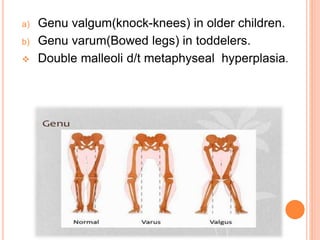
This document discusses rickets, a disease characterized by soft, weak, and deformed bones in children caused by vitamin D deficiency or disorders of vitamin D and phosphate metabolism. It defines rickets as occurring in growing children before bone growth plate closure, while osteomalacia occurs after closure in adults. The key roles and mechanisms of vitamin D in calcium and phosphate homeostasis are described. Causes, signs and symptoms, diagnosis using biochemical markers and radiology, treatment using large vitamin D doses, and prevention through diet and sunlight exposure are summarized. Other types of rickets including genetic and renal forms are also outlined.