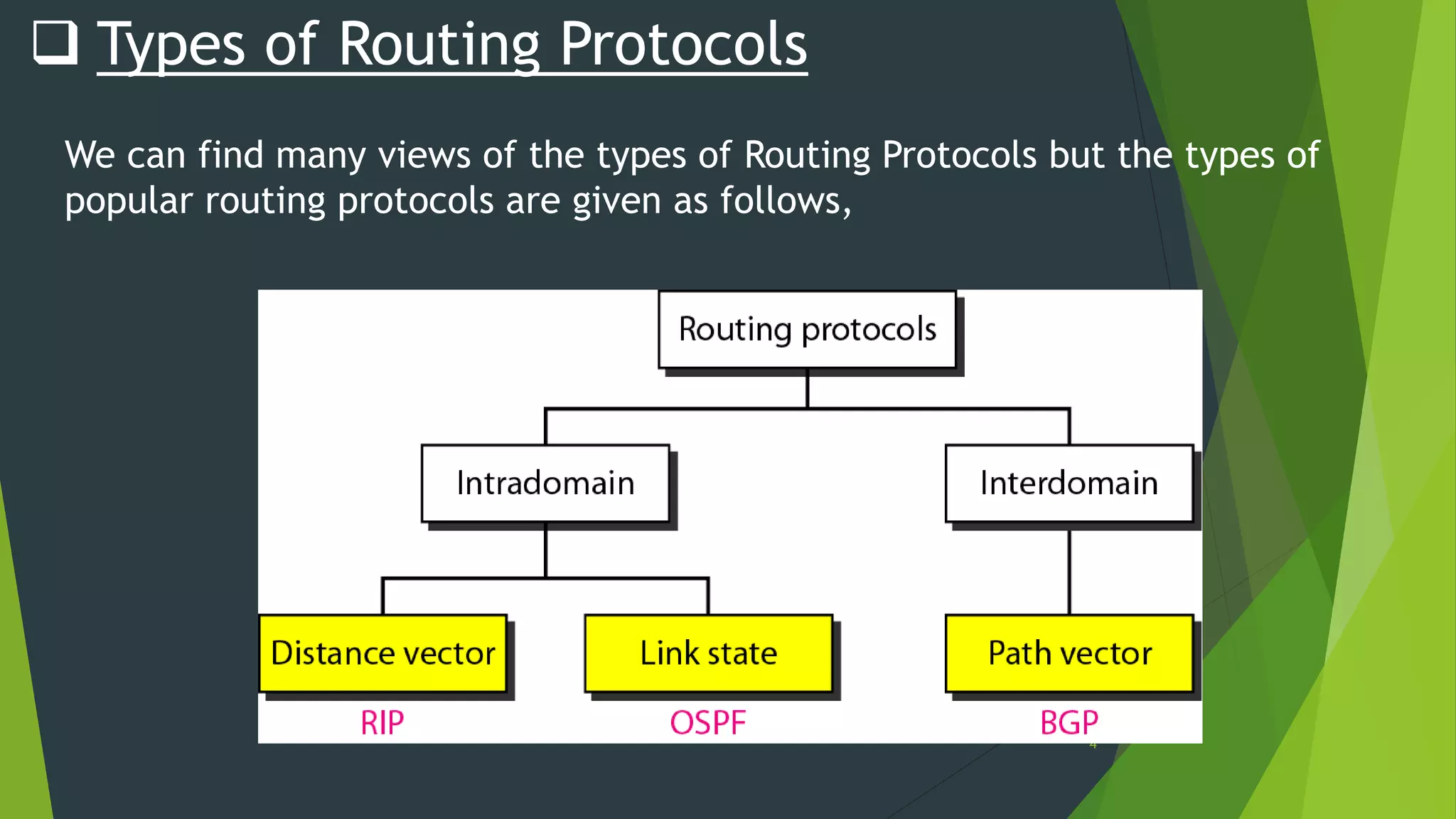
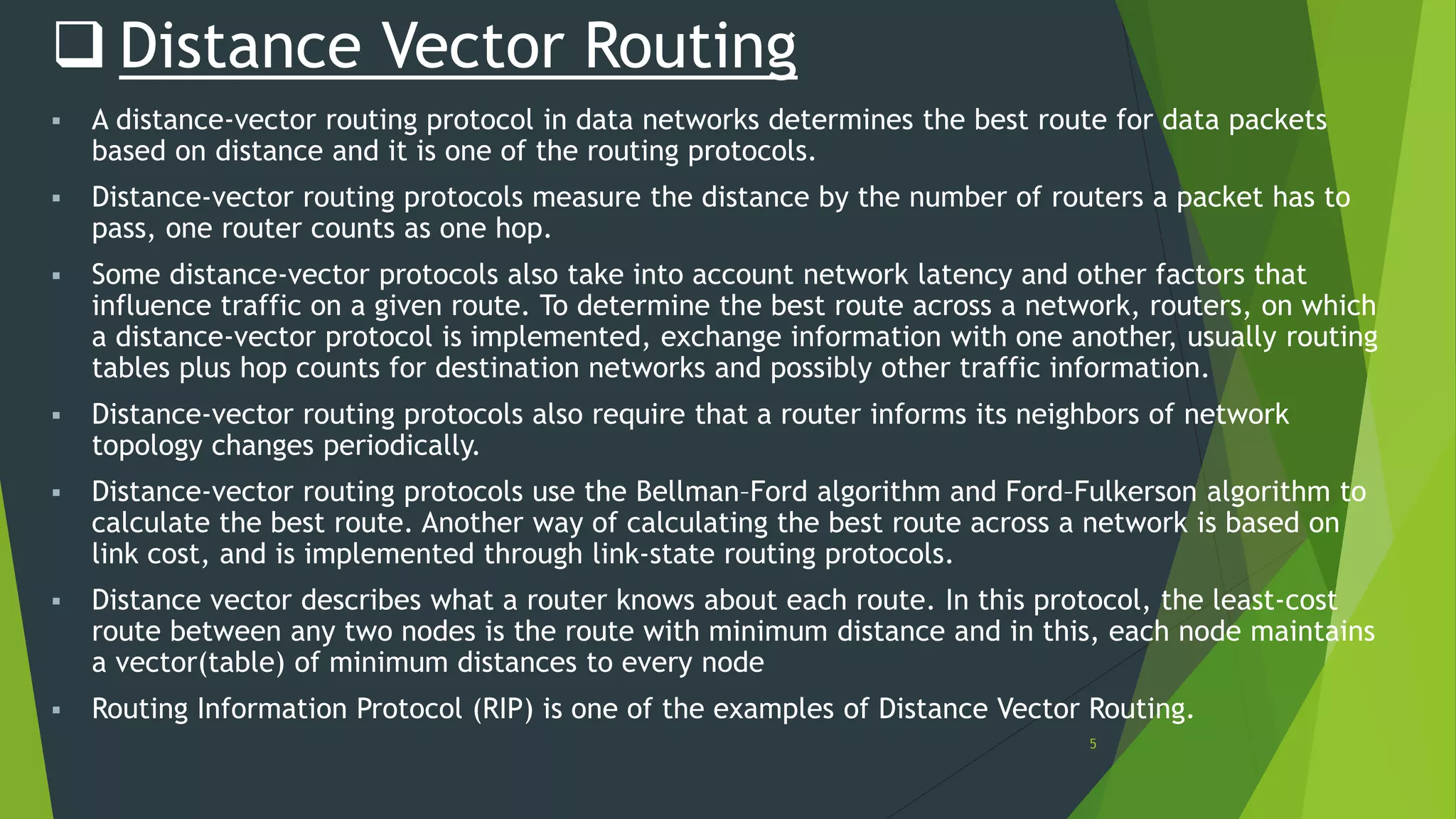
