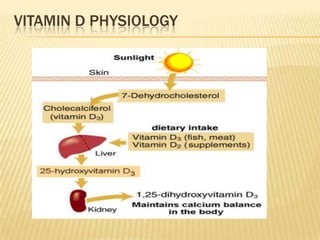
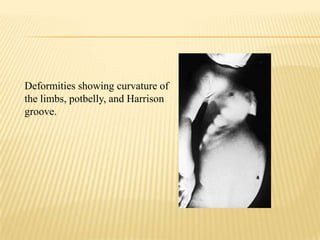
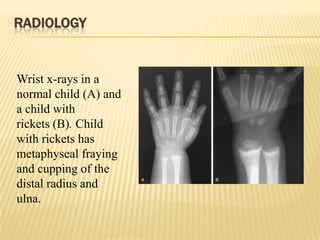
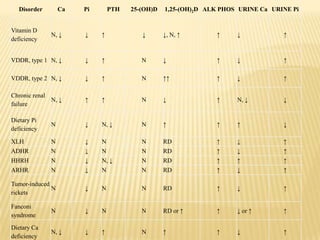
This document provides information on rickets in children. It begins with an overview of vitamin D physiology and the sources of vitamin D. It then discusses the introduction, etiology, clinical features, radiology, diagnosis, and treatment of rickets. The main causes of rickets are outlined as vitamin D deficiencies, calcium deficiencies, phosphorus deficiencies, and renal losses. Symptoms and physical exam findings of rickets are explained. Laboratory tests useful in diagnosis are provided. Treatment involves high dose vitamin D supplementation either orally or via injection. Prognosis is typically excellent with treatment, though severe cases can cause permanent deformities.