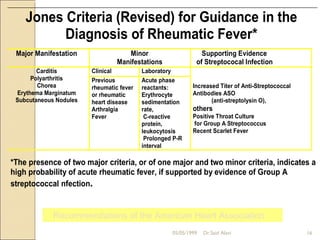
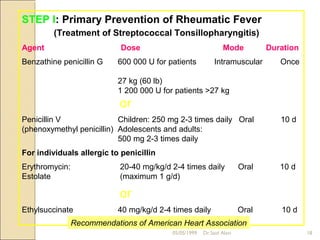
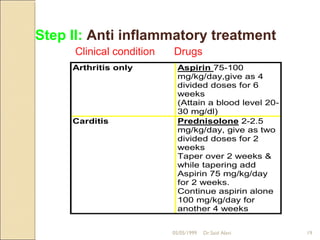
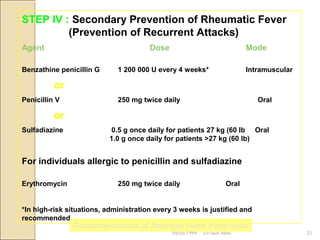
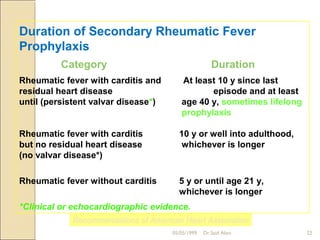
Acute rheumatic fever is a systemic disease that primarily affects children following a group A streptococcal infection. It involves inflammation of the heart, joints, skin, and brain. It is diagnosed using the modified Jones criteria which looks for major manifestations like carditis or chorea along with minor manifestations and evidence of a prior streptococcal infection. Treatment involves antibiotics to treat the initial infection, anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin to reduce inflammation, and long-term prevention of recurrent attacks using antibiotics like benzathine penicillin.