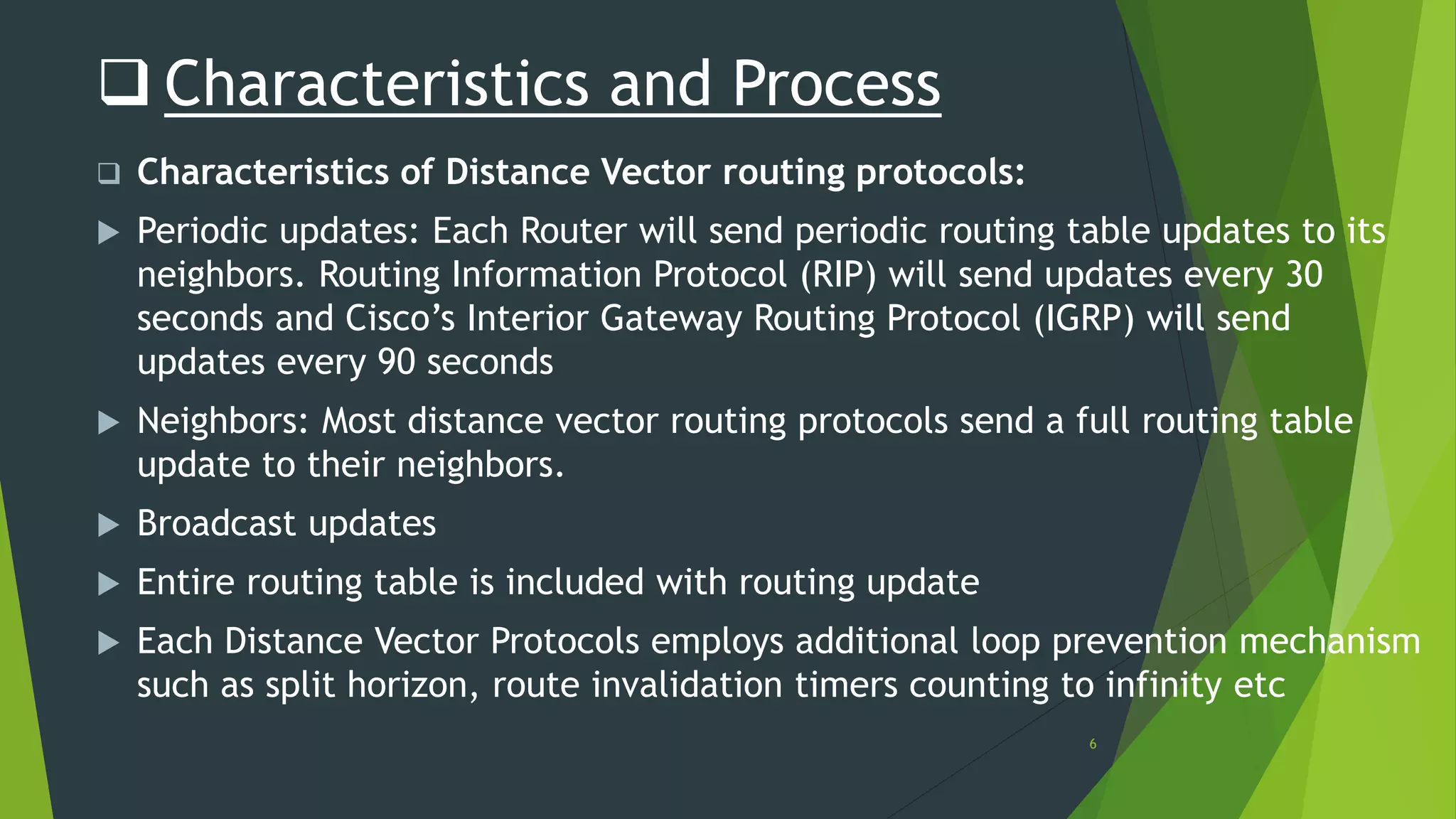
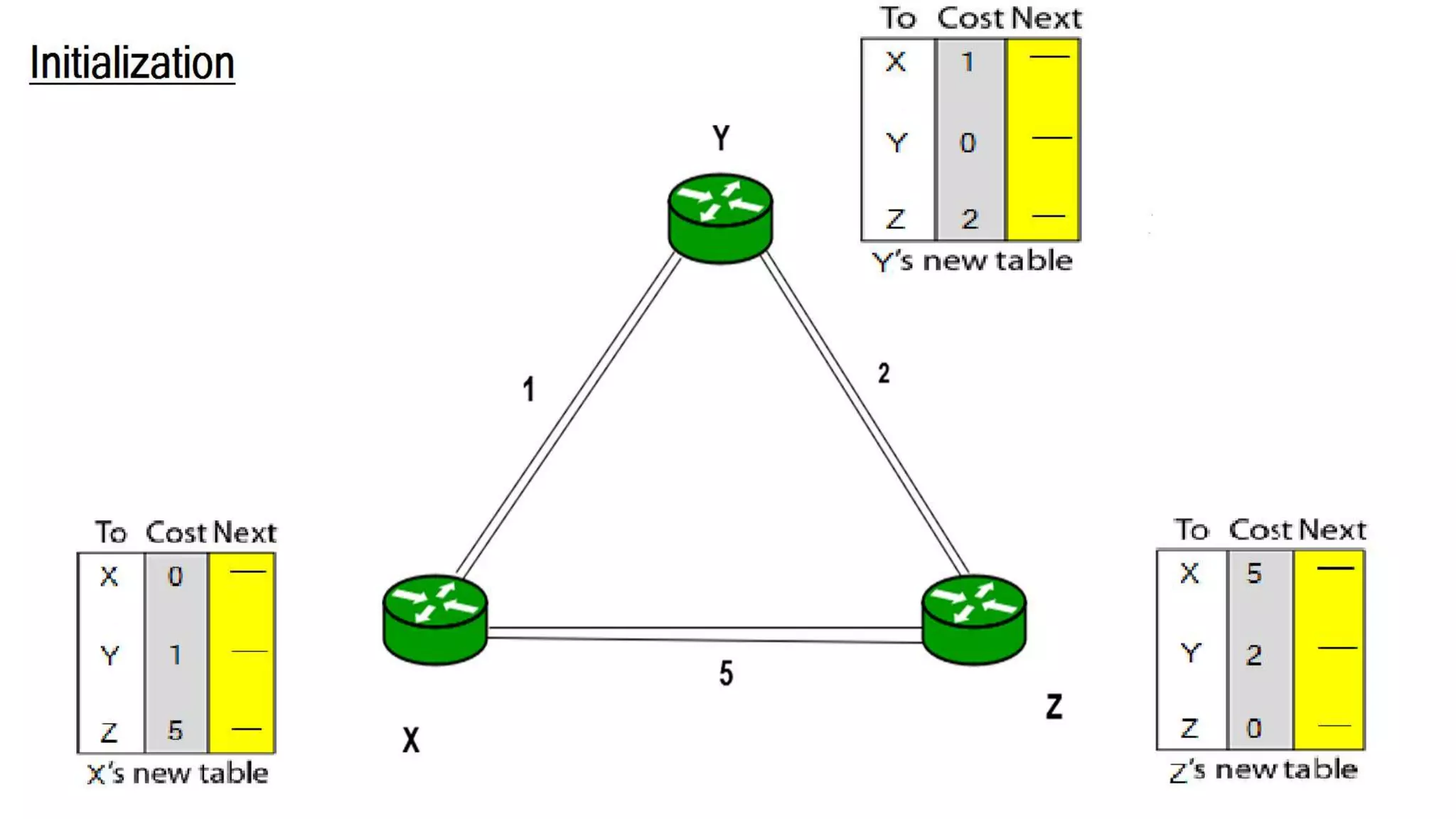
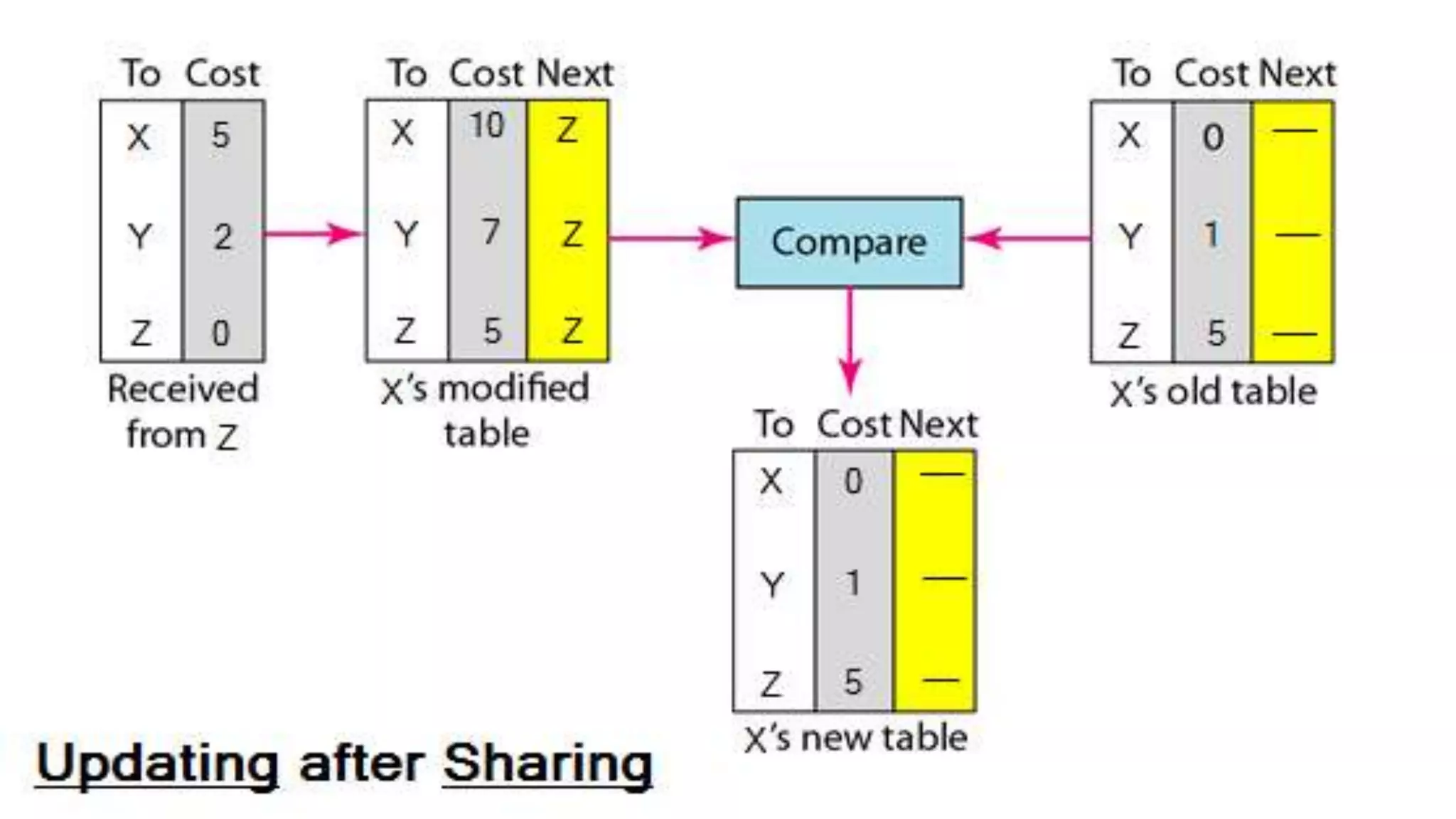
