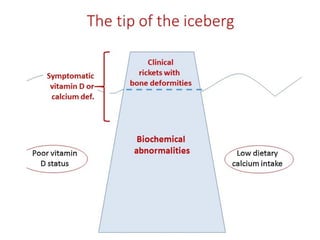
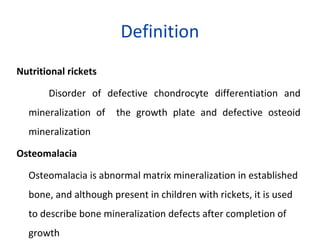
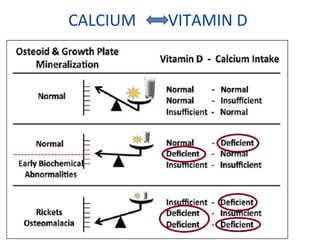
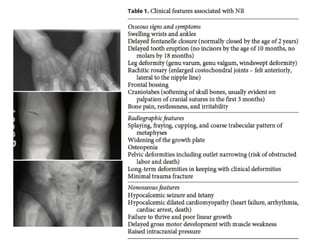
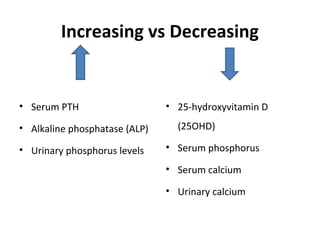
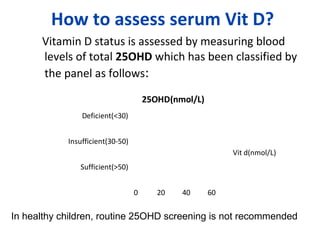
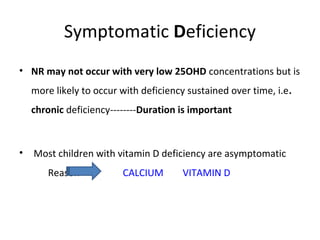
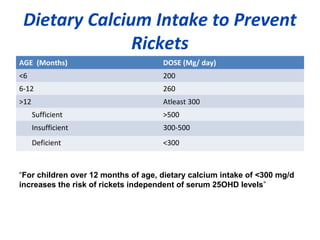
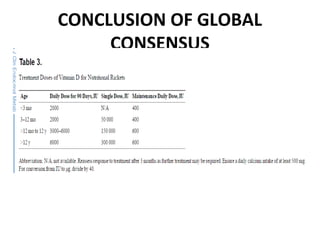
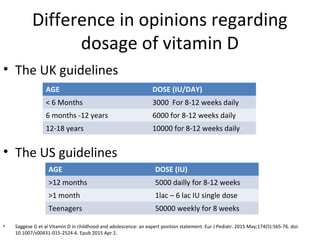
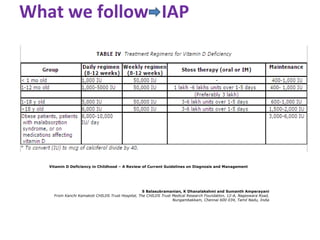
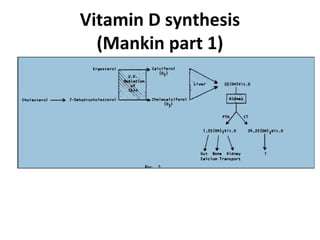
Nutritional rickets is caused by defective bone growth and mineralization due to vitamin D deficiency or low calcium intake. It is diagnosed based on history, physical exam, biochemical testing and confirmed by radiographs. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels below 30 nmol/L indicate deficiency and levels below 50 nmol/L increase risk of rickets. Treatment involves high dose vitamin D supplementation of 2000 IU/day for at least 3 months along with calcium supplementation. Prevention involves adequate dietary vitamin D and calcium intake.