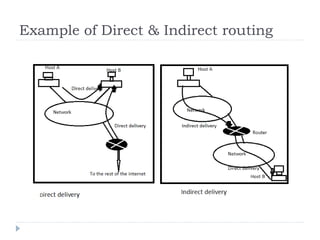
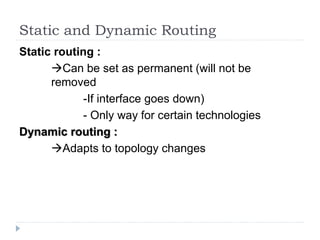
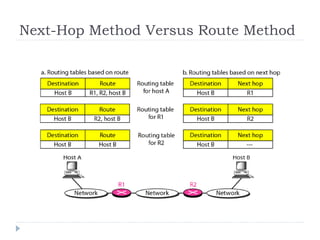
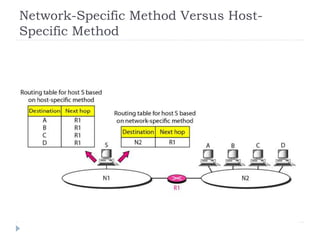
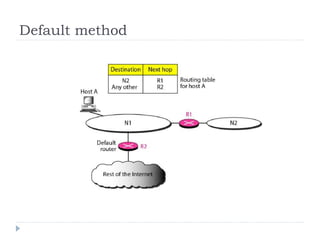
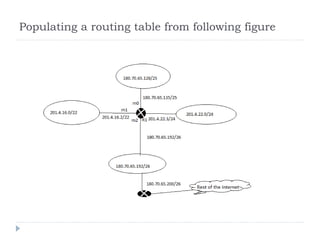
This document discusses different types of routing including direct, indirect, static, and dynamic routing. It describes the fields in a routing table including mask, network address, next hop address, interface, and others. Finally, it explains how routing tables are populated with routing information and provides an example routing table for a router.