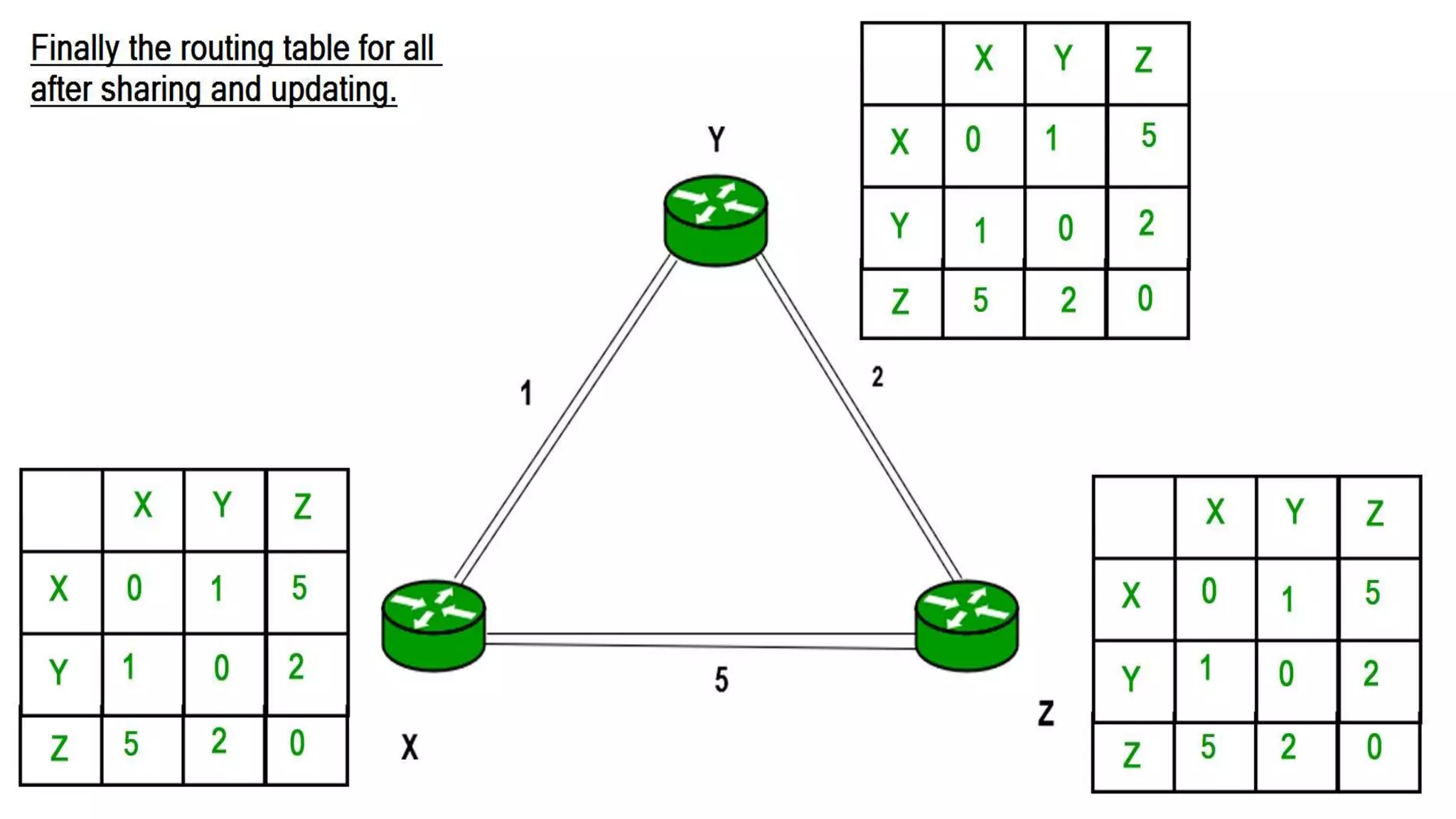
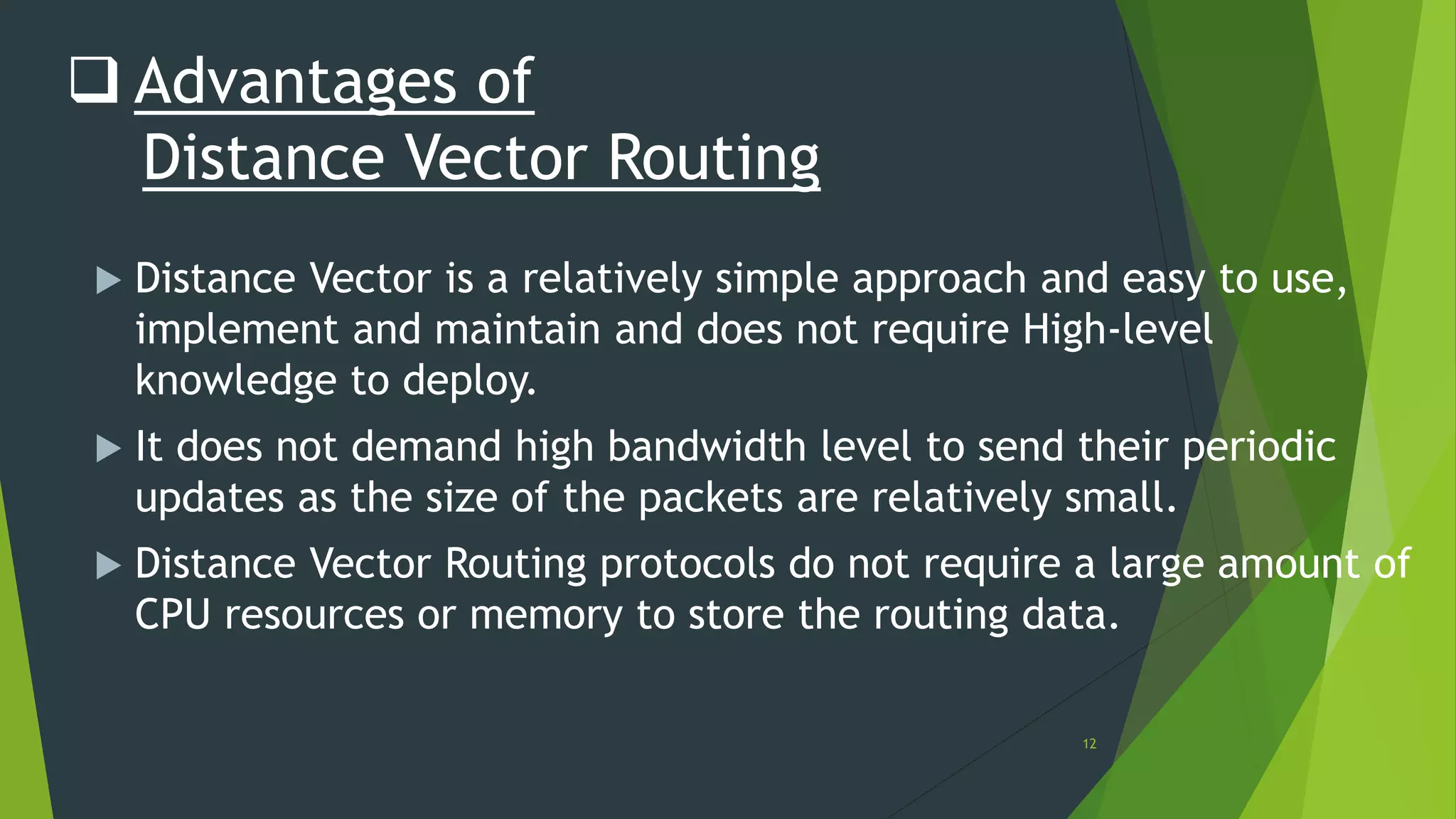
