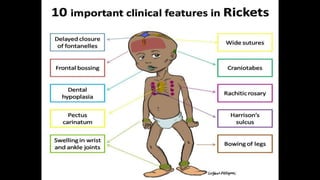
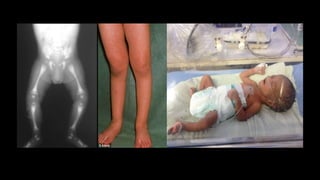
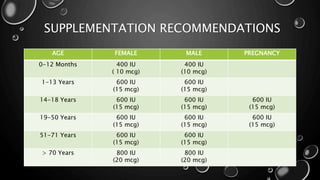
Rickets is a disease characterized by softening and weakening of bones in children, caused by a vitamin D deficiency or impaired metabolism of calcium or phosphorus. It most commonly affects children between 6-24 months old and can lead to fractures and bone deformities. While historically more prevalent, rickets decreased in developed countries in the 20th century but remains common in developing nations and populations with dark skin where access to vitamin D-fortified foods is limited. Treatment involves increasing dietary intake of calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D through supplements, exposure to sunlight, or vitamin D-fortified foods and formula. Physical therapy can help reduce bone and muscle pain through stretching and strengthening exercises.