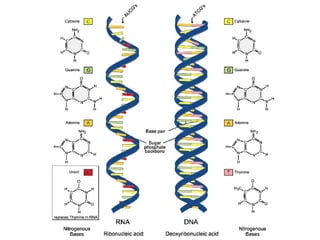
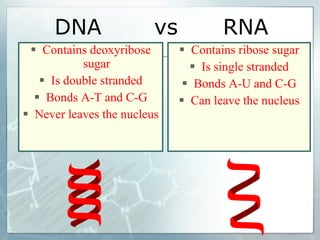
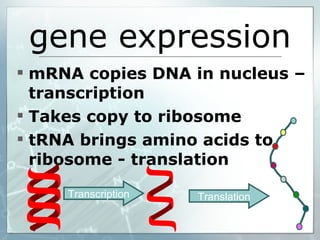
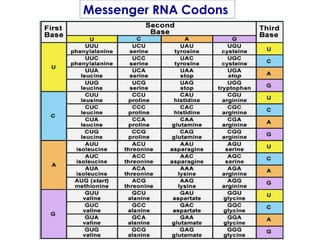
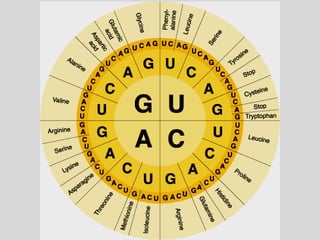
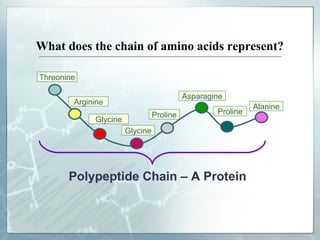
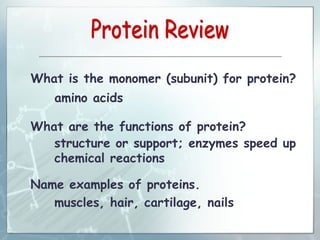
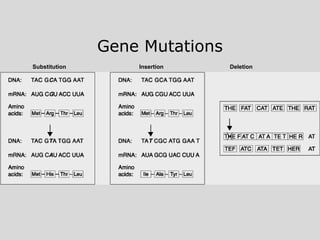
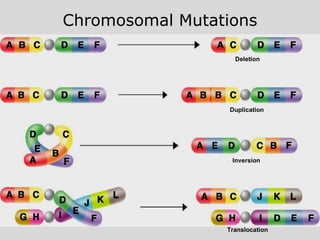
This document summarizes key aspects of RNA and DNA, including that RNA is single-stranded, contains ribose and uracil, and comes in three main types: mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. It also compares RNA and DNA, noting DNA is double-stranded, contains deoxyribose, and remains in the nucleus, while RNA can leave the nucleus. The document then discusses gene expression and protein synthesis, including the roles of transcription, translation, and messenger RNA carrying codons that determine the amino acid sequence of proteins.