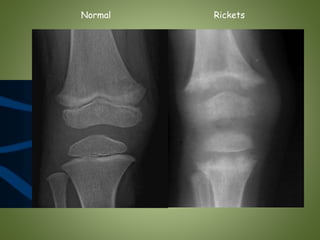
Rickets is a childhood bone disease caused by vitamin D deficiency and lack of calcium or phosphorus. It results in soft, weak bones that can lead to skeletal deformities. The document outlines the pathogenesis of rickets, describing how deficiencies disrupt normal bone mineralization. Clinical signs include bone pain, bowed legs, and chest deformities. Diagnosis involves blood tests and x-rays of bones showing widened growth plates. Treatment is vitamin D supplementation with calcium and phosphorus to correct deficiencies and allow healing. Prevention involves adequate sunlight exposure, vitamin D supplementation in infants, and dietary calcium intake.







![Pathogenesis (Normal) [2]
Proliferation of
chondrocytes
Calcification and
vascular invasion
Reserve
zone
Maturation
zone
Proliferative
zone
Hypertrophic
zone
Primary
spongiosa
2. Shapiro IM, Boyde A. Mineralization of normal and rachitic chick growth cartilage: vascular canals, cartilage
calcification and osteogenesis. Scanning Microsc 1987; 1:599.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/84qnflwkq2ygyucnk6h8-signature-a1cd4323595946abab2cbf07e4a755995bcd3d1fcb0757ca2350e46d1f2cddf3-poli-140825193435-phpapp02/85/Rickets-8-320.jpg)
![Pathogenesis (Rickets) [3-6]
Proliferation of
Thick + Disorganized
chondrocytes
cartilage
Less calcification and
vascular invasion
Hypertrophic
zone
3. Lacey DL, Huffer WE. Studies on the pathogenesis of avian rickets. I. Changes in epiphyseal and metaphyseal vessels in hypocalcemic and hypophosphatemic rickets.
Am J Pathol 1982; 109:288.
4. Huffer WE, Lacey DL. Studies on the pathogenesis of avian rickets II. Necrosis of perforating epiphyseal vessels during recovery from rickets in chicks caused by
vitamin D3 deficiency. Am J Pathol 1982; 109:302.
5. Takechi M, Itakura C. Ultrastructural studies of the epiphyseal plate of chicks fed a vitamin D-deficient and low-calcium diet. J Comp Pathol 1995
6.. Rauch F. The rachitic bone. Endocr Dev 2003; 6:69.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/84qnflwkq2ygyucnk6h8-signature-a1cd4323595946abab2cbf07e4a755995bcd3d1fcb0757ca2350e46d1f2cddf3-poli-140825193435-phpapp02/85/Rickets-9-320.jpg)

![Clinical Manifestations (Skeletal) [13]
1. Delay in closure of the fontanelles
2. Parietal & frontal bossing (due to excess osteoid)
3. Craniotabes ( soft skull bones)
4. Enlargement of the costochondral junction
(rachitic rosary)
5. The development of Harrison sulcus ( caused by pull of the diaphragmatic attachments
to the lower ribs)
6. Pigeon chest deformity (The weakened ribs bend inwards due to the pull of respiratory
muscles, causing anterior protrusion of sternum)
7. Enlargement of the wrist + ankle & bowing of the distal radius & ulna
8. Genus Valgus (knocked), Genus Verus (bowleg), or Windswept deformity (combination
of valgus deformity of 1 leg with varus deformity of the other leg)
13. Misra M, Pacaud D, Petryk A, et al. Vitamin D deficiency in children and its management: review of current
knowledge and recommendations. Pediatrics 2008; 122:398.
Pictures from http://www.thachers.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/84qnflwkq2ygyucnk6h8-signature-a1cd4323595946abab2cbf07e4a755995bcd3d1fcb0757ca2350e46d1f2cddf3-poli-140825193435-phpapp02/85/Rickets-11-320.jpg)