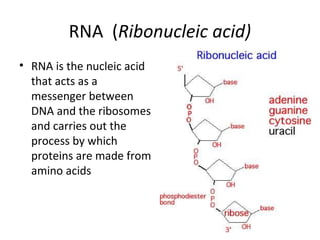
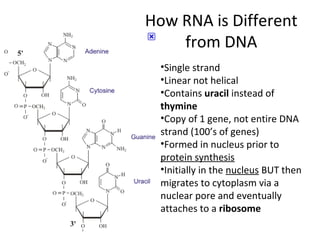
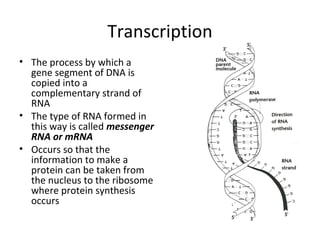
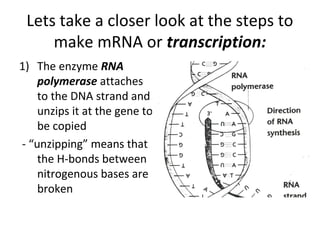
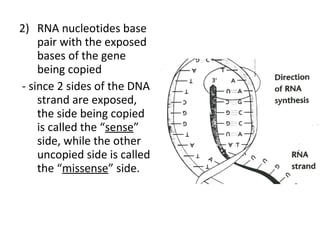
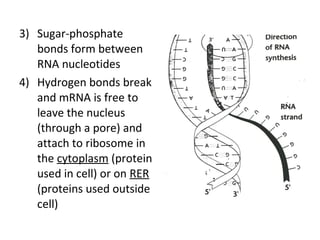
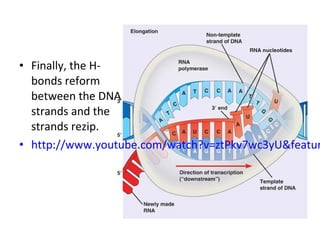
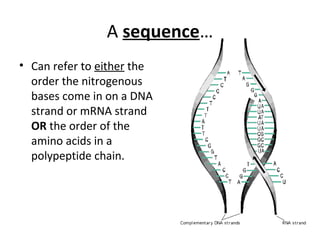
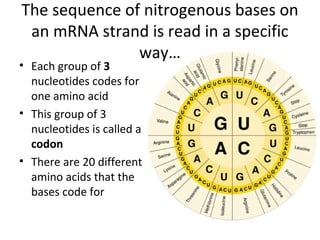
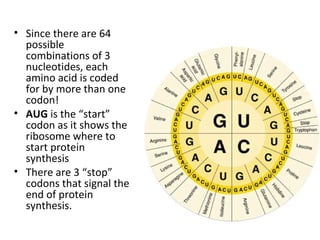
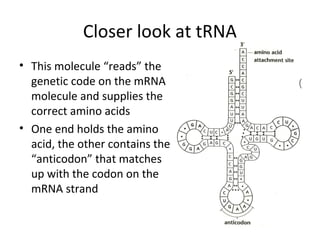
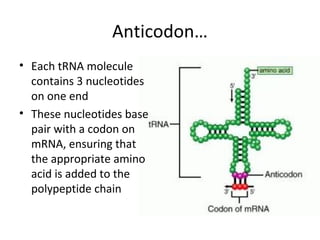
This document discusses RNA synthesis or transcription. It begins by describing RNA and its role in carrying genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis. It then explains how RNA differs from DNA in being single-stranded, linear, and containing uracil instead of thymine. The document goes on to define transcription as the process of copying a gene segment from DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the nucleus, which then transports the information to the cytoplasm to direct protein synthesis at ribosomes. In addition, it mentions two other types of RNA: transfer RNA (tRNA) carries amino acids to ribosomes, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) makes up ribosomes.