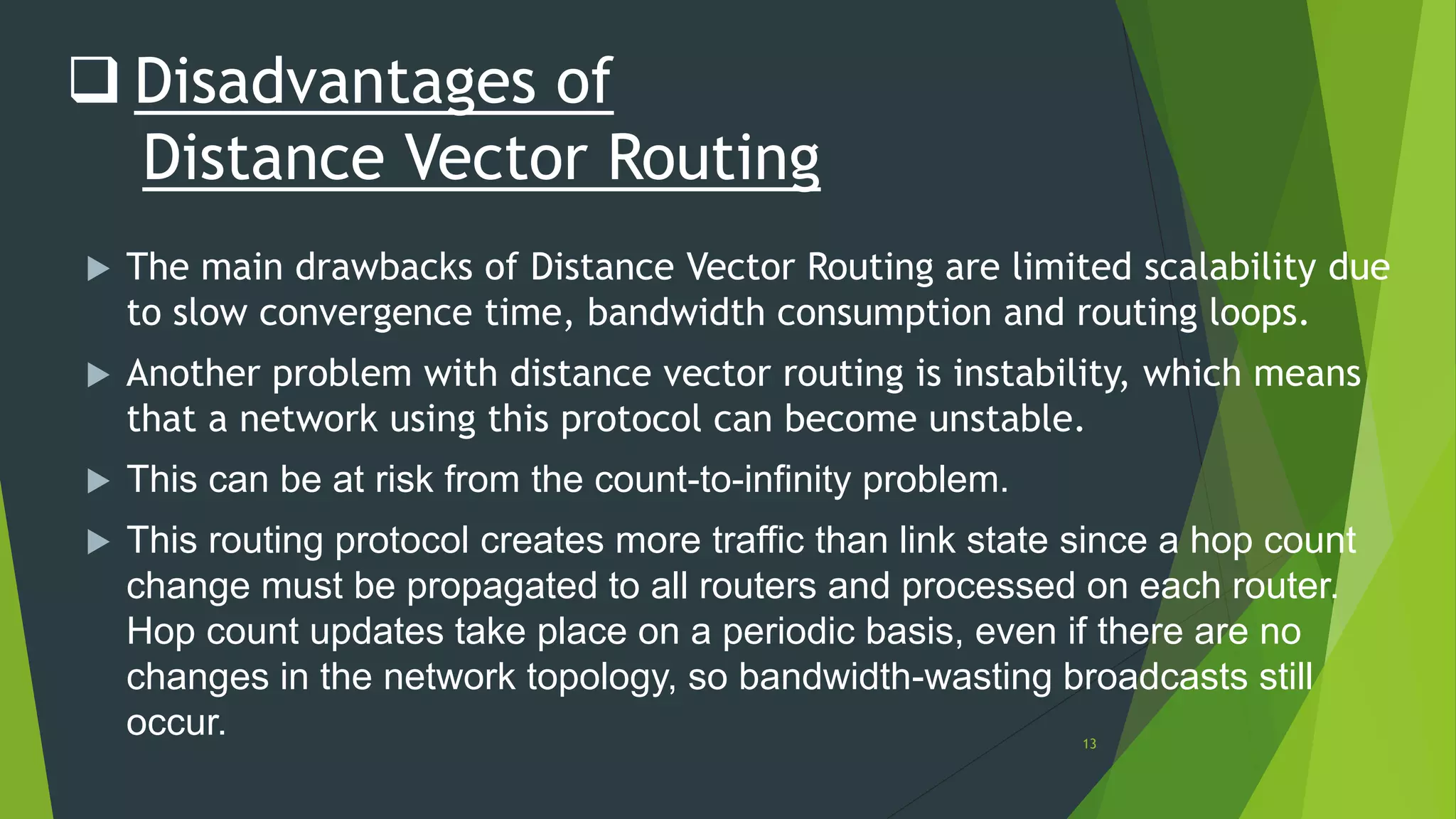
Distance vector routing is a routing protocol that determines the best route for data packets based on distance. Each router maintains a routing table with the minimum distances to every other node and periodically shares its table with neighbors. When a router receives an update indicating a change, it will recalculate its own routing table and propagate changes. While simple to implement, distance vector routing is prone to counting to infinity problems and slow convergence.