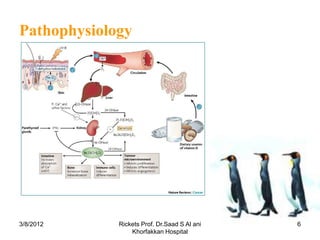
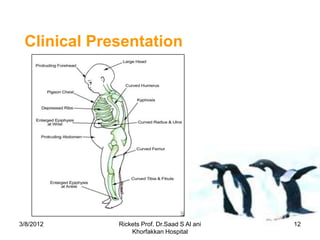
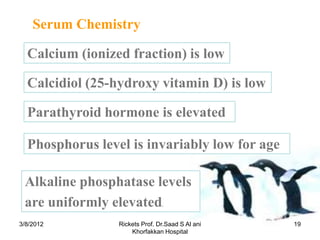
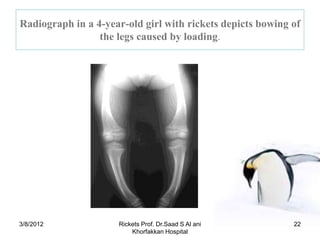
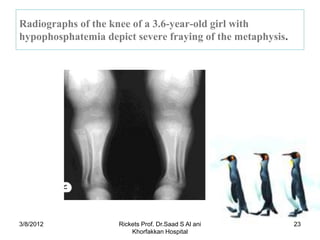
Rickets is a disease caused by vitamin D deficiency or a lack of calcium or phosphorus in children, which results in soft, weakened bones. It occurs when osteoid, or bone matrix, fails to calcify during bone growth. Symptoms include bowed legs, bone pain, and fractures. Treatment involves high dose vitamin D supplementation orally or via injection to restore calcium and phosphorus levels.









![Epidemiology
The frequency increasing internationally
1.Children to wear sunscreen while outdoors
2.Children spend more time
indoors watching television or
playing electronic games, instead
of playing outdoors
•Lowdon J. Rickets: concerns over the worldwide increase. J Fam Health
Care. Mar-Apr 2011;21(2):25-9.[Medline].
3/8/2012 Rickets Prof. Dr.Saad S Al ani 11
Khorfakkan Hospital](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rickets-120309012321-phpapp02/85/Rickets-11-320.jpg)













![References
1. McKay CP, Portale A. Emerging topics in ediatric bone and mineral
disorders 2008. Semin Nephrol. Jul 2009;29(4):370-8.
2. Lowdon J. Rickets: concerns over the worldwide increase. J Fam
Health Care. Mar-Apr 2011;21(2):25-9.[Medline].
3. Chapman T, Sugar N, Done S, Marasigan J, Wambold N, Feldman
K. Fractures in infants and toddlers with rickets. Pediatr Radiol. Dec
9 2009;[Medline].
4. Casey CF, Slawson DC, Neal LR. VItamin D supplementation in
infants, children, and adolescents. Am Fam Physician. Mar 15
2010;81(6):745-8. [Medline].
5. Greer FR. Issues in establishing vitamin D recommendations for
infants and children. Am J Clin Nutr. Dec 2004;80(6 Suppl):1759S-
62S. [Medline].
6. [Guideline] Wagner CL, Greer FR. Prevention of rickets and
vitamin D deficiency in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatrics.
Nov 2008;122(5):1142-52. [Medline].
3/8/2012 Rickets Prof. Dr.Saad S Al ani 29
Khorfakkan Hospital](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rickets-120309012321-phpapp02/85/Rickets-29-320.jpg)
