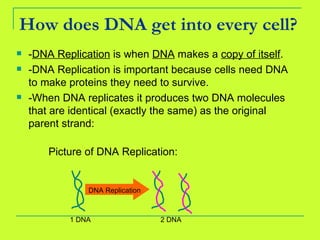
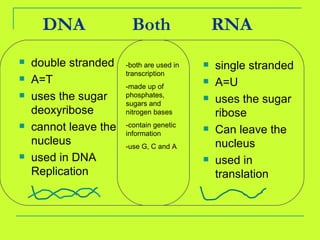
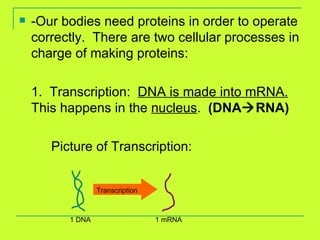
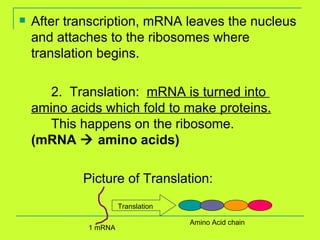
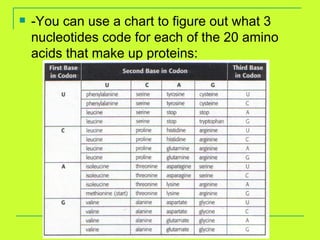
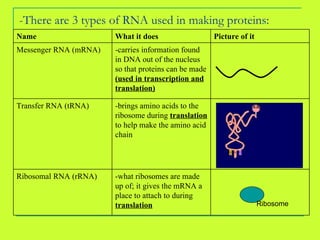
DNA is copied through a process called DNA replication to produce two identical DNA molecules. During DNA replication, the complementary strand is synthesized based on base pairing rules where A pairs with T and G pairs with C. RNA is also synthesized from DNA through transcription. There are three main types of RNA - rRNA, tRNA, and mRNA - that help in the process of protein synthesis by carrying genetic information from DNA and attaching to the ribosome. Proteins are then synthesized through translation of mRNA into amino acids based on the three-nucleotide codon-anticodon pairing on the ribosome.