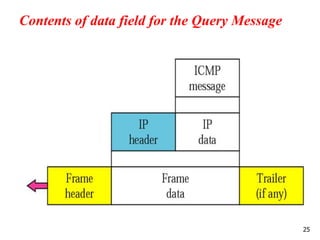
- ICMP query messages like ping are used to check reachability and calculate round-trip times between hosts or routers.
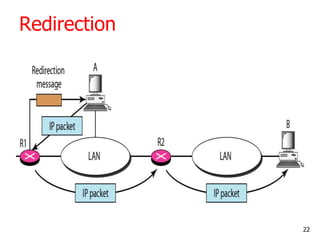
- The main ICMP message types are for error reporting, queries, and network management functions like redirection and router discovery.